Hyperkalemia
advertisement

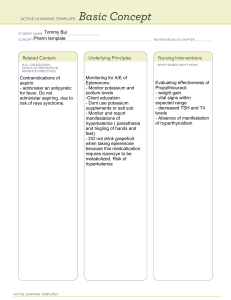
Hyperkalemia • 62 y/o male, diabetic, with chronic kidney disease • Creatinine of 3.5 mg/dL • Estimated GFR of 15ml/min • CC: inability to lift himself from a chair • Eating fruits with each meal for the past 2 weeks Hyperkalemia • PE: Marked proximal weakness and decreased skin turgor • ECG: peaked T waves and widening of the P wave and QRS complex Hyperkalemia Blood Test Plasma Na 130 meq/L K 8.5 meq/L Chloride 98 meq/L HCO3 17 meq/L Creatinine 2.7 meq/L pH Capillary blood glucose Serum acetone 7.32 400 mmol/L (+) Factors responsible for the elevation of plasma potassium • Chronic renal failure – decreased excretion of potassium • Ingestion of foods high in potassium such as bananas and oranges – excessive exogenous potassium load • Some medications such as NSAIDs Pseudohyperkalemia? • This is not pseudohyperkalemia • Pseudohyperkalemia is a result of: – Hemolysis (in laboratory tube) most common – Thrombocytosis – Leukocytosis – Venipuncture technique (ie, ischemic blood draw from prolonged tourniquet application) Clinical manifestations of hyperkalemia • Cardiac and neurologic symptoms predominate • Patients may be asymptomatic or report the following: – Generalized fatigue – Weakness – Paresthesias – Paralysis – Palpitations Clinical manifestations of hyperkalemia • Pathophysiology – Major intracellular ion – Concentration gradient maintained by the Na/KATPase pump – Important in maintaining cellular membrane potential. That is why tissues that are excitable (e.g. muscles and nerves) are affected. Management • Requires prompt treatment since hyperkalemia is severe (>7 meq/L) • ECG monitoring • Medications – Calcium chloride - restores normal gradient between threshold potential and resting membrane potential, since it is elevated in hyperkalemia Management • Medications – Insulin - stimulates cellular uptake of K+ within 2030 mins. It must be administered with glucose to prevent hypoglycemia – Sodium bicarbonate - increase the pH, promotes temporary potassium shift from the extracellular to the intracellular environment – Furosemide – promotes renal excretion of potassium Management • The patient should undergo hemodialysis if deemed necessary