NATIONAL INCOME ACCOUNTING
advertisement

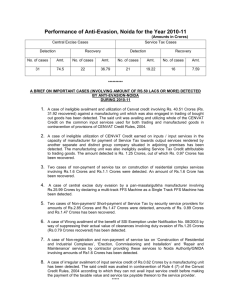
NATIONAL INCOME ACCOUNTING Three methods of measuring national income:-1.Value added method 2.Income method 3.Expenditure method Value added method:-- Value added method measures the value added by each producing enterprise in the production process in the domestic territory of a country on an accounting year. In other words value added is defined as the difference between total value of output of a firm and value of inputs bought from other firms. Q 1. Calculate net value added at factor cost from the following data. Items 1.Purchase of materials 2.Depreciation 3.Sales 4.Excise tax 5.Opening stock 6.Intermediate consumption 7.Closing stock Solution:-- GVA MP (Rs. In crores) 30 12 200 20 15 48 10 = Value of output – Intermediate Consumption Sales + change in stock – Intermediate Consumption = 200+ (10 -15) – 48 = 200 - 5 - 48 = 200 - 53 = Rs.147 Crores NVAMP NVAFC = GVAMP –Depreciation = Rs. 147 – 12 = Rs. 135 crores = NVAMP – Indirect tax = 135 – 20 = Rs. 115 Crores Q 2:- Calculate gross value added at factor cost from the following data. Items 1. Sales 2. Subsidies 3. Consumption of fixed capital 4. Closing stock 5. Purchase of raw materials 6. Opening stock 7. Indirect tax (Rs. In crores) 100 2 5 10 50 15 10 Solution:- GVAMP = Value of output – Intermediate consumption = Sales+change in stock - 50 = 100+ (10-15) – 50 =100- 55 = 45 crores GVAFC = GVAMP – Indirect taxes + subsidies = 45 – 10 +2 = Rs. 37 crores Q 3. From the following data calculate the net value added at factor cost. Items (Rs. In Lacs.) 1.Subsidy 40 2.Sales 800 3.Depreciation 30 4.Exports 100 5.Closing stock 20 6. Opening stock 50 7.Intermediate purchases 500 Solution:-- GVAMP = Value of output – Intermediate consumption = Sales +change in stock – 500 = 800 + (20- 50) – 500 =800- 530 = 270 crores NVAMP = GVAMP – Dep =270 – 30 = 240 crores NVAFC = NVAMP + subsidy = 240 + 40 = Rs. 280 crores CALCULATION OF NATIONAL INCOME BY INCOME METHOD • The income method measures national income from the side of payments made to the primary factors of production in the form of rent, wages ,interest and profit for their productive services in an accounting year. • Components of domestic income:- 1.Compensation of employees (This is the reward or compensation paid to employees for rendering productive services. It includes wages and salaries,Employer’s contribution to social security schemes, dearness allowance, bonus, city allowance, house rent allowace, leave travelling allowance etc.) • 2.Operating surplus:- It includes rent, profit and interest. Profit includes corporate tax, dividend and undistributed profit. 3.Mixed income of self employed:- Income of own account workers like farmers, doctors, barbers etc, and unincorporated enterprises like small shopkeepers, repair shops retail traders etc, is known as mixed income. Q 1:- From the following data, calculate national income by income method – 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. Items Compensation of employees Mixed income of self employed Net factor income from abroad Rent Profit Consumption of fixed capital Net indirect taxes 8. Interest 9. Operating Surplus (Rs. In crores) 800 900 - 50 350 600 200 250 450 1400 Solution:- ( Income method) GDPMP = Compensation of employees + mixed income of self employed + operating surplus + depreciation +net indirect taxes =200+250+800+ 1400 (350+600+450)+900 =3550 GNPMP = GDPMP + NFIA = 3550 +(-50) = 3500 NNPMP = GNPMP – Dep. = 3500- 200 = 3300 NNPFC = NNPMP- NIT =3300- 250 =Rs. 3050 crores Calculation of National income by expenditure method. • Expenditure method measures final expenditure on ‘Gross • • • • • • • • • Domestic Product at market price” during a period of accounting year. In other words “ national income is measured at the point of expenditure. Components of GDPMP:-1.Private final consumption expenditure. 2.Govt. final consumption expenditure. 3.Gross fixed capital formation. 4.Net Exports. 5.Domestic capital formation. 6.Interest on national debt. 7.Investment expenditure. income by income method and Items method. 1. Compensation of employees 2. Net factor income from 3. Net indirect taxes 4. Profit 5. Private final consumption expenditure 6. Net domestic capital formation 7. Consumption of fixed capital 8. Rent 9. Interest 10. Mixed income of self employed 11. Net exports 12. Govt. final consumption expenditure 13. Operating surplus 14. Employer’s contribution to social security scheme expenditure (Rs. In crores.) 1,200 - 20 120 800 2,000 770 130 400 620 700 - 30 1,100 1820 300 Solution:- (Income method) GDPMP = Depreciation + Net indirect taxes +Compensation of employees(Wages+ salaries……) + Operating surplus ( rent + profit + Interest) +mixed income of self employed • =130+120+1,200+1820+700 • =3970 • GNPMP = GDPMP + NFIA • = 3970 + (-20) • =3950 crores • NNPMP = GNPMP- Depreciation • =3950- 130 • =3820 crores • NNPFC = NNPMP__ - NIT • = 3820- 120 • = Rs. 3700 crores • • • • • • • • Solution:- ( Expenditure Method) GDPMP = Depreciation + private final consumption expenditure + net domestic capital formation + net exports + Govt. final consumption expenditure. = 130 + 2,000 + 770 + (- 30) + 1,100 = 3,970 crore GNPMP = GDPMP + NFIA =3,970 + (-20) =3,950 crore NNPMP = GNPMP – Depreciation = 3,950 – 130 = 3,820 crore NNPFC = NNPMP – NIT = 3,820 – 120 = Rs.3,700 crore