Facts - Pennsylvania Health Care Association
advertisement

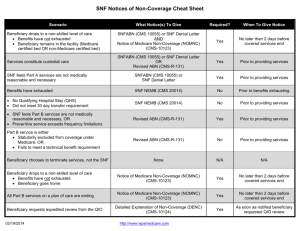
Care Transition Opportunities for LTC Naomi Hauser , RN, MPA Director Care Transitions Quality Insights of Pennsylvania August 14, 2013 Care Transitions A continuous process in which a patient’s care shifts from being provided in one setting of care to another Affordable Care Act New care transition/30-day readmission reduction programs Increase incentives to improve coordination between settings and providers that help reduce health care costs through prevented readmissions Supporting individuals and caregivers who experience a transition in their care setting Financial Incentives/Penalties Medicare began financial incentives to reduce potentially avoidable hospital transfers through payfor-performance initiatives, bundled payments and other strategies October 2013 Facts Avoidable rehospitalizations drivers – A failure in hospital discharge processes – Patients’ ability to manage self-care – Quality of care in the next community settings (skilled nursing facilities, home health care agencies, and office practices) Facts IHI faculty discovered that the failures in care coordination between the hospital and SNF that led to rehospitalization within 30 days after discharge fell into two main categories: – Those related to care provided within the skilled nursing facility – Those related to care provided during the transition from the hospital to the skilled nursing facility Facts Nursing home residents transferred to hospitals for acute change in their clinical condition 1 of 4 Medicare patients admitted to SNF from hospitals – Readmitted within 30 days – 2/3 potentially avoidable Opportunities Identify improvement opportunities/RCA Use Interact tools Start the conversations with partners/ER Collaborate Transparency Establish goals/measures/collect data/trends Spread/sustainability interventions Changing Image of LTC Important to understand consumers’ emerging and changing needs, wants and expectations, especially concerning – Quality of their experience with providers position as • Trusted advocates in helping consumers access services and supports • While assisting consumers and their families – In navigating complex aging challenges Action Steps Identify and implement effective programs and practices Promote safe, effective care transitions while decreasing potentially avoidable 30-day readmissions Get started now! Interventions Hickory House COACHING C.O.A.C.H. Customer Service and Education Based Elaine Doyle, BSN BA RAC- CT Mary Zebert, SW What does C.O.A.C.H. mean? Communicate Expectations Organize Goals Assign Coach Continued Review Handoff Homework Team Roster Case Manager Coach Rehab Social Services Clinical Services Registered Dietician 72-Hour Meeting Introductions Prior level of functioning Our goals Patient’s goals 72-Hour Meeting Goal is to shift the patient’s “time oriented” focus to a “goal oriented” focus Rehab initiates the checklist and hands it off to the CM before the meeting – CM adds the nursing goals Determine patient’s education needs and place patient on “alert charting” Incorporate the patient’s expectations into your goal sheet then review it with patient and family Introduce the COACH Continued Communications Update the goal sheet at the weekly rehab meeting; discuss possible need for a home assessment Share the changes with the patient If the patient is off track, their coach meets with the CM, CM determines if an extra meeting is needed Nursing will monitor patient for early warning signs of change in condition using the INTERACT tools to enable early treatment of illness and avoid unnecessary hospital readmission Discharge Meeting 72 hours before discharge date Case Manager approaches the patient regarding their safe transition home, reviews their progress and offers a general overview of what to expect as they transition from SNF to home The Case Manager and Social Worker coordinate the logistics of the discharge; DME and transitional services are arranged Verify that transport to home has been secured, confirm date and time of transition home CM issues the Patient Education Handbook to the patient and explains how it will benefit the patient CM issues printed handouts related to patient’s needs CM instructs patient that an appointment with his PCP needs to be made in a one week Day of Transition Each team member will meet with the patient to review the Patient Education Handbook in relation to their corresponding area of expertise. Instructional notes will be made in the book CM will review the safe transition instructions with the patient Transition Follow-Up SS places a call on day 2 or 3 to inquire about PCP appointments SS places a second call on day 7 to 10 to find out if the appointment was made SS places a third call on day 21 to 24 days to find out if the appointment was kept SS places a fourth call on day 31 to find out if the patient was readmitted to the hospital Results The two months of data showed: 22 patients had a Post-Discharge Follow-up phone call on day 2 or 3 20 patients were connected on day 2 or 3 with a follow-up phone call 16 patients reported appointment made on day 2 or 3 phone call. Results The two months of data showed: – 18 patients reported keeping appointment on day 7 followup phone call – 17 patients were not readmitted within 30 days of hospital discharge Facts Research highlights that – Nearly one-fourth of Medicare beneficiaries discharged from the hospital to a SNF – Are readmitted to the hospital within 30 days – Cost Medicare $4.34 billion in 2006 QUESTIONS This material was prepared by Quality Insights of Pennsylvania, the Medicare Quality Improvement Organization for Pennsylvania, under contract with the Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services (CMS), an agency of the U.S. Department of Health and Human Services. The views presented do not necessarily reflect CMS policy. Publication number 10SOW-PA-ICPCKD-080513. App. 8/13.