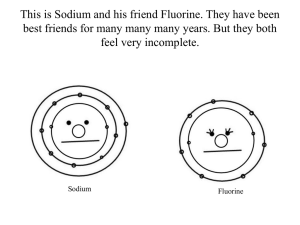
Structure and Properties
advertisement
Molecular Geometry 1 Molecular Geometry 2 VSEPR Theory VSEPR: Valence Shell Electron Pair Repulsion This theory is useful in predicting the geometry of a molecule Our focus will be to look at the arrangement of electron pairs around the central atom 3 VSEPR Theory Assumptions: – the structure around a given atom is determined principally by minimizing electron pair repulsions – electron pairs (both bonding and nonbonding) around a given atom should be positioned as far apart as possible to minimize electron-electron repulsion 4 Valence Shell Electron Pair Repulsion Theory Nonbonding pairs Bonding pairs 5 Valence Shell Electron Pair Repulsion Theory 6 Valence Shell Electron Pair Repulsion Theory 7 VSEPR:Four or Fewer Valence-Shell Electron Pairs Around a Central Atom 8 VSEPR:Four or Fewer Valence-Shell Electron Pairs Around a Central Atom 9 Common Bonding Geometries AB2 AB2 AB3 AB4 •Atoms (B) which are bonded to a central atom (A): ABn 10 VSEPR:The Effect of Nonbonding Electrons and Multiple Bonds on Bond Angles Nonbonding electron pairs exert greater repulsive forces on adjacent electron pairs and thus tend to compress the angles between the bonding pairs Nonbonding electron pairs 109. 5° Methane (CH4) 107° Ammonia (NH3) 2 Nonbonding electron pairs 104 .°5 Water (H2O) 11 VSEPR: Molecules with No Single Central Atom Tetrahedral Trigonal Planar Bent H H O C C .. ..O H H 12 Example: Determine the molecular geometry of CO2 O C The central atom (C) has 2 bonding pairs, 0 lone pairs Shape is linear, bond angle = 180 O=C=O 13 O