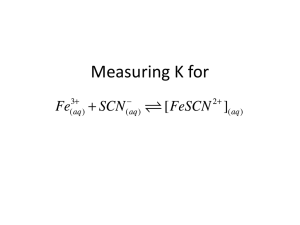Equilibrium Constant
advertisement

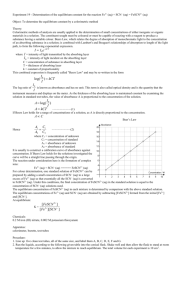
Equilibrium Constant Today’s Experiment: I. Fe3+(aq) + HSCN(aq) FeSCN2+(aq) + H+(aq) orange dark red colorless K [FeSCN [Fe 1. 2. 3. 4. 3 2 colorless ][H ] ??? ][HSCN] Determine [FeSCN2+] using Spec20 and Beer’s Law Determine the other concentrations from an ICE Table Calculate K at three different Temperatures Use the Temperature data to determine DH, DS, and DG for the reaction II. Take a look at the Pre-Lab Problems III. Beer’s Law and Making a Calibration Curve 1. 2. Colored compounds absorb light that is shined through them A = elC Absorbance = (Extinction Coefficient)(length)(Concentration) 3. We will use test tubes #1-5 to make a calibration curve using Beer’s Law 4. Excess Fe3+ (0.200 M) pushes the reaction to the right: [HSCN]o = [FeSCN2+] 5. We must use Fe3+ solution as a blank to cancel out Fe3+ absorbance 6. Record %T and calculate A for the five different [HSCN] concentrations %T I Io 100 A log %T 7. Plot A vs. [FeSCN2+] to give a straight line. Calibration Curve A Slope = el A εlC C A εl A slope [FeSCN2+] 8. Once you find the Absorbance of any other [FeSCN2+] solution, you can find its concentration from the calibration curve. IV. Procedure for finding K (Tubes #6-9) 1. 2. 3. 4. 2 Make 4 different solutions of HSCN, Fe3+ [FeSCN ][H ] K Find A with the Spec20 3 [Fe ][HSCN] Find [FeSCN2+] from the Calibration Curve Use an ICE Table to find all the other concentrations Solution 6 Temperature Room Initial Molar Concentration Species Fe3+ HSCN FeSCN2+ H+ 0.00100 0.000200 0 0.500 -x -x +x +x x 0.500 + x Change in Molar Concentration Equilibrium Molar Concentration 0.00100 - x 0.000200 - x Calculated Values 5. 6. 0.500 All solutions are made with 0.500 M HNO3, so [H+] = 0.500 Other initial concentrations are found using the Dilution Equation M 1 V1 M 2 V 2 M2 M 1 V1 [HSCN] V 2 o 0.002M 0.001L 0.00020M 0.010L Procedure for finding DH, DS, and DG (Tubes #6-9 at different T’s) V. You will use the same tubes (#6-9) at an ice bath (around 5 oC) Hot tap water bath temperature (around 45 oC) [Not too hot! Boils off HSCN!) You already have the room temperature data from these tubes (around 25 oC) 1. 2. 3. ΔG o RTlnK lnK - ΔH R 4. 5. o ΔH TDS o 1 ΔS R T o Slope = -DH/R Intercept = DS/R o lnK 1/T Plot lnK vs. 1/T for your three different temperatures Use the following equations to calculate DH, DS, and DG for the reaction ΔH (slope)(R) D S (intercept )(R) DG DH - TDS D G -RTlnK 6. (use average K at Room Temp. in Kelvins) R 8.3145 J/mol K Notes: a. Use parafilm to cover the test tubes as you mix the solutions thoroughly b. Spec20: 0% with nothing in it; 100% with Iron Solution only as Blank c. Fill cuvet with most dilute first, rinse with next most dilute, and so on