ECE 448 * FPGA and ASIC Design with VHDL
advertisement

ECE 448
Lecture 5
FPGA Devices
& FPGA Design Flow
ECE 448 – FPGA and ASIC Design with VHDL
George Mason University
Required reading
• Spartan-6 FPGA Configurable Logic Block:
User Guide
CLB Overview
Slice Description
2
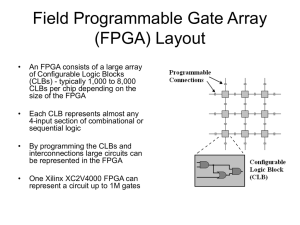
What is an FPGA?
Configurable
Logic
Blocks
Block RAMs
Block RAMs
I/O
Blocks
Block
RAMs
ECE 448 – FPGA and ASIC Design with VHDL
3
Modern FPGA
RAM blocks
RAM
blocks
Multipliers
Multipliers/DSP
units
Logic
blocks
Logic
resources
(#Logic resources, #Multipliers/DSP units, #RAM_blocks)
Graphics based on The Design Warrior’s Guide to FPGAs
Devices, Tools, and Flows. ISBN 0750676043
Copyright © 2004 Mentor Graphics Corp. (www.mentor.com)
4
Major FPGA Vendors
SRAM-based FPGAs
~ 51% of the market
• Xilinx, Inc.
• Altera Corp.
~ 34% of the market
• Lattice Semiconductor
• Atmel
• Achronix
• Tabula
~ 85%
Flash & antifuse FPGAs
• Microsemi SoC Products Group (formerly Actel Corp.)
• Quick Logic Corp.
ECE 448 – FPGA and ASIC Design with VHDL
5
Xilinx
Primary products: FPGAs and the associated CAD
software
Programmable
Logic Devices
ISE Alliance and Foundation
Series Design Software
Main headquarters in San Jose, CA
Fabless* Semiconductor and Software Company
UMC (Taiwan) {*Xilinx acquired an equity stake in UMC in 1996}
Seiko Epson (Japan)
TSMC (Taiwan)
Samsung (Korea)
ECE 448 – FPGA and ASIC Design with VHDL
6
Xilinx FPGA Families
Technology
220 nm
180 nm
Low-cost
Spartan-II,
Spartan-IIE
120/150 nm
90 nm
65 nm
45 nm
40 nm
28 nm
Highperformance
Virtex
Spartan-3
Virtex-II,
Virtex-II Pro
Virtex-4
Virtex-5
Spartan-6
Artix-7
Virtex-6
Virtex-7
FPGA Family
8
Spartan-6 FPGA Family
ECE 448 – FPGA and ASIC Design with VHDL
9
CLB Structure
ECE 448 – FPGA and ASIC Design with VHDL
George Mason University
General structure of an FPGA
Programmable
interconnect
Programmable
logic blocks
The Design Warrior’s Guide to FPGAs
Devices, Tools, and Flows. ISBN 0750676043
Copyright © 2004 Mentor Graphics Corp. (www.mentor.com)
ECE 448 – FPGA and ASIC Design with VHDL
11
Xilinx Spartan-6 CLB
ECE 448 – FPGA and ASIC Design with VHDL
12
Row & Column Relationship Between
CLBs & Slices
ECE 448 – FPGA and ASIC Design with VHDL
13
SLICEX
ECE 448 – FPGA and ASIC Design with VHDL
14
4-input LUT (Look-Up Table)
(used in earlier families of FPGAs)
x1
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
x2
0
0
0
0
1
1
1
1
0
0
0
0
1
1
1
1
x3
0
0
1
1
0
0
1
1
0
0
1
1
0
0
1
1
x4
0
1
0
1
0
1
0
1
0
1
0
1
0
1
0
1
x1
x2
x3
x4
y
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
0
0
0
0
LUT
y
x1 x2 x3 x4
x1
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
x2
0
0
0
0
1
1
1
1
0
0
0
0
1
1
1
1
x3
0
0
1
1
0
0
1
1
0
0
1
1
0
0
1
1
x4
0
1
0
1
0
1
0
1
0
1
0
1
0
1
0
1
y
0
1
0
0
0
1
0
1
0
1
0
0
1
1
0
0
• Look-Up tables
are primary
elements for
logic
implementation
• Each LUT can
implement any
function of
4 inputs
x1 x2
y
y
ECE 448 – FPGA and ASIC Design with VHDL
15
6-Input LUT of Spartan-6
ECE 448 – FPGA and ASIC Design with VHDL
16
17
Reset and Set Configurations
•
•
•
•
•
