Antihypertensive Agents
advertisement

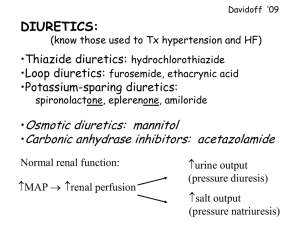
Antihypertensive Agents Dr S. O. Olayemi HYPERTENSION Chronically persistent elevated blood pressure>/=140 mm Hg systolic blood pressure and or diastolic >/= 90 mmHg in individual above 18 years of age Controlled BP SBP <140mmHg and DBP<90mmHG Expert Committee on non Communicable diseases • One third of Nigerian adults above 15 years of age are hypertensives, from this one third are aware of the hypertensive status, and one third are on treatment. • Control definition?Complex?compliance/cost etc TREATMENT GOAL Prevent morbidity and mortality associated with high blood pressure. Achieving control through least intrusive means possible Control other modifiable cardiovascular risk factors. Ace Inhibitors: • Captopril (Capoten) 12.5 – 150mg daily • Enalapril (Vasotec) 5 – 40 mg daily • Lisinopril (Zestril) 5 – 40mg daily • Ramipril (Tritace) 2.5 – 10mg daily • Perindopril (Aceon) 4 – 16 mg daily • Fosinopril (Monopril) 5 – 40mg daily • Action: ACEI block conversion of Angiotensin 1 to Angiotensin 11 thereby blocking stimulation of aldosterone. • Major site of Angiotensin II production – Vessels and not the kidneys. • reduce peripheral resistance and salt and water retention. • Side Effect: Cough, Rashes, Leukopenia, Hyperkalaemia, AngioOdema ACE inhibitors • Reduce dose in volume depleted pt, elderly(hypotension) • May be combined with diuretics • Hyperkalaemia – CKD pts, potassium sparing diuretics and angiotensin receptor blockers. • ARF- renal artery stenosis • Contraindicated in pregnancy and pt with hx of angioodema. ANGIOTENSIN II RECEPTOR ANTAGONISTS • Losartan (Cozaar) 50 – 100 mg daily • Valsartan (Diovan) 80 – 320 mg daily • Temilsartan (Micardis) 20 – 80 mg daily • Irbesartan (Avapro) 150 –300mg daily • Olmesartan (Benicar) 20 – 40 mg daily • Candesartan (Atacand) 8 – 32 mg daily ANGIOTENSIN II RECEPTOR ANTAGONISTS: ARBs • Action: They directly block the angiotensin II type 1 (AT1) receptors – vasoconstriction, aldosterone release, sympathetic activation, ADH release, constriction of efferent renal arterioles • Beneficial AT2-vasodilation,tissue repair and inhibition of cellular growth in blood vessels (reduce peripheral resistance and salt/water retention) • Side Effects: Rashes, Leukopenia,Hyperkalaemia but no cough ARBs • Reduce dose in volume depleted pt, elderly(hypotension) • May be combined with diuretics • Hyperkalaemia – CKD pts, potassium sparing diuretics and angiotensin receptor blockers. • ARF- renal artery stenosis • Contraindicated in pregnancy • Do not induce cough as in ACEIs VASODILATORS ; Hydralazine (Apresoline 20 – 100 mg daily, Minoxidil (Loniten) 10 – 40mg daily, • Action: They decrease peripheral resistance by • • • • • dilating arteries/arterioles. Combined with diuretic/B blockers –diminish fluid retention/reflex tarchycardia. Side Effect: Hydralazine (Headache, lupus-like syndrome), Minoxidil (Orthostasis, facial hirsutism), Diazoxide (Hyperglycaemia. CALCIUM CHANNEL BLOCKERS • Dihydropyridines : • Nifedipine (Adalat/ProcardiA) 20 – 90 mg dly, • • • • • • I, Felodipine (Plendil) 5 – 20 mg dly, Amlodipine (Norvasc) 2.5 – 10 mg dly Nicardipine (Cardene) 60 – 120 mg dly Phenylakylamine: Verapamil 100 – 400 mg dly Benzothiazepine: Diltiazem 120 – 480 mg dly. Action: Reduce smooth muscle tone and cause vasodilation: may reduce cardiac output. Verapamil/diltiazem: decrease HR/delay A-V Calcium channel blockers • Avoid immediate release nifedipines etc • Dihydropyridines are more potent peripheral vasodilators compared to non-dihydropyridines. • Side effect: Dihydropyridines – reflex sympathetic discharge (tarchycardia) Headache, flushing, peripheral oedema. • Non dihyropyridines – variable heart block DIURETICS • Loop diuretics – Frusemide (Lasix) 