Mini-CEX
advertisement

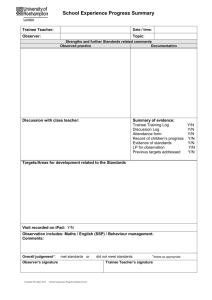
Mini-clinical evaluation exercise Mini-CEX Assessment of Overall Clinical Skills What is a mini-CEX ? A workplace-based assessment a short episode of real student-patient interaction within the workplace observed and judged by the supervising clinician (observer) followed by feedback Why do mini-CEX ? Workplace-based assessment drives experiential learning? Are Clinical Skills Important? Clinical skills are essential for patient care Clinical skills : Medical interviewing Physical examination Clinical judgment Communication skills Evaluation of clinical skills requires direct observation diagnosis and medical interview Hampton (BMJ, 1975): Medical interview: 82% – Physical exam: 9% – Laboratory: 9% Kirch (Medicine, 1996) – Medical interview (+Ph/Ex): 70% – Imaging: 35% Importance of complete Clinical Skills To decrease diagnostic errors – Inaccurate/ incomplete medical interview is one important reason of diagnostic errors. Wrong information leads to wrong decisions To increase patient satisfaction – Higher with better communication skills To improve patient self-care – Better adherence and outcomes associated with better physician communication skills Miller’s Pyramid Mini.cex DOES Faculty Observation Faculty Observation SHOWS HOW KNOWS HOW KNOWS OSCE PMP.KFP MCQ.SAQ how to do miniCEX ? too simple Triangulation DESK Patient Resident(trainee) Attending(observer) In the mini-CEX, a single faculty Member(observer) observes the trainee`s interact with a patient in any of a variety of settings including the hospital, outpatient clinic, and E.D In fact, the mini CEX can assess a range of core competencies that a trainee uses during day to day encounters with patients. Encounters should … take place In the normal working environment . take place In different working environment. cover different cases and different specialty areas. be observed by different skilled observers. During the encounters … Observer must assess trainee`s clinical skills & fill the feedback form. Observer must note some extra information such as complexity of patient`s problem One encounter takes 20 min & has 2 steps Exam : 15_20 min Feedback : ~5 min The trainee conducts a focused history and physical examination and then provides a diagnosis and treatment plan. The faculty member(observer) scores the performance using a structured document and then provides educational feedback. FEEDBACK The feedback session is the most important part of the mini-cex & it should occure immediately after the encounter. The observer should discuss both the positive & negative aspects of encounter with the trainee. The observer should also discuss a plan to improve any areas of weakness. To be most effective, feedback needs to be interactive strengths and weaknesses. → (agreement & signature) Mini_CEX program Trainees have to complete at least one encounter for every 3 months (4 encounters in a year) in order to be eligible for central exam at the end of the year. The trainee should meet an educational supervisor during the program . During this meetings they can map out a learning plan for next period, according to trainee`s rotations & his/her past encounters. The trainee is responsible for instigating each mini- CEX encounter. Each assessment should focus on a limited number of competencies & different encounters should include a range of cases with each focusing on specific aspects of the clinical skills. (e.g. history taking, PH/EX, … ) Each observer may have his/her own way to run the encounters with the trainees. One accepted format is : To choose the last patient of a day ( e.g : the last outpatient in the clinic or the last patient on the ward round) →To be less disruptive to the flow of the clinical workload. →To allow for feedback to occur straight after the encounter. How many encounters must be observed to provide a reliable mean rating? Changes in reliability as a function of the number of observed encounters 1 0.9 0.8 0.7 0.6 0.5 1 4 6 8 10 12 14 16 18 Mini-CEX: Reliability Reliability Coefficients > 0.80 with 6 observations > 0.90 with 12 observation > 0.95 with 24 observations Mini-Clinical Examination (Mini-CEX) The evidence will be rated and recorded in the Portfolio. Immediate feedback will be provided by the observer rating the student. A learning plan will be developed, based on the strengths and developmental needs observed Summary Basic clinical skills are important: so is the need to observe them! Observation is a complex skill that requires training and practice Direct observation by educators will remain a critical component of both evaluation and feedback