Liver “Function” Test 2 0 1 3
advertisement
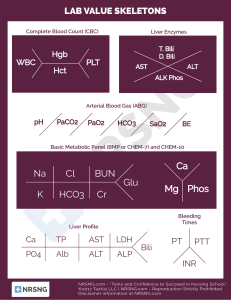
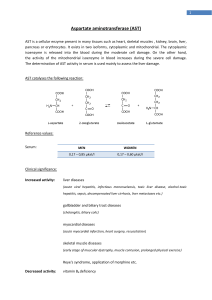
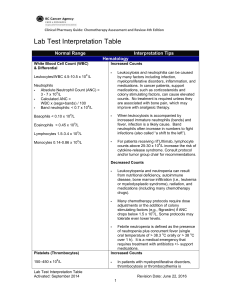
Liver “Function” Test 2013 MINI-LECTURE Objectives Understand the significance of Liver Function Tests Identify the patterns that indicate specific disease categories Identify the appropriate further work up of abnormalities Case 49 year old Female presents with chest pain and negative troponins admitted for monitoring, LFT in ED show AST: 57, ALT: 62, Alk Phos: wnl, T. Bili: wnl. What is the next step in management? A: RUQ Ultrasound B: Hepatitis Panel C: Screen for Alcohol Use D: CT Scan Abdomen Etiology Synthetic Function: Total protein, serum albumin, total bilirubin, prothrombin time ALT: found primarily in Hepatocytes AST: found in many sources- Liver, heart, intestine, pancrease Alkaline phosphatase: found in liver, bones, intestines, and placenta Bilirubin: Two sources- indirect (old red cells), Direct (conjugated in liver) Patterns Elevation in ALT & AST: primarily cellular injury Etiology: Acute Viral Hepatitis, Acetaminophen toxicity, shock liver Elevation in Alk Phos and Bilirubin: cholestasis or obstruction Etiology: choledocholithiasis, biliary stricture, malignancy Mixed: Serum Bilirubin can be elevated in both conditions Pearls for further evaluation Albumin Low Albumin- suggests chronic process (cirrhosis/cancer) Normal- suggests acute process Prothrombin Prolonged suggests vitamin K deficiency 2/2 prolonged jaundice or malabsorption Significant hepatocellular dysfunction (failure to correct w/ vit K administration indicates severe injury) Bilirubin in Urine Indicates hepatobiliary disease (indirect not excreted by kidney) Mild Aminotransferase Elevation Workup Primary Causes Screen for alcohol abuse (AST/ALT > 2:1) Review medications If Negative: then serology for hepatitis B/C, screen for hemochromatosis, then evaluate for fatty liver w/ RUQ US Secondary Exclude muscle disorders Thyroid function tests Celiac disease Adrenal insufficiency IF All negative: Autoimmune, Wilson’s dx, alpha 1 antitrypsin, consider biopsy or observe (pt w/ ALT/AST less that 2x ULN) Hyperbilirubinemia Unconjugated Over production: hemolysis, extravasation of blood into tissue, ineffective erythropoiesis Impaired Uptake: Heart failure, portosystemic shunts, Gilberts, Drugs (Rifampicin and probenecid) Impaired conjugation: Gilberts, hyperthyroidism, Liver Dx, Crigler-Najjar Conjugated Extrahepatic: choledocholithiasis, tumors, PSC, AIDS, pancreatitis, strictures, parasitic infxn Intrahepatic: hepatitis, PBC, Drugs, Sepsis/hypoperfusion, infiltrative disease, TPN, Sickle cell, pregnancy, Dubin Johnson and Rotor Syndrome Alkaline Phosphatase Source includes: bone, liver, placenta, varies w/ age Serum GGT: elevated in Liver Disease not Bone disease Most common cause: chronic cholestasis or infiltrative disease Primary biliary cirrhosis, primary sclerosis cholangitis Sarcoidosis, amyloidosis, liver metastasis Initial Workup: RUQ Ultrasound Anti-mitochondrial Antibody Consider- MRCP or ERCP Observe: if Alk phos <50% above normal Elevation of Several LFT’s Hepatocellular pattern ALT/AST > 25 ULN only seen in hepatocullular dx With Jaundice Alcholic AST:ALT.2 AST rarely > 300 units/L Viral Aminotransferase> 500 u/L w/ ALT >AST Toxic: i.e. Acetaminophen Shock liver Autoimmune and Wilson’s Dx Elevation of Several LFT’s Predominantly Cholestatic Pattern Determine Intra vs Extra hepatic RUQ U/S: assess for Biliary dilation Extrahepatic: consider CT or MRCP or ERCP Common Causes: choledocholithiasis, malignancy, PSC, Pancreatitis Intrahepatic: broad differential Work-up determined by clinic situation Summary Described significance of each Liver function test Identified common LFT abnormalities Familiarized with basic initial work up of elevated Liver function Tests