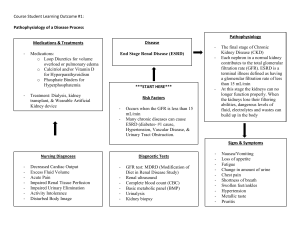
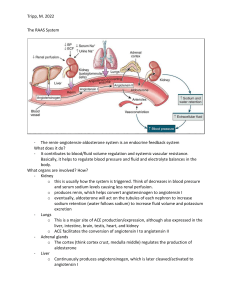
The Urinary System COMPONENTS: • Kidneys (2) • Ureters (2) • Bladder • Urethra Kidneys are responsible for urine formation General Functions • Elimination of waste products • Acid-base balance • Controls the plasma volume in the body • Controls the blood pressure • Produce hormones Controls the BP= enzyme is RENIN (activates the RAAS) Controls the BP • ENZYME = RENIN Activates the ReninAngiotensin-AldosteroneSystem (RAAS) Renin-Angiotensin-Aldosterone-System Dehydration/ Excessive bleeding ↓ Decrease blood volume ↓ Decrease BP ↓ Activation of juxtaglomerular cell (Production of renin) Active form of Vitamin D 1,25-dihydroxycholecalciferol ERYTHROPOIETIN Stimulates new RBC in the bone marrow - Removal of kidney/kidney failue= decrease erythropoietin= decrease RBC= anemia= pt. Can't tolerate exercise Anatomy of the Kidneys Kidney - bean-shaped - location: retroperitoneal - level: T12-L3 - R is lower than L External Anatomy RENAL CAPSULE Barrier to trauma ADIPOSE TISSUE Composed of fats RENAL FASCIA Anchors the kidney on the abdominal wall Increase renin ↓ Renin: Angiotensinogen Angiotensin I ↓ Increase Angiotensin I ↓ As blood flow occurs in the capillaries of the lungs (ACE: Angiotensin I Angiotensin II) Renin-Angiotensin-Aldosterone-System Hormones CALCITRIOL Internal Anatomy RENAL CORTEX Outer region