No set or reset
Synchronous set
Synchronous reset
Asynchronous set (preset)
Asynchronous reset (clear)
ECE 448 – FPGA and ASIC Design with VHDL
18
Three Different Types of Slices
50%
ECE 448 – FPGA and ASIC Design with VHDL
25%
25%
19
SLICEL
20
Fast Carry Logic
Each CLB contains separate
logic and routing for the fast
generation of sum & carry
signals
MSB
Carry Logic
Routing
• Increases efficiency and
performance of adders,
subtractors, accumulators,
comparators, and counters
Carry logic is independent of
normal logic and routing
resources
LSB
21
Accessing Carry Logic
All major synthesis tools can infer carry
logic for arithmetic functions
•
•
•
•
Addition (SUM <= A + B)
Subtraction (DIFF <= A - B)
Comparators (if A < B then…)
Counters (count <= count +1)
22
SLICEM
ECE 448 – FPGA and ASIC Design with VHDL
23
Xilinx Multipurpose LUT (MLUT)
16-bit
SR
32-bit SR
16
64xx11 RAM
RAM
4-input
LUT
64 x 1 ROM
(logic)
The Design Warrior’s Guide to FPGAs
Devices, Tools, and Flows. ISBN 0750676043
Copyright © 2004 Mentor Graphics Corp. (www.mentor.com)
24
Single-port 64 x 1-bit RAM
25
Memories Built of Neighboring MLUTs
Memories built of 2 MLUTs:
• Single-port 128 x 1-bit RAM:
• Dual-port
64 x 1-bit RAM :
RAM128x1S
RAM64x1D
Memories built of 4 MLUTs:
•
•
•
•
Single-port 256 x 1-bit RAM:
RAM256x1S
Dual-port 128 x 1-bit RAM:
RAM128x1D
Quad-port 64 x 1-bit RAM:
RAM64x1Q
Simple-dual-port 64 x 3-bit RAM:
RAM64x3SDP
(one address for read, one address for write)
26
Dual-port 64 x 1 RAM
•
•
Dual-port 64 x 1-bit RAM :
Single-port 128 x 1-bit RAM:
ECE 448 – FPGA and ASIC Design with VHDL
64x1D
128x1S
27
Total Size of Distributed RAM
28
MLUT as a 32-bit Shift Register (SRL32)
ECE 448 – FPGA and ASIC Design with VHDL
29
Input/Output Blocks
(IOBs)
ECE 448 – FPGA and ASIC Design with VHDL
George Mason University
Basic I/O Block Structure
D Q
EC
Three-State
FF Enable
Clock
SR
Three-State
Control
Set/Reset
D Q
EC
Output
FF Enable
Output Path
SR
Direct Input
FF Enable
Registered
Input
Q
D
EC
Input Path
SR
ECE 448 – FPGA and ASIC Design with VHDL
31
IOB Functionality
• IOB provides interface between the
package pins and CLBs
• Each IOB can work as uni- or bi-directional
I/O
• Outputs can be forced into High Impedance
• Inputs and outputs can be registered
• advised for high-performance I/O
• Inputs can be delayed
ECE 448 – FPGA and ASIC Design with VHDL
32
Spartan-6 Family Attributes
ECE 448 – FPGA and ASIC Design with VHDL
George Mason University
Spartan-6 FPGA Family Members
ECE 448 – FPGA and ASIC Design with VHDL
34
FPGA device present on the
Digilent Nexys 3 board
XC6SLX16-CSG324C
Spartan 6
family
Size
Logic
Optimized
324 pins
Package type
(Ball Chip-Scale)
Commercial
temperature range
0° C – 85° C
ECE 448 – FPGA and ASIC Design with VHDL
35
FPGA Design Flow
George Mason University
FPGA Design process (1)
Design and implement a simple unit permitting to
speed up encryption with RC5-similar cipher with
fixed key set on 8031 microcontroller. Unlike in
the experiment 5, this time your unit has to be able
to perform an encryption algorithm by itself,
executing 32 rounds…..
