Heriot-Watt University
advertisement
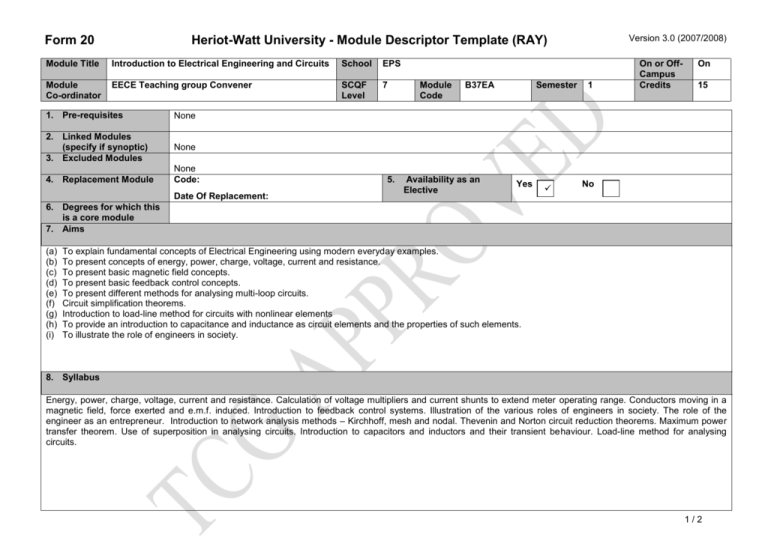
Form 20 Version 3.0 (2007/2008) Heriot-Watt University - Module Descriptor Template (RAY) Module Title Introduction to Electrical Engineering and Circuits School EPS Module Co-ordinator EECE Teaching group Convener SCQF Level 7 1. Pre-requisites None 2. Linked Modules (specify if synoptic) 3. Excluded Modules None 4. Replacement Module None Code: Date Of Replacement: 5. Module Code B37EA Availability as an Elective Semester Yes 1 On or OffCampus Credits On 15 No 6. Degrees for which this is a core module 7. Aims (a) (b) (c) (d) (e) (f) (g) (h) (i) To explain fundamental concepts of Electrical Engineering using modern everyday examples. To present concepts of energy, power, charge, voltage, current and resistance. To present basic magnetic field concepts. To present basic feedback control concepts. To present different methods for analysing multi-loop circuits. Circuit simplification theorems. Introduction to load-line method for circuits with nonlinear elements To provide an introduction to capacitance and inductance as circuit elements and the properties of such elements. To illustrate the role of engineers in society. 8. Syllabus Energy, power, charge, voltage, current and resistance. Calculation of voltage multipliers and current shunts to extend meter operating range. Conductors moving in a magnetic field, force exerted and e.m.f. induced. Introduction to feedback control systems. Illustration of the various roles of engineers in society. The role of the engineer as an entrepreneur. Introduction to network analysis methods – Kirchhoff, mesh and nodal. Thevenin and Norton circuit reduction theorems. Maximum power transfer theorem. Use of superposition in analysing circuits. Introduction to capacitors and inductors and their transient behaviour. Load-line method for analysing circuits. 1/2 Form 20 Version 3.0 (2007/2008) Heriot-Watt University - Module Descriptor Template (RAY) Module Title Introduction to Electrical Engineering and Circuits School EPS Module Co-ordinator EECE Teaching group Convener SCQF Level 7 Module Code B37EA Semester 1 On or OffCampus Credits On 15 9. Learning Outcomes (HWU Core Skills: Employability and Professional Career Readiness) Subject Mastery Understanding, Knowledge and Cognitive Skills Scholarship, Enquiry and Research (Research-Informed Learning) To provide an understanding into the basics of electrical engineering circuit concepts in order to be able to solve fairly simple problems. Identify and solve problems using Ohm's Law Understand the principle of superposition Identify and solve problems using the superposition theorem Apply Thevenin and Norton’s theorems to simple dc circuits Analyse dc networks using source conversion Understand and apply node analysis to dc networks Understand the concept of maximum power transfer and apply in practice. To provide fundamental knowledge of capacitance and inductance concepts and to be able to solve basic problems with these circuit components. Personal Abilities Industrial, Commercial & Professional Practice Autonomy, Accountability & Working with Others Communication, Numeracy & ICT At the end of this module, the student should be able to apply the fundamental and core concepts of the underlying principles of electrical engineering to simple electrical engineering circuits. Understanding of the different important roles engineers play in society. 10. Assessment Methods Method 11. Re-assessment Methods Duration of Exam Weighting (%) Synoptic modules? Method (if applicable) Coursework Examination 2 hours Duration of Exam (if applicable) 30 70 No Examination 2 hours 12. Date and Version Date of Proposal 26 February 2010 Date of Approval by School Committee Date of Implementation Version Number 1.0 2/2