Hand, Foot and Mouth
advertisement

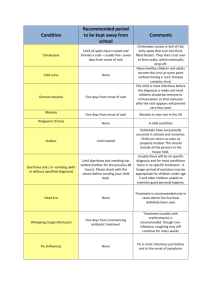
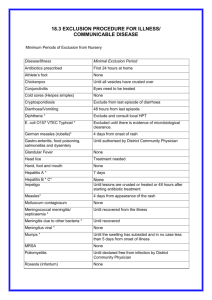
HAND FOOT and MOUTH DISEASE Information Leaflet What is Hand Foot and Mouth Disease (HFMD)? HFMD is a viral illness that causes mild fever and rash, usually in young children. The rash is non-tender and vesicular or macular; it is found on the tongue and buccal mucosa. One day later ~75% develop rash commonly on the sides of the fingers, hands and soles; rash can also be found on buttocks, trunk, genitalia, face and limbs. What Virus causes HFMD? Enteroviruses, including coxsachieviruses, echoviruses and other enteroviruses. Coxsachie A16 and Enterovirus 71 are associated with epidemics. HFMD and pregnancy No congenital infection is anticipated. How is HFMD spread and what is the epidemiology? HFMD is spread via droplets or contact from one person to another. The incubation period is 3-6 days. HFMD is most common in children aged 1-4 years. It is more common in summer/autumn. HFMD is endemic; however, epidemics occur from time to time especially in pre-school groups. Is there any treatment for HFMD? No. The disease is usually mild and self-limiting. How can HFMD be prevented? There is no vaccine. Children with the rash should remain at home until the rash has settled. Parents/carer’s should be advised about hand hygiene. Produced by Dr S Knowles, Microbiologist. 14th June 2011 How is HFMD diagnosed? Clinical diagnosis. Usually no laboratory tests are required. There are no serological tests. Occasionally if severe infection, virus may be cultured from viral throat swab or faeces. Infection Control, June 2011 Produced by Dr S Knowles, Microbiologist. 14th June 2011