Mealy state machine
advertisement

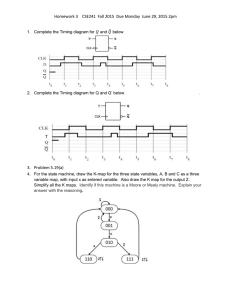
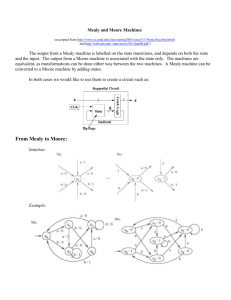
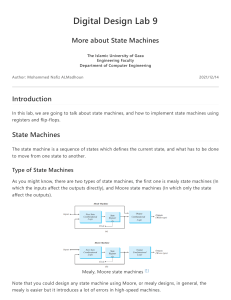
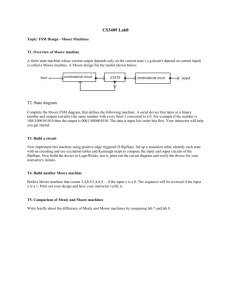
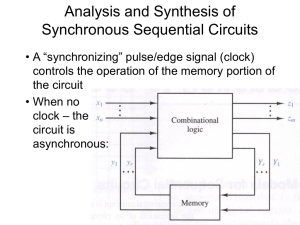
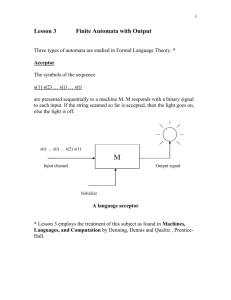
Mealy state machine • In the theory of computation, a Mealy machine is a finite state transducer that generates an output based on its current state and input. This means that the state diagram will include both an input and output signal for each transition edge. • • In contrast, the output of a Moore finite state machine depends only on the machine's current state; transitions are not directly dependent upon input. The use of a Mealy FSM leads often to a reduction of the number of states. • However, for each Mealy machine there is an equivalent Moore machine. Mealy state machine Moore state machine • In the theory of computation, a Moore machine is a finite state transducer where the outputs are determined by the current state alone (and do not depend directly on the input). The state diagram for a Moore machine will include an output signal for each state. Compare with a Mealy machine, which maps transitions in the machine to outputs. • The advantage of the Moore model is a simplification of the behavior. Moore state machine Example • Q3.Derive a minimal state table for a single-input and single-output Moore-type FSM that produces an output of 1 if in the input sequence it detects either 110 or 101 patterns. Overlapping sequences should be detected. (Show the detailed steps of your solution.) State Diagram Reset w=0 w=0 w=1 A/z=0 w=0 w=1 B/z=0 E/z=0 w=1 F/z=1 w=1 w=1 w=0 C/z=0 w=0 State Diagram D/z=1 w=1 Sate Table (Moore FSM) Present state Next State w=0 Output Z w=1 A A B 0 B E C 0 C D C 0 D A F 1 E A F 0 F E C 1 6 states need 3 flip-flops State state state state state Assignment (Mealy FSM): A: Got no 1 B: Got”1” C: Got”11” D: Got”10” Reset 1/0 1/0 0/0 1/0 B A 1/1 0/0 0/0 State Diagram C 0/1 D Sate Table (Mealy FSM) Present state Next State w=0 Output Z w=1 w=0 w=1 A A B 0 0 B D C 0 0 C D C 1 0 D A B 0 1 4 states need 2 flip-flops