quality use of cardiovascular medication
advertisement

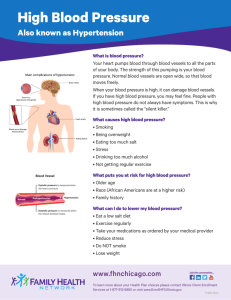
QUALITY USE OF CARDIOVASCULAR MEDICATION Dr Mark Abelson Prescription Drugs and Drug Trials • Drug development - basic science research in a laboratory - chemical patented (20 years) - laboratory testing - Phase 1 trials – tested for safety and efficacy in animals - Phase 2 trials – tested for safety in normal humans - Phase 3 trials – show effective (better than placebo or current standard treatment) and safe in many thousands of patients around the world (double blind • Drug launched (5 years patent remaining) - post marketing surveillance • $ +100 million • Register with FDA / MCC (years) “Alternative” Drugs • Vitamins • Minerals • Cholesterol vaporises • Tissue salts NO RESEARCH NO EVIDENCE OF EFFICACY NO PRODUCTION CONTROL NO REGISTRATION PROCESS Trials done consistently show NO benefit eg. Folate, antioxidant vitamins Conspiracy Theory • Doctors and Universities – bribed / kick backs from pharmaceutical companies? • Lack of patient trust? • Only want “natural” treatment ( death?) Commonly Used Drugs • Statins -reduce cholesterol - Zocor, Simvastatin, Lipitor, Aspavor, Crestor, Prava, Lescol – primary prevention (at risk but currently asymptomatic) benefit in high risk persons or - secondary prevention (known with coronary artery disease) 30% reduction in future heart attack and stroke • Aspirin - reduces blood stickiness – primary (little benefit) or secondary prevention (25% ) • ACE-I / ARB – lower BP, improve heart failure - Prexum, Coversyl, Lisinopril, Zetomax, Pharmapres, Enalapril, Cozaar, Zartan, Diovan Commonly Used Drugs • Beta Blockers – reduce heart rate (angina) and BP, heart failure - Concor, Bilocor, Bisocor, Carloc, Dilatrend • Calcium Channel blockers – reduce heart rate and BP - Verahexal, Calcicard, Ravamil, Amloc, Norvasc, Zildem New Comers • Coralin – reduces heart rate without decreasing BP and no BB side effects (lethargy, impotence) - angina and heart failure • Dabigatran – thins blood like Warfarin but no INR (blood) testing needed - atrial fibrillation Guideline recommendations for BP goals – <140/90mmHg for essential hypertension – <130/80mmHg for hypertensive patients with diabetes • Most patients with hypertension will require two or more antihypertensive agents to achieve BP goal *ESH/ESC: European Society of Hypertension/European Society of Cardiology **JNC 7: Joint National Committee on Prevention, Detection, Evaluation, and Treatment of High Blood Pressure, seventh report Guidelines Committee. J Hypertens 2003; 21: 1011-53. Chobanian AV, et al. JAMA 2003; 289: 2560-72. Combination therapy needed to achieve target SBP goals Trial/SBP achieved INVEST (136mmHg) ALLHAT (138mmHg) IDNT (138mmHg) RENAAL (141mmHg) UKPDS (144mmHg) ABCD (132mmHg) MDRD (132mmHg) HOT (138mmHg) AASK (128mmHg) 1 INVEST; data on file. ALLHAT Collaborative Research Group. JAMA 2002; 288: 2981-97. Brenner BM, et al. N Engl J Med 2001; 345: 861-9. Lewis EJ, et al. N Engl J Med 2001; 345: 851-60. Adapted from Bakris GL, et al. Am J Kidney Dis 2000; 36: 646-61. 2 3 Number of antihypertensive drugs 4 Hypertension: a risk factor for cardiovascular morbidity and mortality Biennial age-adjusted rate per 1000 Coronary 50 artery disease Stroke Peripheral Cardiac arterial disease failure Normal Hypertensiv e 40 30 20 10 0 MenWomen MenWomen MenWomen MenWomen Risk ratio 2.0 2.2 3.8 2.5 2.0 3.7 4.0 3.0 Excess risk 22.7 11.6 9.1 3.8 4.9 5.3 10.4 4.2 Kannel WB. JAMA 1996; 275: 1571-6. MRFIT: association of systolic BP and diabetes with cardiovascular risk CVD deaths per 10,000 person-years 300 Non-diabetic Diabetic 250 200 150 100 50 0 <120 120-139 Stamler J, et al. Diabetes Care 1993; 16: 434-44. 140-159 160-179 Systolic BP (mmHg) 180-199 200+ Early morning BP surge coincides with peak incidences of stroke and myocardial infarction Stroke (n=1,167) Early morning BP surge 50 160 45 140 40 35 120 30 100 25 80 20 60 15 40 20 0 McInnes G. J Am Soc Hypertens 2008;2:S16–22. 18.00 0.00 Time of day 06.00 12.00 10 5 0 MI (per hour) Cerebrovascular events (per 2 hours) MI (n=2,999) 180