Liver Function Tests
advertisement

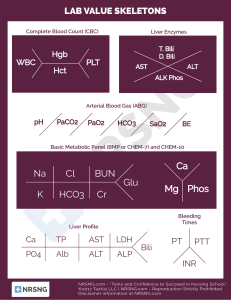
Liver Function Tests Steve Bradley Chief Medical Resident, HMC Inpatient Services What are “Liver Function Tests” Few are truly associated with function – Albumin: protein synthetic function – INR: clotting factor synthesis Most are related to cell injury – Patterns point to specific cell injury Tests of Liver Injury AST/ALT – Cytoplasmic enzymes found in hepatocytes – Very sensitive marker for hepatocyte injury Specificity is poor (other sources, e.g. muscle) – Mitochondrial isoenzyme AST increased by ethanol (explains 2:1 ratio) Alkaline Phosphatase/GGT – Canicular enzymes Gradual increase in plasma levels with obstruction of canicular flow Patterns of Enzyme Elevation Hepatocellular injury – AST/ALT Cholestatic – Bilirubin/alkaline phosphatase Mixed Isolated/predominant alkaline phosphatase elevatioin Caveats to Patterns Hepatocellular injury – Also results in release of bilirubin – Alkaline phosphatase also found in hepatocyte Cholestatic – Biliary obstruction can lead to hepatocellular injury History and Physical guide your thinking!! Patient #1: Suzie Duzie Presents with two days of fever, abdominal pain, yellow skin, nausea, vomiting. Labs demonstrate the following: – – – – – – AST 3210 ALT 3060 Alk phos 249 TBili 6.2 (Direct 4.3) Albumin 3.1 INR 1.2 What targets the hepatocyte? Toxins – Alcohol – Medications – Severe hypotension – Vasoconstriction – Sepsis Tylenol – Mushrooms Viral – Hepatitis A/B/C – EBV/HSV/CMV Ischemia Autoimmune Wilson’s Alpha-1 antitrypsin deficiency Degree of elevation points to etiology >1000 to 2000 – Ischemia – Toxin – Virus >500 to 1000 – Acute biliary obstruction <300 – Alcoholic liver disease, cirrhosis, chronic obstruction – AST/ALT>2 and each <300 suggests EtOH or cirrhosis If >500, unlikely EtOH Back to our patient Transaminases in the 1000s – Suggests ischemia/toxin/viral IVDU – Risk of acute Hep B or acute Hep C Cocaine – Risk of ischemia Recent infection – Doxycycline Patient #2: Ima Hurtin 40 year-old overweight woman presents with right UQ abd pain, fever, chills. Previous episodes after fatty meals. Laboratory Studies – – – – – – AST 67 ALT 57 Alk Phos 293 TBili 4.1 (Direct 2) Albumin 4 INR 1 Increased Bilirubin Sources – Increased production – Hemolysis, hematoma reabsorption – Impaired uptake/conjugation – Dubin-Johnson, Gilbert’s – Impaired excretion – Renal failure, biliary obstruction Conjugated=direct=processed by liver Unconjugated=indirect=not processed by liver – Fractionation – helpful to assess for unconjugated hyperbilirubinemia < 20% direct AND indirect >1.2 Biliary Obstruction Canicular cell injury – Alkaline phosphatase Liver and bone major sources Increased synthesis and release in liver disease – Up to 3x normal in variety of liver disease – GGT Sensitive indicator of canicular cell injury Parallels alkaline phosphatase increase when of liver origin Causes of Biliary Obstruction Extrahepatic – Choledocholithiasis – Malignancy Cholangiocarcinoma Pancreatic cancer Gallbladder cancer Ampullary cancer – Primary sclerosing cholangitis – AIDS Cholangiopathy Intrahepatic – TPN – Sepsis – Primary sclerosing cholangitis – Primary biliary cirrhosis – Intrahepatic mass How would you like to approach this patient? Finding the source of obstruction – Ultrasound: good for extrahepatic cause – CT/MRI/ERCP: for both intra or extrahepatic cause In our patient? Patient #3: Biggie Smalls 46 yo man with history of IVDU and longstanding alcohol use following up in clinic. Laboratory – AST 68 – ALT 37 – Alk phos 194 – TBili 1.3 – Albumin 2.9 Mixed Patterns of Elevated Liver Function Chronic Liver disease – Hepatitis B, Hepatitis C – NASH – Alcoholic liver disease – Hemochromatosis – Autoimmune hepatitis Patient#4: Iva Fallen 72 yo man fell in bathroom. Found the next day. Laboratory – AST 167 – ALT 58 – Alk phos 127 – TBili 1.8 – Albumin 3.9 What else do you want to know? Where else is AST and ALT found? How can you look for evidence of muscle injury? Additional Laboratory CK 7260 Myoglobin 23390 UA – 2+ blood, microscopic no RBC Diagnosis? Isolated or Predominant Alk Phos Chronic Biliary Disease – Primary biliary cirrhosis – Primary sclerosing cholangitis Infiltrative disorder – Amyloid – Granulomatous diseases – Metastatic carcinoma – abscesses Last Case: Sue Sadd 32 yo woman, depressed, “took some pills” a few days ago Laboratory – AST 1450 – ALT 1620 – Alk phos 242 – TBili 8 (direct 4) – Albumin 2.9 – INR 1.7 Fulminant Hepatic Failure Rapid development of severe acute liver injury with impaired synthetic function and encephalopathy – Previously had a normal liver or had wellcompensated liver disease Causes Treatment Directed therapy – Acetaminophen - mucomyst – Acute fatty liver of pregnancy - delivery of infant – Amanita mushroom poisoning - penicillin and silibinin – Wilson's disease - D-penicillamine – Herpes Simplex Infection – acyclovir Liver transplant