Liquid #2
advertisement

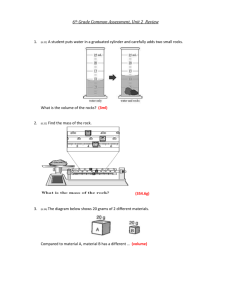
Matter *** Matter… • Makes up all of the objects and living organisms in the universe • Anything that has mass AND takes up space • Light and sound are NOT matter…why? – Matter is made of particles called atoms…matter IS atoms. – Atoms have mass – Air is made of atoms – Sound and light waves traveling through air do not have mass OR take up space Three (of five) forms of Matter: • Solid matter - has a fixed volume and shape of the object or substance. • Liquid matter - has a definite volume but not a definite shape. • Gas matter - does not have a definite shape and volume. Mass… • A physical property of matter • Measure of how much matter an object contains • Standard unit: Kilogram (kg) – 1 kg = 1000 grams (g) – Ex: grapefruit: 500 g, penny: 2-3 g • Measure mass using a triple-beam balance Mass vs Weight Mass is a measurement of the amount of matter something contains Weight is the measurement of the pull of gravity on an object. Mass is measured by using a balance comparing a known amount of matter to an unknown amount of matter. Weight is measured on a scale. The Mass of an object doesn't change when an object's location changes. Weight does change with location. • A triple beam balance compares a known mass to an unknown mass, so it is unaffected by gravity. • A scale measures weight, the triple beam balance gives a true measure of mass. • On the moon the mass on the left side of the balance may 'exert less force', but then less force will be needed to balance it. Weight and Gravity • Recall… • Gravity is the force that pulls two masses toward each other • Standard unit: Newton (N) – Common unit: Pound (lb) • Force = mass * acceleration (F=ma) – Newton = kilogram*meter/second^2 (N = kg m/s2) • Weight is a force! – Mass is amount of matter of an object, weight is how strongly gravity is pulling on that matter F = G[M 2 m/r ] • What will cause the force of attraction to increase or decrease? – If either mass increases the force of attraction increases proportionally. Since the moon has 1/6 the mass of earth, it would exert a force on an object that is 1/6 that on earth. • Why is the 1/r2 factor so important? – This is an inverse square relationship which seems to show up a lot in physics. How does it affect the force? – When r=1 the value 1/r 2 is 1.0, but at r=10 it deceases to 1/100. That means gravity gets weak 'quick' as we move away from the earth. Compute Mass and Weight • If a cube has a mass of 90.91 kilograms and a weight of 200 pounds on Earth, what will its mass and weight be on another planet? – The Moon has a gravity that is 0.165 of Earth's. The cube will have a weight of ________________ pounds and a mass of _______________ kilograms – Jupiter has a gravity that is 2.34 times greater than Earth's…weight? Mass? Compute Mass and Weight • On the moon: – Weight = 33 lb – Mass = still 90.91 kg! • On Jupiter – Weight = 468 lb – Mass = 90.91 kg Volume • Volume is the amount of space an object occupies. • The volume of an object can be calculated geometrically using mathematical equations or by measuring liquid displacement. • Measure the volume of a cube using the formula V=(side)x(side)x(side) (length times width times height) and by using a graduated cylinder to measure liquid displacement. • Volume = L x W x H (cm3 or in3 etc.) • The side of the cube is approximately 3.1 centimeters. How many inches does this convert to (use 2.54 cm. = 1 inch)? Measure Volume by Displacement • What was the amount of water displaced by the object? (1 ml = 1cm3) Before After Density • Each box has the same volume. • If each ball has the same mass, which box would weigh more? Why? Density • The box that has more balls has more mass per unit of volume. D = m/V • The density of a material helps to distinguish it from other materials. • Mass: grams (g) or kilograms (kg) • Volume: cubic centimeters (cm3) or cubic meters (m3) • Density: grams/cubic centimeter (g/cm3) or kilograms/cubic meter (kg/m3) Periodic Table masses: One gram is about 600,000,000,000,000,000,000,000 amu (a 6 followed by 23 zeros) = 6 x 1023 amu. Density of a Liquid • Problem: You are given two unknown liquids. Find the density of each. Materials: 100ml graduated cylinder, triple beam balance, calculator, 2 unknown liquids. • Procedure: • 1) Find the mass of the empty graduated cylinder. • 2) Pour unknown liquid #1 into the graduated cylinder to the 50 ml. level. • 3) Find the mass of the graduated cylinder with 50ml of unknown liquid #1. • 4) Repeat steps 1-3 for unknown liquid #2. Density of a Liquid • Liquid #1: • Given: Mass of empty graduated cylinder = 78 grams • Mass of graduated cylinder with unknown liquid #1= 128 grams. • Find: • a) Mass of just the liquid = ____ b) Volume of liquid=_____ c) Density of liquid #1 =____ • Liquid #2: • Given: Mass of empty graduated cylinder = 78 grams • Mass of graduated cylinder with unknown liquid #2= 117.5 grams. • Find: • a) Mass of just the liquid = ____ b) Volume of liquid =_____ c) Density of liquid #2=____ What is the Liquid? • What is each liquid? Using the table below it is now possible for you to determine what each liquid is. • Densities for some common liquids are: Substance Density (gm/cu.cm) Water 1.00 Cooking oil 0.92 Sea Water 1.025 Carbon tetrachloride 1.58 Benzene 0.87 Glycerin 1.26 Methanol 0.79 Extension: Air Pressure • Air pressure is the force exerted by the weight of a column of air above a particular location. • Imagine a sealed container full of air • Change the pressure – Increase the density of the air by either putting more air molecules into the container or reducing the volume of the container. • Therefore, changes in air pressure can come about by changes in air density • Atmospheric pressure is defined as the force per unit area exerted against a surface by the weight of the air above that surface. • If the number of air molecules above a surface increases, there are more molecules to exert a force on that surface and consequently, the pressure increases. •The opposite is also true, where a reduction in the number of air molecules above a surface will result in a decrease in pressure. Air Pressure & Altitude • Air pressure decreases as one moves upward through the atmosphere because the length of the column of air shortens and hence there is less mass above a given location. • Because air is highly compressible, the air is closely packed together near the surface (high density) and less densely packed aloft