TOPIC : Finite State Machine(FSM) and Flow Tables
advertisement
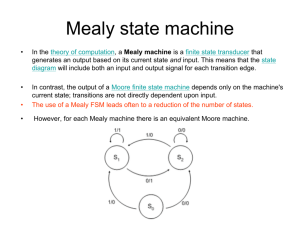
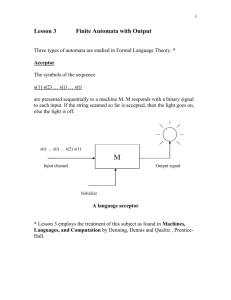
UNIT 1 : Modeling Module 1.4 : Modeling Sequential circuits TOPIC : Finite State Machine(FSM) and Flow Tables FSM : Introduction A finite state machine (FSM) is a model of behavior composed of a finite number of states, transitions between those states, and actions Any Circuit with Memory is a Finite State Machine Even computers can be viewed as huge FSMs Designing FSM Defining states : Total states that system can take. Defining transitions between states: Logic behind going from one state to another. Optimization / minimization : Optimizing a FSM means finding the machine with the minimum number of states that performs the same function. FSM in digital circuits In digital circuits FSM can be made using two types of elements : ◦ Sequential : Any storage element such as Registers which will store the state of System. ◦ Combinational : 1) How the states are changing from one to another. 2) How the output is calculated. FSM are of two types : ◦ Moore FSM ◦ Mealy FSM Moore FSM Output only depend on the present state. 0 1 0 1 S0 / 0 NOTE: S0/0 = State/output S1 / 0 1 0 In state S2 output = 1, since 10 sequence is detected Moore FSM for “10” sequence detector S2 / 1 Mealy FSM Output Is a Function of a Present State and Inputs 0/0 1/0 S0 reset 1/0 S1 0/1 Mealy FSM for “10” sequence detector Mealy always have less number of state than Moore. HDL code for Moore FSM IF(reset = ‘1’) Moore_state <= S0; ELSIF (clock = ‘1’ AND clock’event) THEN CASE (Moore_state) S0 : IF (input = ‘1’) Moore_state <= S1; Else Moore_state <= S0; S1: S2: If (input == 0) Moore_state = S2; Else Moore_state = S1; If (input = ‘0’) Moore_state <= S0; Else Moore_state <= S1; End Case; example: A simple vending machine Here is how the control is supposed to work. The vending machine delivers a package of gum after it has received 15 cents in coins. The machine has a single coin slot that accepts nickels and dimes, one coin at a time. A mechanical sensor indicates to the control whether a dime or a nickel has been inserted into the coin slo The controller’s output causes a single package of gum to be released down a chute to the customer. One further specification: We will design our machine so it does not give change. A customer who pays with two dimes is out 5 cents! Coin Sensor Reset Vending Machine FSM Open Gum Release Mechanism CLK Vending Machine block diagram States: 0C 5C 10C 15C 8 — The figure below show the Moore and Mealy machine state transition diagrams. Reset / 0 Reset ( N D Reset)/0 0 cent [0] Reset ND D ( N D Reset)/0 Reset / 0 N 5 cent [0] D N 10 cent [0] N+D 15 cent [1] Moore machine 0 cent N D /0 N/0 5 cent D/0 D/1 N/0 ND 10 cent N D /0 N+D/1 15 cent Mealy machine Moore and Mealy machine state diagrams for the vending machine FSM 9 Flow Tables FSM can be represented in a tabular form which is known as Flow Table. In a flow table the states are named by letter symbols. Input Present state X1 X2 X3 X4 S0 S1,0 S3,0 S3,0 S0,1 S2 S1,0 S2,0 S3,0 S0,0 S3 S2,0 S2,0 S2,0 S0,0 S4 S3,0 S3,0 S3,0 S0,1 S0,1 = next state, output Flow Table for Vendor machine Example