20mg – 1 g, Bumetanide (Bumex) 0.54mg Torsemide (Demadex) – 5mg dly. • Site of Action: Loop of Henle, Reduce Na+/K+/Cl- cotransporter: reduce urine concentration; Increase calcium excretion. • Preferrably morning/afternoon (avoid nocturnal diuresis) • Higher doses in patients with CKD. • Side effect: Ototoxicity, Hypokalaemia, Hypotension, Gout. DIURETICS: • Thiazides: Chlorthalidone (Hygroton) 6.25 – • • • • 25mg dly, Hydrochlorothiazides (Esidrix) 12.5 – 50mg dly Bendrofluazide 2.5 – 5mg dly Site of Action: Early distal tubule, they reduce NaCl reabsorption thereby reducing the diluting capacity of nephron. Decrease Calcium excretion. Dose in Morning (avoid noctunal diuresis) More effective antihypertensives than loops except in CKD (GFR <30ml/min Side effects: Hypokalaemia, Hyponatreamia, Hypercalcemia, Hyperglyceamia, Hyperlipidaemia, Hyperuricaemia (Problematic in gout), Potassium sparing diuretics • Aldosterone antagonist: Spironolactone • • • • • • (Aldactone) 25 –50 mg dly, Epleronone (Inspra) 50 – 100 mg dly Site of Action: Cortical collecting tubule, They block Na+ channels Side effects: Hyperkalemia, Sexual dysfunction Potassium Sparing: Amiloride/hydrothiazModuretic 5 – 10/50 –100 mg dly, Triamterene/hydrothiaz 37.5 – 75/25 50 mg dly Aldosterone antagonist : Gynaecomastia. Action: Reduce extracellular fluid volume CENTRALLY ACTING DRUGS: Methyl dopa (Aldomet) 250mg – 1g dly, Clonidine (Catapres) 0.1-0.8mg dly, • Action:They inhibit Sympathetic Nervous • • • • System via Central Alpha 2 Adrenergic Receptors. Clonidine withdrawal –Rebound BP elevation Side Effects : Somnolence, Orthostasis, Impotence, Rebound Hypertension RESERPINE (0.05-0.25mg) dlyCombined with diuretics-reduce fluid retention BETA BLOCKERS • Selective Cardioselective: Atenolol • • • (Tenormin) 25 – 100 mg dly, Metropolol (Lopressor) 50 – 200mg dly, Bisprolol (Zebetal) 2.5-10mg dly Bexalolol (Kerlone) 520 mg dly. Non Selective: Propranolol (Inderal) 40320mg dly, Nadolol(Corgard) 40 – 120mg dly, Timolol Blocaden) 10 – 40 mg dly. Intrinsic Sympathomimetic activity: Pindolol (Visken) 10 – 60mg dly, Penbutolol(Levatol) 10 – 40mg dly, Acebutolol (Sectral) 200 – 800 mg dly. Alpha and Beta Blockers: Labetalol (Trandate Beta Blockers • Actions: They reduce cardiac contractility and Rennin release. • Additional benefitTarchyarrythmias,essential tremor, migraine headache and thyrotoxicosis • Side Effect: Bronchospasm ( in severe asthma), bradycardia (A-V Block), Congestive Heart Failure exacerbation, impotence, fatigue, depression. • Abrupt withdrawal-rebound hypertension. Antihypertensive Medications indicated in specific Patient Population • Diabetes with proteinuria • Ace Inhibitors (ACEI) • Congestive Heart Failure ACEI, Diuretics +/-Beta Blockers • Isolated systolic Hypertension • Diuretics preferred: long acting dihyropyridine calcium channel blockers CONTD • MI Beta Blockers without intrinsic • • • sympathomimetic activity, ACEI Osteoporosis Thiazide diuretics BPH Alpha antagonists Pregnancy Methyldopa, Beta blockers, Labetalol, Hydralazine +/-calcium antagonists Antihypertensives in pregnancy • Methyldopa-preferred based on safety data • B Blockers- Safe, but IUGR reported • Labetalol-preffered over methyldopa because • • • • of fewer side effects Clonidine- Limited data available CCBs-Limited data available, no teratogenicity with exposure Diuretics-not first line agents but probably safe in low doses ACEIs/ARBs- major teratogenicity on exposure JNC 7 MANAGEMENT OF HYPERTENSION • Prehypertension 120-139/80-89- Life style modification. • Stage 1 140-159/90-99-Thiazides, may consider ACEI,ARB, B Blockers Calcium blockers or a combination • Stage 2 >160/>100 – Two drug combination (usually a thiazide diuretic+an ACEI, an ARB, a B blocker, or calcium blocker THE END • THANK YOU.