Sales Projections
advertisement

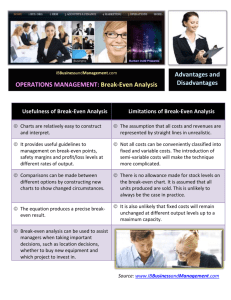
Use of Sales Projections Factors/Terms Associated with Making Sales Projections 1. Sales Ratio 5. Sales Quota 2. Sales Forecast 6. Product Positioning 3. Break-Even point 7. Market Share 4. Economic Outlook 1. Sales Ratio •An expression of any component of the income statement as a percentage of total sales. •The value of the component is divided by the value of sales. •Example: Rent expenses . . . . . . . . . . . . . . $500 divided by sales . . . . . . . . . . $10,000 equals sales ratio of . . . . . . . . . . . .5% Current Ratio • A comparison of current assets with current liabilities. This is one indicator of the ability of the business to pay its debts. • Assets divided by liabilities • Ratio of 2:1 is usually considered sufficient. (Value of 2.0 or higher) • Example: Assets of 70,000 divided by liabilities of $35,000 equals a current ratio of 2:1 (which means $2 in assets for every $1 in liabilities) Math: 70,000/35000 = 2 (second number is always 1) = 2:1 2. Sales Forecast • An estimate of sales for a specified period. • Current sales plus (% increase times the current sales) OR • Current sales times (100% plus % increase) • Example Current sales . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . $5,000 projected increase of . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .7% yields a new sales forecast of . . . . . . $5,350. Math: 5000 x .07 = 350 5000 + 350 = 5350 3. Break-Even Point (BEP) • The point at which the money from product sales equals the costs of making and distributing the product and you can begin making a profit. • Once you reach the break-even point, you will neither make nor lose money. When sales can exceed the break even point, you will begin to make a profit. • BEP=Total fixed expenses divided by (unit sale price minus unit variable expense) 3. Break-Even Point (BEP) Break-Even Point Formula Total fixed expenses divided by (unit sale price minus unit variable expense) Example: If you have: fixed costs . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .$4 per unit variable costs . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . $2 per unit expect to provide . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 4,000 units at a selling price of . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . $12 per unit Compute the break-even point. $4 (fixed cost per unit) x 4,000 units = $16,000 total fixed costs $16,000 (total fixed costs) / ($12 (selling price) - $2 variable costs) = $1,600 units as break-even point. 4. Economic Outlook: • Trends associated with the economy that can impact a business's sales • Example: Lower airline fares equals increased travel and tourism. 5. Sales Quota: • A goal assigned to a sales person for a specified period. • The strength or weakness of your sales operation is indicated if these goals are met. • Providing a sales staff with a goal can be a measure of his/her effectiveness. 6. Product Positioning • Placing a product in a certain market to get a desired customer response. • Example: Putting umbrellas at the front of the store on a rainy day. Placing gum at a checkout counter 7. Market Share •The percentage of a product/service that is sold in the total market for that product/service. •To be able to succeed in the business world, you must be able to capture market share from other competitors. Financial Tools That Utilize Sales Projections •Cash Flow Statement •Repayment Plan •Inventory Inventory Cash Flow Statement Repayment Plan Cash Flow Statement • A financial statement that shows the flow of money in and out of the business. • The sales projection provides the income factor to determine how much money you may have coming in to the business. Repayment Plan •A plan or statement showing how and when the debt of a business will be paid. •The plan is often a document prepared by the business owner and the lender. Calculating Repayment In order to calculate repayment, you must know at least two of three things. You need to know: •The amount of the entire loan •Your payment amount •How long you have the loan for. For an example: Bob takes out a $100,000 loan. His payments are $1000 per month. How long will it take him to pay it off? Math: 100,000/1000= 100 payments (divide by 12) 8.3 years or 8 years and 4 months. Inventory •Ensuring that adequate inventory is on hand to meet sales demand. •Sales projections help to determine the amount of inventory to have on hand to meet these projections. •Having too much or too little inventory can be a problem for a business.