File
advertisement

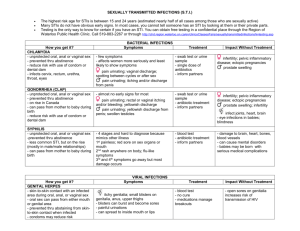
Vaginal lesions Prof Greta Dreyer University of Pretoria Outline Infections Vaginal Intra-epithelial Lesions Vaginal cancer Primary Secondary Infections Viral Bacterial Vaginosis Vaginitis / cervicitis Fungal HPV HSV 2 Candida albicans, glabrata, etc Immunocompromise Viral infections HPV Condyllomata accuminata = warts • Benign neoplasm • Associated with ”LOW RISK” HPV types 6 and 11 • Preventable with vaccination that targets these viral types • Treated with: • Chemicals = podophyllin NOT in vagina, absorbed = toxin • Local destruction = cauterisation, laser • Cytotoxins = chemoRx, 5FU = BURNS the vagina due to cytotoxic effect, EFFECTIVE • Immunostimulants = ALDARA,= imiquimod = EFFECTIVE vulva, vagina Viral infections HSV TYPE 2 Cold sore, fever ulcer Typically vulvar lesion, cervical lesion Nerve distribution, Zoster type, can be chronic, severe Treat systemically NOT locally (placebo) AB, urination, keep clean (NaCl H2O) Bacterial infections Vaginosis CHANGE in vaginal flora for the worse! Often associated with sexual intercourse pH alkaline (>4,5), watery discharge, fishy Gardnerella vaginalis and friends colonise Not major inflammatory reaction Treatment Kill offensives – metronidazole, clindamycin Change environment – lower the pH Enhance “good” bacteria = Lactobacillus Bacterial infections Vaginitis Also change in vaginal flora watery discharge, itch, burning Often Streptococcus culture Can have inflammatory reaction Pre- and post-menopausal condition Treatment: Kill offensives – Penicillin Change environment – increase the estrogen, enhance “good” bacteria = Lactobacillus Bacterial infections Vaginitis STI’s – NOT a problem if vagina only Chlamydia and Gonococcus = friends Identical clinical picture / Cervicitis PAIN, RED, discharge Upper abdomen, peri-hepatitis, peritonitis Difficult to confirm, culture, identify Treated empirically Ciprofloxacin stat Doxycyclin for 21 days Fungal infections Vaginitis / Vulvitis NOT an STI Can be transmitted, aggrevated Opportunistic infection Commensal in GIT After AB, hospitalisation, ICU, UTI Fungal infections Also associations with: Low estrogenic states OC use Eczema, dermatitis High glucose states Chronic trauma Fungal infections Treatment: Local antifungals • Creams, vaginal tablets, suppositories, SR tabs Systemic antifungals • Stat, repeat (1x pw, 1x pm), courses • Equally effective, preference dictates • Better choice for recurrent, hypersensitivity states • NOT for pregnant, LIPID soluble Immuno-compromise HIV, transplant, severe malnourishment MIXED infections Severe Candida, also C. glabrata SEVERE HPV related disease KS, other HSV, Zoster Lymphoma, carcinoma (Spontaneous) non-malignant fistulation Immuno-compromise Improve immunity if possible Improve nutrition Improve hygiene Saltwater sit and douche Chronic AB (TMP-SMZ), AF (Flu-conazole) Repeated AV (Acyclovir) Diagnosis including serology, cytology, histology VA ginal I ntra-epithelial N eoplasia – VAIN now SIL With or without current cervical lesions Prior cervical lesions HPV “HIGH RISK” viral types 16, 18, 31, 33, 35, 45 Diagnosis: Cytology HPV typing Colposcopy = vagina-scope Iodine = Schiller’s TEST (not LIST) = Iodine NEG Acetic acid = AWE VAIN or Vaginal SIL: Treatment Exclude invasion = histology = biopsy Increase immunity, smoking cessation Imiquimod 5FU local application Excision Vault excision In theatre, mark area carefully MONOCLONAL disease, usually confluent Can be multi-focal Destruction Laser Caterisation With or without current cervical lesions PRIMARY Vaginal cancer Squamous OR Adenocarcinoma Staging = FIGO cervical cancer Treatment usually (chemo) radiation HPV related SCARCE!! PRIMARY Vaginal cancer Sarcoma OR Melanoma Treatment usually surgery Systemic recurrence NOT HPV related VERY SCARCE!! SECONDARY Vaginal cancer Direct spread CERVIX VULVA ENDOMETRIUM OVARIAN RECTUM BLADDER / URETHRA Metastatic disease COLON OVARY STOMACH BREAST THYROID LYMPHOMA SECONDARY Vaginal cancer BIOPSY FIND SOURCE STAGE and TREAT appropriately Summary Infections Vaginal Intra-epithelial Lesions Vaginal cancer Primary Secondary Thank You