Great circle
advertisement

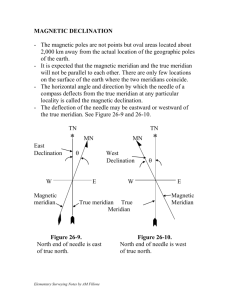
CHARTS •Graticule - grid over the globe made up of circles •Parallels of Latitude •Meridians of Longitude •Prime Meridian •International Date Line Meridians of Longitude Circles that pass directly through the North and South poles (true poles) Meridians are measured 180 degrees east and west of the prime meridian Prime meridian passes through Greenwich, England International Date Line is the meridian 180 degrees opposite the prime meridian Parallels of Latitude Circles on the earth surface that lie parallel to the equator The equator is the line of latitude that is equidistant between the poles. Small Circles Circles of latitude get smaller and smaller towards the poles Equator = Great Circle Both Longitude and Latitude are measured in degrees, minutes, seconds. (60 minutes in a degree, 60 seconds in a minute) Longitude 0o to 180o East and West from prime meridian Degrees 0 Minutes ’ Seconds ” Meldrum Bay is at 450 55 ’ 35 ” lat 830 07 ’ 10 ” long One nautical mile is 6080 feet, a statute mile is 5280 A nautical mile is one minute of arc along a great circle 6080 feet to 5280 feet 70 to 60 1.15 to 1 1 knot is slighter faster than 1 mph 60 knots = about 70 mph Questions What is located at N44˚27’30”W080˚09’30” ? Collingwood Airport What is located at N42˚50’10”W081˚33’20” ? Melbourne Airport What is the distance from the Equator to the North Pole? 5400 NM What is the distance between N42˚00’00” W081˚33’20” and N43˚50’00”W081˚33’20” ? 110 NM MEAN TIME Time between two transits of a meridian is apparent solar day – varies Mean sun travels at assumed constant speed Mean solar day same all year 360o passes in 24 hours so 24 hr = 360o 1 hr = 15o 1 min = 15’ 1 sec = 15” Local mean time set to mid-meridian 15o Great Circles Great circles are lines drawn directly around the Earth that will cut it into two equal halves. The cut would take place directly through the center of the Earth Great circles are the shortest distances between two points on the Earth Great Circle route ADIS ABABA LONDON GREENLAND CHARTS VANCOUVER •Great circle or great circle route will be a circle that cuts through the center of the globe •Small circles – all parallels of latitude except the equator •All meridians are great circles Rhumb Lines A rhumb line crosses each meridian of longitude at the same angle. Represents the path of constant heading between two points. Not the shortest distance. How do we make a 2-dimensional map from a 3-dimensional Earth? Waldseemuller’s Map of 1507 Mercator Projection Maintains constant distance between meridians. This causes distortion towards the poles. Straight line on this map is a rhumb line. Transverse Mercator projection Similar to mercator, except the mapping cylinder is rotated 90 degrees. This allows the map-maker to center the projection on a meridian of longitude. Good for small maps (VTAs) or for mapping a long narrow country like Chile Map begins to distort once you move away from the central meridian Lambert Conformal Conic Projection Map maker fits a cone over the Earth. The points where the cone is touching the surface of the Earth are called the standard parallels. Map is accurate at the standard parallels but distorts as you move away. Used for medium scale maps (majority of aviation charts) Lambert Conformal Conic Projection Meridians of Longitude curve in towards the poles. Straight lines represent great circles and therefore do not maintain constant headings (unless due north-south) Great Circle/Rhumb Line on Mercator Great Circle/Rhumb Line on Lambert Conformal Conic VNC 5000 WAC Chart VTA Scale The scale used on a map depends on it’s use. Large scale (WAC charts) displays a large area, but not a lot of detail Small scale (VTA charts) displays a small area, and lots of detail Medium scale (VNC charts) compromise between area and scale. Scale Ratio of chart length to the distance on the Earth it represents. For example 1:500,000 means 1 inch on the map equals 500,000 inches on the ground. *Remember* 1 minute latitude = 1 NM Magnetic Variation The magnetic north pole does not coincide with the true north pole. Maps are aligned with true north, however our magnetic compass aligns with magnetic north The difference between true north and magnetic north varies depending on your location and is called magnetic variation. East Magnetic Variation Subtract East Variation from true track to get magnetic track Variation East – Magnetic Least West Magnetic Variation Add west variation to true track to get magnetic track Variation West – Magnetic Best Isogonal vs. Agonal An isogonal line is a line joining points on the Earth with equal magnetic variation. An agonal line is a line joining points on the Earth with zero magnetic variation MAGNETIC DEVIATION Magnetic field from airframe, engine, electrical system. Compass card shows deviation & correction MORE CHART STUFF •CYR 511 all listed in CFS •Military airfield •Parachute area •Abandoned airfield •Isogonic line •vs Agonic line AGONIC LINE CYKZ 1 CYKZ 2 CYKZ 3 OO 1 OO 2 PQ 1 PQ 2 QA 2 YZ TERMINAL