Covalent Bonding

Collect the Crossword
Puzzle Homework
6.2 Covalent
Bonding and
Molecular
Compounds.
H
2
Covalent Bond
-
+ +
-
Covalent Bond Formation
E=0
H-H Distance
Bond Formation
Covalent Bonding (cont.)
A point is reached where the attractive and repulsive forces are balanced and potential energy is at a minimum.
Results in a stable covalent bond.
Why Does Bonding Occur
A bond will form if the system can lower its total energy in the process.
Characteristics of the
Covalent Bond
Bond length is the average distance between two bonded atoms, that is, the distance of minimum potential energy.
Bond energy is the energy required to break a chemical bond and form neutral atoms.
Bonding Parameters (cont.)
For H
2
, the bond length is 74 pm
(1 picometer =10 -12 m).
For H
2
, the bond energy is 436 kJ/mole.
As bond length decreases the bond energy increases.
Octet Rule
Chemical compounds tend to form so that each atom, by gaining, losing or sharing electrons, has an octet of electrons in its highest occupied energy level.
H
2
Molecule
H 1s 1
H 1s 1
Filled outer shell like Helium
Octet Rule -- F
2
F=1s 2 2s 2 2p 5
Molecule
F=1s 2 2s 2 2p5
Octet Rule -- HCl Molecule
H=1s 1
Cl = 1s 2 2s 2 2p 6 3s 2 3p 5
1s 2s 2p x
2p y
2p z
3s 3p x
3p y
3p z
Electron Dot Notation
An electron-configuration notation in which only the valence electrons of an atom of a particular element are shown indicated by dots placed around the element’s symbol.
Electron Dot Notation
Lewis Structures
A build on electron dot notations and electron configuration notation
For molecules.
Most simply, a hydrogen atom,
H
2
, is represented as H
H
Lewis Structure – H
2
H:H or
H-H
Lewis Structure
Atomic symbols represent nuclei and inner-shell electrons
Dot pairs or dashes represent electron pairs in covalent bonds
Dots adjacent to only one atomic symbol represent unshared electrons.
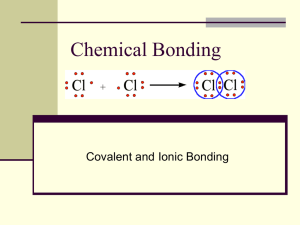
Lewis Structure -- Cl
2
Z = 17
[Ne] 3s 2 3p 5
Dot Diagram?
Cl
2
Note: shared pair of electrons
Lewis Structures (cont.)
Note: each Cl is surrounded by three pairs of electrons that are not involved in bonding but “belong” to the Chlorine.
Lone Pair/Unshared Pair
A pair of electrons that is not involved in bonding, but instead belongs exclusively to one atom.
Structural Formula
Indicates the kind, number, arrangement, and bonds of the atoms in a molecule.
Ethane...C
2
H
6