Presentation on Payment Reduction Initiatives from Medicare
advertisement

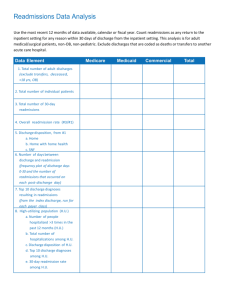
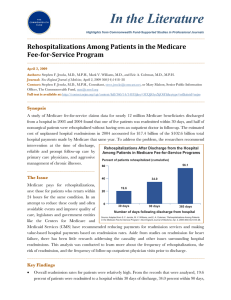
Payment Reduction Initiatives from Medicare Ranae N. Beeker, RN,MSN,CCM,ACM Admissions Coordinator/RN Case Manager Sue Noyes, RN,BSN,CCM Manager Case Management/Social Services Definition: A readmission is a return hospitalization after an earlier hospital admission. ◦ Medicare is reviewing “all cause” readmissions for 30 days post hospitalization Exception: Same-day readmissions for the same condition to the same hospital Current focus of Center for Medicare and Medicaid Services (CMS) with goal to achieve three-part aim outcomes: 1) Better Care 2) Better Health 3) Lower Costs Readmissions national cost $17 billion annually. 76% considered avoidable Affordable Care Act directed by Medicare (CMS) will financially penalize hospitals July 2012 Readmission data publicly reported Readmissions are expensive, adverse events for patients Indicator for level of quality of care received Effective October 1, 2012 (FFY 2013). Medicare payment reductions under this program will be capped at 1.0% in FFY 2013. The capped reduction amount will increase over time. Identified Acute Myocardial Infarction ( AMI) Heart Failure (HF) and Pneumonia (PN) readmissions as common, costly and often preventable. These conditions impose a substantial burden on patients and the healthcare system and there is marked variation in outcomes by institution. Measure CTMC Rate Readmission National Rate AMI 19.6% 19.2% Heart Failure 24.6% 24.7% Pneumonia 17.0% 18.5% Based on discharges from July 2008-June 2011 Data from Hospital Compare website. Working to promote transitions of care are smooth, seamless (Transitions of Care Committee) Identifying patients with readmission potential on admission Working with area nursing homes/skilled nursing facilities Working with our Home Health (as well as other Home Health agencies that service our area). Sepsis Altered Mental Status related to infection or encephalopathy Acute Kidney Failure Anemia, Gastrointestinal Bleed Dehydration related to diarrhea or N/V Pneumonia Cardiac Dysrhythmias Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease Acute on Chronic Congestive Heart Failure Acute Myocardial Infarction Evaluate the spectrum of care for patients Identify systemic or condition-specific changes to make care safer and more effective Invest in interventions that reduce complications of care Improve process for assessing the readiness of patients for discharge Improve discharge instructions Reconcile medications More carefully transition patients to next level of care i.e outpatient care or other institutional care End of Life Care Planning opportunity Partner with Home Health Agencies Partner with Nursing Homes Promote smooth transition of care (regardless of disposition) Establish high-risk criteria for discharge staff (i.e. Social Workers, Case Managers and nursing staff) Create readmission evaluation tool New concept idea: Huddle (5min) with identified readmission (team approach) Promote f/u appt for all discharge patients within 5-7 days of discharge CTMC will be providing information as Medicare continues to move forward on budget reduction initiatives. Work collaboratively with physicians & health care community . Mode of contact: via your office staff, email, & Medical Staff office. Do not hesitate to call Case Management or Administration with questions… This is definitely a work in progress for all hospital systems. http://www.hret.org/care/projects/resources /Readmission_Guide.pdf www.rarereadmissions.org/documents/RARE_ Discharge_Observation.doc · 21st Annual Midas+User Symposium: Potentially Preventable Readmissions Wagonhurst, Patrice “Tools to Successfully Apply for the CMS Community-Based Care Transitions Program 2012.Nikiforakis,K. Cheshire Medical Center. Keene, NH http://www.qualitynet.org/dcs/ContentServer ?cid=1219069855273&pagename=QnetPubli c%2FPage%2FQnetTier2&c=Page http://www.hospitalcompare.hhs.gov/hospita lcompare.aspx#vwgrph=1&cmprTab=3&cmprI D=450272%2C670056&stsltd=%20TX&loc=S an%20Marcos%2C%20TX&lat=29.8832749&ln g=97.94139410000002&version=alternate..&As pxAutoDetectCookieSupport=1