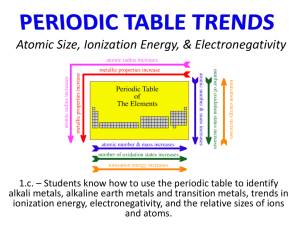
PowerPoint
advertisement

Electronegativity Ionic covalent continuum When chlorine and hydrogen react the covalently bonded HCL is made When chlorine and sodium react ionicly bonded NaCl is formed Why does Cl share electrons with H yet remove electrons from Na? Why does Cl share electrons with H yet remove electrons from Na? Hydrogen holds its electrons really tightly in H-H gas Sodium is a metal the doesn’t hold it’s valance electrons as tightly Chemists use the term electronegativity Electronegativity What is it? • Electronegativity is the power of an atom to attract electron density in a covalent bond Remember the above definition … Or in layman's terms the “attractiveness” of an atom to electrons in a bond Electronegativity Pauling’s electronegativity scale • The higher the value, the more electronegative the element • Fluorine is the most electronegative element • It has an electronegativity value of 4.0 Electronegativity Pauling’s electronegativity scale Electronegativity Pauling’s electronegativity scale F Electronegativity Pauling’s electronegativity scale F 4.0 Electronegativity Pauling’s electronegativity scale Li 1.0 F 4.0 Electronegativity Pauling’s electronegativity scale Li 1.0 Be 1.5 F 4.0 Electronegativity Pauling’s electronegativity scale Li 1.0 Be 1.5 B 2.0 F 4.0 Electronegativity Pauling’s electronegativity scale Li 1.0 Be 1.5 B 2.0 C 2.5 F 4.0 Electronegativity Pauling’s electronegativity scale Li 1.0 Be 1.5 B 2.0 C 2.5 N 3.0 F 4.0 Electronegativity Pauling’s electronegativity scale Li 1.0 Be 1.5 B 2.0 C 2.5 N 3.0 O 3.5 F 4.0 Electronegativity Pauling’s electronegativity scale Li 1.0 Be 1.5 B 2.0 C 2.5 N 3.0 O 3.5 F 4.0 Na 0.9 Mg 1.2 Al 1.5 Si 1.8 P 2.1 S 2.5 Cl 3.0 Electronegativity Pauling’s electronegativity scale H He Li 1.0 Be 1.5 B 2.0 C 2.5 N 3.0 O 3.5 F 4.0 Ne Na 0.9 Mg 1.2 Al 1.5 Si 1.8 P 2.1 S 2.5 Cl 3.0 Ar Electronegativity Pauling’s electronegativity scale H 2.1 He Li 1.0 Be 1.5 B 2.0 C 2.5 N 3.0 O 3.5 F 4.0 Ne Na 0.9 Mg 1.2 Al 1.5 Si 1.8 P 2.1 S 2.5 Cl 3.0 Ar Electronegativity Pauling’s electronegativity scale H 2.1 He - Li 1.0 Be 1.5 B 2.0 C 2.5 N 3.0 O 3.5 F 4.0 Ne - Na 0.9 Mg 1.2 Al 1.5 Si 1.8 P 2.1 S 2.5 Cl 3.0 Ar - So what does all this mean? Same atoms bonding = same electronegativity = pure covalent bond Different atoms bonding =different electronegativity = Polar covalent or Ionic bond Confused? How do we tell which one? Difference in electronegativity Covalent and ionic are a opposite ends of the same scale Ionic Bond Polar Covalent Covalent If the difference in electronegativities is between: 1.7 to 4.0 = Ionic Bond 0.3 to 1.7 = Polar Covalent 0.0 to 0.3 = Non-Polar Covalent