Hodgkin lymphoma - AMC Hematologie

Hodgkin lymphoma
Clinical presentation and treatment
Hodgkin lymphoma
• Malignant cell is a B lymphocyte
• Enlarged lymph nodes important clinical sign
• Thus: Confusion!
– Patients
– Students
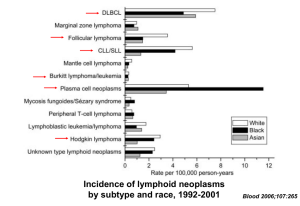
• Q: what is difference with non-Hodgkin lymphomas where in most cases malignant cell is also of B cell origin?
Differences Hodgkin and non-Hodgkin lymphomas (NHL)
• Age distribution
– NHL : > 60 years peak incidence
– Hodgkin: bimodal
• Variabilty of clinical presentation
– Hodgkin: limited stage; rarely extranodal
– NHL: higher stage; frequently extranodal
• Treatment
– Radiotherapy very important part of treatment in
Hodgkin's disease
Hodgkin lymphoma
Clinical presentation
In general less complex than NHL!
• Lymphadenopathy
– Enlarged painless lymphnodes
– Supra-diaphragmatic in 90% (cervical, mediastinal)
• Hepato-splenomegaly: initially infrequent
• B symptoms in 25-30%
• Fever, often periodical; classically Pel-Ebstein
• Night sweats
• Weight loss (> 10% within 6 months)
Hodgkin lymphoma
Clinical Staging
• History/ Physical examination
• CT scan neck, thorax, abdomen
• 18 FDG-PET scan
• Bone marrow biopsy
Hodgkin lymphoma
Ann Arbor staging
Hodgkin lymphoma
Standard therapy in 2012
• Stage I/II
– Favorable
– Unfavorable
(2-)3 x ABVD + 30 Gy IN-RT
4 x ABVD + 30 Gy IN-RT
• Stage III/IV 8 x ABVD
Role of radiotherapy in stage III/IV
Hodgkin lymphoma
• CR after adequate chemotherapy no radiotherapy
• PR after adequate chemotherapy radiotherapy
Treatment Results ?
Survival after Hodgkin lymphoma
Radiotherapy and/or chemotherapy radiotherapy
No therapy
From H.S. Kaplan, 1981
Long term survival of Hodgkin lymphoma
EORTC/GELA
Favier et al, Cancer 2009;115:1680-1691
Treatment results in Hodgkin lymphoma at 5 years
Stage Prognosis RFS
I/II Favorable 92 % unfavorable 89 %
III/IV 75 %
OS
98 %
94 %
86 %
Treatment of Hodgkin lymphoma summary Stage I/II
• Excellent results
• Future
– maintain results
– reduce (late) toxicity
- reduce/ omit Radiotherapy?
- reduce Chemotherapy
– PET guided treatment (interim; post Tx)?
“Early” interim FDG-PET predicts prognosis
M Hutchings et al, Blood 2006;107:52-9
Treatment of Hodgkin lymphoma summary Stage III/IV
• Results moderate/good (cf DLBCL!)
• Future
– Improve results without increasing (late) toxicity
- more intensive chemotherapy?
– PET guided treatment
• Interim: escalate if positive?
• Post Tx: if positive radiotherapy/ HDT+ AuSCT?
Treatment for relapsed
Hodgkin lymphoma
• 15-30% of all HL patients will relapse and require secondline treatment
• High-dose chemotherapy and autologous stem cell transplantation:
- superior over conventional chemotherapy
(Linch et al., Lancet 1993, Schmitz et al., Lancet 2002)
- remains the standard of care for relapsed HL
(except very late relapse?)
High Dose CT + AutoSCT in relapsed HL
Relapse
Primary resistant
PFS @ 5 yrs
%
45-60
OS @ 5yrs
%
50-65
20-30 20-30
The reverse of the success
Successfull treatment of HL
Long term survival
Late effects of treatment
m Hodgkin: Late Toxicity of Treatment
• Excess mortality
– secondary malignancies
– cardiac disease
• Excess morbidity / decreased Q.O.L
– cardiac disease
– pulmonary disease
– infertility
– fatigue
m.Hodgkin : Late Toxicity of Treatment
Secondary Malignancies
Relative
Risk
AML
NHL
70.8
18.6
Solid 2.4 tumors
-- lung 4.2
-- breast 2.5 all 3.5
Absolute
Excess Risk per 10,000 pat. per yr
15.5
10.7
29.3
13.5
11.3
56.2
Absolute
Excess Risk in 10-yr survivors
9.0
27.8
74.4
33.8
39.5
111.7
m.Hodgkin : Late Toxicity of Treatment
Cardiac disease
• coronary insufficiency myocardial infarction
• acute cardiac arrest
• pericarditis
• cardiomyopathy
• valvular abnormalities
RR 1.9 - 3.7
RR 1.9 - 3.1
RR 1.4 - 5.1
m.Hodgkin : Late Toxicity of Treatment
Risk Factors for Cardiac Disease
• Mediastinal RT dose > 30 Gy
• Orthovolt RT (before 1967)
• Adriamycine containing CT
• Age at RT < 20 yr
• Hypertension
Veranderingen bestralingsgebied
H9
CT+RT klierregio
Klassiek mantelveld
Dank aan: R vd Maazen
H10
CT+RT klier
Treatment of Hodgkin lymphoma
• Progress can only be made by including patients in clinical studies!!