Handout 1 of 2
February 16, 2015
NURS 330
Human Reproductive Health
Today’s Agenda
Review 2/9/15 In-Class Assignment
STD Lecture
Infertility & Sexuality Lecture
Quiz Study Guide
In-Class Assignment
What Are STDs?
Sexually – relating to having sex, personal intimate
contact (e.g., rubbing of genitals, masturbating a
partner), etc.
Transmitted – passed by means of, spread by
Disease – being sick (with or without symptoms),
body not working properly
So, an STD = a disease/infection you can get from or
give to someone else by having oral, vaginal, or anal
sex or other intimate contact with him/her.
Source: County of Los Angeles STD Program
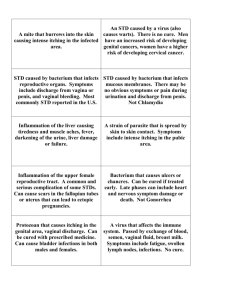
Health Consequences of STDs
Source: County of Los Angeles STD Program
STDs in the United States
• The CDC estimates that there are approximately 19
million new cases each year in the US 1
• There are an estimated 65 million people in the US
living with a viral STD 2
• More than half of all people will have an STD/STI at
some point in their lifetime. 2
• One in two sexually active persons will contact an
STD/STI by age 25. 2
• The cost of STDs to the U.S. health care system is
estimated to be as much as $15.9 billion annually 1
1
2
Source: Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, cdc.gov
Source: American Social Health Association, www.ashastd.org
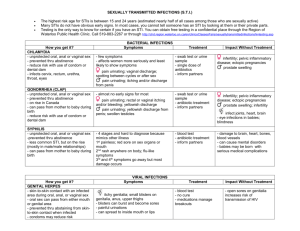
BACTERIAL Chlamydia
STDs
Gonorrhea
Syphilis
Transmission
Pre-cum, semen, Pre-cum, semen, Skin-to-skin; genital
vaginal secretions vaginal secretions to genital rubbing
Perinatal
Perinatal
Symptoms
NOTHING or
Discharge from
penis, vagina
NOTHING or
Discharge from
penis, vagina
1-chancre
2-skin, genital rash
3- organ damage
Complications
PID in females
Epidimytis in
males
PID in females
Epidimytis in
males
Blindness, paralysis,
heart problems, etc
Diagnosis
Urine sample
Urethral, cervical
swab
Urine sample
Blood sample
Urethral, cervical
swab
Treatment
Curable with
antibiotics
Curable with
antibiotics
Curable with
antibiotics
Source: County of Los Angeles STD Program
CHLAMYDIA
Risk factors:
Unprotected oral, vaginal or anal sex
GONORRHEA
Risk factors:
Unprotected oral, vaginal or anal sex
SYPHILIS
Oral, vaginal or anal sex
(protected or unprotected)
VIRAL
STDS
HPV
HERPES
HEP B
Transmission
Skin-to-skin;
genital to genital
rubbing
Skin-to-skin; genital Blood, pre-cum,
to genital rubbing;
semen, vaginal
social kissing
secretions
Symptoms
NOTHING –orHigh Risk: Cervical
changes
Low Risk: Warts in,
on around genitals
NOTHING –orBlisters in, on
around genitals
(HSVII) or
mouth (HSV I)
NOTHING –orFatigue, flu-like
symptoms,
jaundice
Complications
Cervical Cancer
Psychosocial
Psychosocial
Complications of
the liver
Diagnosis
HPV test
Pap smear screening
Blood test, blister
sample
Blood sample
Treatment
Not curable
Vaccine available
Not curable
Not curable
Vaccine available
Human Papilloma Virus (HPV)
Vaginal or anal sex
(protected or unprotected)
Pap Smears
Screens for pre-cancerous cells in cervix
When to start
3 years after sexual debut or at age 21, whichever comes first
Remember, you do NOT have to be sexually active to get a pap
smear
Does not necessarily test for STDs
You have to ask for specific STD tests
It is important to be your own health advocate
How often should I get pap smears?
It varies, depending on your pap results
Your doctor or nurse will let you know
HPV Vaccine
Vaccine
Gardasil® by Merck approved in 2006
•
•
•
Provides protection against four HPV types which together cause
70% of cervical cancers and 90% of genital warts
Three shots over six-month period Licensed for use in girls/women
9-26 years old
In October 2009, FDA approved for use in boys/men 9-26 years old
Another HPV vaccine by GSK currently in final stages of
development
•
Would provide protection against two HPV types that cause most
(70%) cervical cancers
Source: County of Los Angeles STD Program
HERPES
Risk Factors:
Oral, vaginal or anal sex
(protected or unprotected)
HEPATITIS B
Risk factors:
Unprotected sex, sharing needles,
tattoos, sharing household items
such as razors, toothbrushes
OTHER
Yeast
Bacterial
Vaginosis (BV)
Trichomoniasis
Cause
Not an STD.
Caused by an
overgrowth of yeast.
Sexual transmission STD
possible.Overgrowth
of bacteria.
Symptoms
Women - Thick,
cloudy discharge
from vagina, itching
Men – rash on penis
White or yellow
Bubbly, frothy
discharge, fishy odor discharge.
Irritation upon
urination
Complications
No major
complications
Excessive scratching
can cause irritation in
genital area
Increases chance of
HIV infection; If
pregnant, a woman
runs the risk of
pregnancy
complications
Increased risk of
getting HIV
Can cause
Complications
during pregnancy
Diagnosis
Vaginal culture
Whiff test
Vaginal culture
Treatment
Anti-fungal cream
Prescription Drugs
Prescription Drugs
STD Prevention Review
Abstinence
Use latex or polyurethane condoms (male or female) and
barriers as much as possible
Water-based lubricants
Reduces friction
Get tested regularly
Reduce number of sex partners
Reduce frequency of risky situations
Spectrum of sexual risk, depending on the STD
e.g., oral sex may be considered low risk for HIV but not
for syphilis
Talk to partners
Vaccines - Hepatitis B, HPV
Get to know your bodies!