Chapter 16 - Richsingiser.com
advertisement

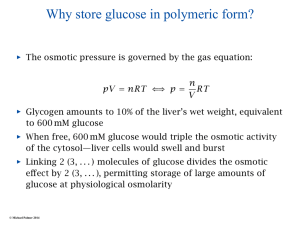
Fundamentals of Biochemistry Third Edition Donald Voet • Judith G. Voet • Charlotte W. Pratt Chapter 16 Glycogen Metabolism and Gluconeogenesis Copyright © 2008 by John Wiley & Sons, Inc. Glycogen Breakdown Enzymes for Glycogen Breakdown • Glycogen phosphorylase – Glycogen + Pi Glycogen (n-1) + G1P • Glycogen Debranching Enzyme • Phosphoglucomutase – G1P G6P • Glycogen Phophorylase – Homodimer – Regulation • -- ATP, G6P, glucose • + AMP • Phosphorylation – R & T states – Crevase that holds 4-5 linear carbohydrates – Cofactor of PLP, a B6 derivative Debranching Enzyme Phosphoglucomutase Diseases • G6P generated via glycogen has multiple fates – Glycolysis – Pentose phosphate – Transport to other tissues • In liver, G6Pase, removes phosphate for transport out of cell • G6Pase is in the ER, but G6P is in cytosol – G6P translocase • Glucose exits cell via GLUT2 – Muscles lack G6Pase and therefore retain G6P Glycogen Synthesis • G’ for glycogen phosphorylase is +3.1 kJ/mol – Under physiological conditions it is -5 to -8 kJ/mol – This reaction then, cannot go both directions spontaneously via the same enzymes UDP-Glucose Pyrophosphorylase • Since synthesis is thermodynamically unfavorable, we must put in energy. G1P + UTP ↔ UDPG + PPi = 0 kJ/mol H2O + PPi 2 Pi = -19.2 kJ/mol Net G1P + UTP UDPG + 2 Pi = -19.2 kJ/mol Glycogen Synthase The second step is spontaneous under physiological conditions. It comes at a cost of 1 ATP (UTP) Glycogen synthase only adds to a chain Need Glycogenin to build initial starting chain Branching Enzyme Must transfer 7 carbohydrates at a time (only). There must be at least 4 left over. Activated by phosphorylation and Ca2+ Calcium is regulated by calmodulin PP1c Hormonal Control Increase Glycogen Breakdown • Low Glucose • ↑ Glucogon • ↑ Epinephrine – B-adrenergic receptor (muscle) • ↑cAMP – A-adrenergic receptor (liver) • ↑ Glucogon • ↑ cAMP • ↑ Ca2+ Increase Glycogen Synthesis • High Glucose • Insulin – GLUT4 • Muscle, fat • ↓ cAMP Gluconeogenesis • Most of Gluconeogenesis is Glycolysis in reverse. • Only irreversible steps must be different • Oxaloacetate is the required molecule to start gluconeogenesis Step 1 – Make oxaloacetate normal Oxaloacetate is only formed in the mitochondria, remaining steps occur in cytosol. anaerobic Same enzyme different domains PFK F1,6BP O-linked N-linked N-linked