Chapter 8 - Richsingiser.com
advertisement

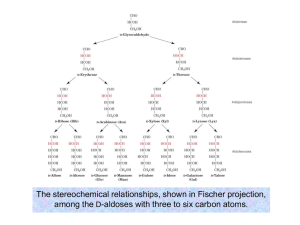
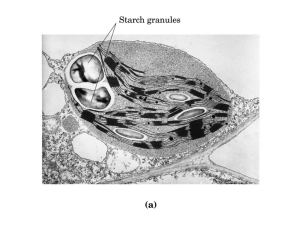
Fundamentals of Biochemistry Third Edition Donald Voet • Judith G. Voet • Charlotte W. Pratt Chapter 8 Carbohydrates Copyright © 2008 by John Wiley & Sons, Inc. Section1 – Monosaccharides • • • • • Monosaccharide Polysaccharide Aldose Ketose Chiral Carbons 2n This reaction happens freely (slowly) in solution: 64% beta, 36% alpha Preferred Oxidation of aldehyde -onic acid Oxidation of primary alcohol -uronic acid Mild conditions, reduction to polyhydroxy alcohols -itol added to most names Amino sugars – add amino group in place of -OH Sialic acids are important for glycoproteins and glycolipids; recognition site of Influenza Viruses Glycosidic bonds – reaction of anomeric group to an alcohol Reducing Non-Reducing Section 2 – Polysaccharides O-β-D-galactopyranosyl(1→4)-D-glucopyranose O-α-D-glucopyranosyl-(1→2)β-D-fructofuranoside Sucralose (Splenda) Steviol (Stevia) Sodium cyclamate β(1→4) linkages Cannot be broken down in vertebrate digestion Exoskeletons α(1→4) linkages Energy Storage in plants 1 every 24-30 units Digestion: amylase α-glucosidase debranching enzymes glycogen debranching enzyme Glycogen has more branch points than amylopetin (1 every 814 units Figure 8-12 Section 3 - Glycoproteins N-linked oligosaccharides O-linked oligosaccharides Biological Activity • Define protein structure – Usually on surface – limit conformation; stabilize fold • Recognition – Glycoconjugates • Lectins – identify specific oligosaccharides • Selectins – attachment of leukocytes – Blood groups All chapter questions