Angiotensin Converting Enzyme inhibitor (ACEI)
advertisement

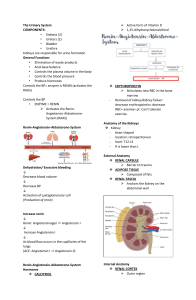
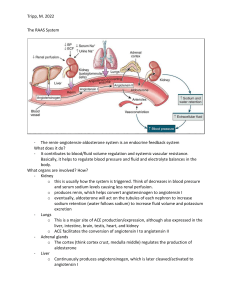
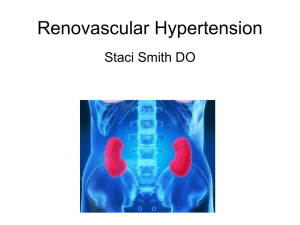
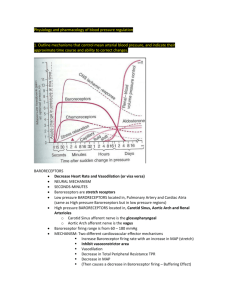
Angiotensin Converting Enzyme inhibitor (ACEI) Vilasinee Hirunpanich B. Pharm(Hon), M.Sc in Pharm(Pharmacology) Renin angiotensin system (RAS) Control the balance of electrolyte, blood volume, BP renin Release from juxtaglomerular cell of cortex Factors which stimulate renin release 1. 2. 3. 4. BP drop Beta-adrenergic receptor stimulation The stimulation of sympathetic system The decrease of Na+-load Function of renin Angiotensin converting enzyme inhibitors (ACEI) • Inhibit enzyme ACE • Decrease ATII • Decrease the destroy of bradykinin • Increase NO, PGI2 and PGE2 angiotensinogen kinogen renin Angiotensin I kallikrin ACEI. Angiotensin II vasodilation inactive Aldosterone release Na+&H2O retention PVR BP bradykinin PG syn. vasodilation PVR BP 1. Vascular smooth muscle • • • Vasodilate & venodilate Dilate afferent and efferent arteriole at renal Increase capillary compliance 2. Cardiovascular effect Decrease both preload and afterload Increase cardiac out put Decrease left ventricular hypertrophy (LVH) No reflex tachycardia 3. renal • Increase renal blood flow • Decrease excretion of protein in urine which good for pts with DM • Inhibit the secretion of aldosterone 4. CNS • Decrease NE release • Increase parasympathetic system so not increase reflex tachycardia • May increase cerebral blood flow Divided into 3 groups 1. Direct action but internalized metabolite to disulfide group Ex. captopril 2. Prodrug (ester dicarboxylic acid) They have the effects when they are changed to active metabolized Ex enalapril, benazepril, cilazapril 3. Soluble in water and not change in the body Ex lisinopril กลไกการยับยั้ง ACE ของยา ACEI structure Drugs captoril •Contain sulhydril (SH) in the structure •Bioavailability 70% •Food interfere with absorption …AC •Metabolized into disulfide group Enalapril • The first prodrug which was used in clinic • It is metabolized into dicarboxylic group …enalaprilat which is the active metabolized. • Elanaprilat has long T1/2 than parent drug. Lisinopril • Direct action in the body • Excrete by renal Other drugs Benazepril Cilazapril (Inhibace) Delapril (Cupressin) Fosinopril (Monopril) Perindopril (Coversyl) Ramipril (Ramace, Tritace) 1. Dry cough • Common SE • Cause by increase cough reflex, from the accumulation of bradykinin and others substance such as substance P, PG 2. Hypotension…esp. first dose 3. Hyperkalemia esp. used with K+ sparing diuretic 4. Fetopathic category X…….not use in pregnant women ADR (cont) 6. Renal failure bilateral renal artery stenosis Severe single renal artery stenosis Need ATII 7. Angioedema...บวมของจมูก ปาก ลิ้น กล่องเสี ยง (พบน้อย) 8. Rash ……..SH group, bradykinin accumulation 9. loss of taste….most in captopril 10. Protein in urine (less) Angiotensin receptor blocker(ARB) Lorsartan Valsartan Candesartan Eprosartan Irbesartan telmisartan Mechanism of action • Direct inhibit at angiotensin II receptor (type I) • More selective than ACEI • No or less Side effect of dry cough and angioedema Angiotensin I ACEI Angiotensin II Cellular response vasoconstric tion Cardiac hypertrophy ARB Aldosterone release Na+ reabsorption Limitation of ACEI 1. Bilatery artery stenosis, unilatery artery stenosis 2. Pragnancy women….esp 1st trimester 3. Chronic cough 4. Black people…low renin activity Drug interaction 1. Beta-blocker …decrease renin release 2. K+-sparing diuretic……increase K+ 3. NSAID……decrease PG synthesis, bradykinin 4. Probenecid….inhibit abs 5. Antacid……decrease abs Clinical uses Treatment HT with other condition Ex 1. HT with Dyslipidemia, Gout, DM, renal 2. CHF 3. Atherosclerosis 4. LVH