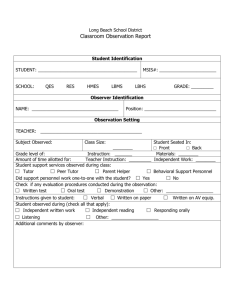
Classroom observation and post
advertisement

Classroom observation and post-observation interview 呂曉娟 98.10.09 Principles of teaching children English • Know students well (background, interests, abilities, and learning needs) • Fun and learning parallel • Contextualized teaching • Effective teaching (various from of group teaching, interdisciplinary approaches, etc.) • Questioning strategies • Multiple intelligences • Multiple assessment procedures • Effective classroom management Definition and significance of observation • Observation is one effective means of learning how certain teaching methods are employed in the schools, how classrooms are organized, and how students respond to the classroom environment. • School-based observation and teaching experiences are the bridge between the worlds of theory and practice. Peer observation • Peer observation refer to a teacher or other observer closely watching and monitoring a language lesson or part of a lesson in order to gain an understanding of some aspect of teaching, learning, or classroom interaction. Purpose and benefits of peer observation • Observation is a basic part of the learning of many occupations. • In teaching, observation provides an opportunity for novice teachers to see what more experienced teachers do when they teacher a lesson and how they do it. But experienced teachers can also benefit from peer observation. • For both teachers, observation also has social benefits. It brings teachers together who might not normally have a chance to interact and provide an opportunity for the sharing of ideas and expertise, as well as a chance to discuss problems and concerns. General guidelines for peer observation • Observation should have a focus. The value of observation is increased if the observer knows what to look for. An observation that concludes with a comment such as, ”Oh , that was a really nice lesson,” is not particularly helpful to either party. • Observers should use specific procedures. Lessons are complex events with many different activities occurring simultaneously. • The observer should remain an observer. Suggested procedures for peer observation • • • • • Arrange a per-observation orientation session Identify a focus for the observation Employ appropriate procedures to suit the purpose of the observation Carry out the observation Arrange a post-observation session (interview) Arrange a pre-observation orientation session • Before beginning the observation, the two teachers meet to discuss the nature of the class observed, the kind of material being taught, the teacher’s approach to teaching, the kinds of students in the class, typical patterns of interaction and class participation, and so on. Identify a focus for the observation Many aspects of a lesson can be the focus of an observation. Typical” how –to” dimensions of teaching include the following: • how the teacher stars and ends a lesson • how the teacher allots time within a lesson • how the teacher assigns tasks to students • how the teacher organizes learning groups • how the teacher supervises students when they are learning • how the teacher asks questions Employ appropriate procedures to suit the purpose of the observation • written narrative • field notes • checklists Carry out the observation • careful observation: your first task • effective observation: an objective and a procedure • effective observation: being objective Arrange a post-observation session (interview) • The two teachers meet as soon as possible after the lesson. The observer reports on the information collected during the lesson and discusses it with the teacher. use positive language. talk about the strengths of teaching first, watch for language use (be non-evaluative and nonjudgmental) Things to be aware when doing the observation • Appropriate manners: wear a smile on your face • Stay focused and keep writing • Categorized the content while writing • Analyze while writing (strengths, weaknesses)