Specification / Pseudocode
On-paper hardware design
(Block diagram & ASM chart)
VHDL description (Your Source Files)
Library IEEE;
use ieee.std_logic_1164.all;
use ieee.std_logic_unsigned.all;
Functional simulation
entity RC5_core is
port(
clock, reset, encr_decr: in std_logic;
data_input: in std_logic_vector(31 downto 0);
data_output: out std_logic_vector(31 downto 0);
out_full: in std_logic;
key_input: in std_logic_vector(31 downto 0);
key_read: out std_logic;
);
end AES_core;
Synthesis
Post-synthesis simulation
FPGA Design process (2)
Implementation
Timing simulation
Configuration
On chip testing
Tools used in FPGA Design Flow
Functionally
verified
VHDL code
Design
VHDL code
Xilinx XST
Synplify Premier
Synthesis
Netlist
Xilinx ISE
Implementation
Bitstream
39
Synthesis
George Mason University
Synthesis Tools
Xilinx XST
Synplify Premier
… and others
41
Logic Synthesis
VHDL description
Circuit netlist
architecture MLU_DATAFLOW of MLU is
signal A1:STD_LOGIC;
signal B1:STD_LOGIC;
signal Y1:STD_LOGIC;
signal MUX_0, MUX_1, MUX_2, MUX_3: STD_LOGIC;
begin
A1<=A when (NEG_A='0') else
not A;
B1<=B when (NEG_B='0') else
not B;
Y<=Y1 when (NEG_Y='0') else
not Y1;
MUX_0<=A1 and B1;
MUX_1<=A1 or B1;
MUX_2<=A1 xor B1;
MUX_3<=A1 xnor B1;
with (L1 & L0) select
Y1<=MUX_0 when "00",
MUX_1 when "01",
MUX_2 when "10",
MUX_3 when others;
end MLU_DATAFLOW;
42
Circuit netlist (RTL view)
43
Mapping
LUT0
FF1
LUT1
FF2
LUT2
44
Implementation
George Mason University
Implementation
• After synthesis the entire implementation
process is performed by FPGA vendor
tools
46
Implementation
47
Translation
Synthesis
Circuit
Netlist
Timing
Constraints
Constraint Editor
or Text Editor
UCF
User Constraint File
Translation
NGD
Native Generic Database file
48
Mapping
LUT0
FF1
LUT1
FF2
LUT2
49
Placing
FPGA
CLB SLICES
50
Routing
FPGA
Programmable Connections
51
Configuration
• Once a design is implemented, you must create a
file that the FPGA can understand
• This file is called a bit stream: a BIT file (.bit extension)
• The BIT file can be downloaded directly to the
FPGA, or can be converted into a PROM file
which stores the programming information
52
Two main stages of the
FPGA Design Flow
Implementation
Synthesis
Technology
dependent
Technology
independent
RTL
Synthesis
- Code analysis
- Derivation of main logic
constructions
- Technology independent
optimization
- Creation of “RTL View”
Map
Place & Route
- Mapping of extracted logic
structures to device primitives
- Technology dependent
optimization
- Application of “synthesis
constraints”
-Netlist generation
- Creation of “Technology View”
Configure
- Placement of generated
netlist onto the device
-Choosing best interconnect
structure for the placed
design
-Application of “physical
constraints”
- Bitstream
generation
- Burning device
Synthesis Report Example –
Resource Utilization (1)
Device utilization summary:
--------------------------Selected Device : 6slx4tqg144-3
Slice Logic Utilization:
Number of Slice Registers:
Number of Slice LUTs:
Number used as Logic:
Slice Logic Distribution:
Number of LUT Flip Flop pairs used:
Number with an unused Flip Flop:
Number with an unused LUT:
Number of fully used LUT-FF pairs:
Number of unique control sets:
53 out of 4800
163 out of 2400
163 out of 2400
198
145 out of 198
35 out of 198
18 out of 198
7
1%
6%
6%
73%
17%
9%
54
Synthesis Report Example –
Resource Utilization (2)
IO Utilization:
Number of IOs:
Number of bonded IOBs:
Specific Feature Utilization:
Number of BUFG/BUFGCTRLs:
Number of DSP48A1s:
43
43 out of
102
42%
1 out of 16 6%
5 out of
8 62%
55
Synthesis Report Example –
Timing
Timing Summary:
--------------Speed Grade: -3
Minimum period: 6.031ns (Maximum Frequency: 165.817MHz)
56
Map Report Example –
Resource Utilization (1)
Design Summary
-------------Slice Logic Utilization:
Number of Slice Registers:
54 out of
Number used as Flip Flops:
53
Number used as Latches:
0
Number used as Latch-thrus:
0
Number used as AND/OR logics:
1
Number of Slice LUTs:
149 out of
Number used as logic:
148 out of
Number using O6 output only:
133
Number using O5 output only:
0
Number using O5 and O6:
15
Number used as ROM:
0
Number used as Memory:
0 out of
Number used exclusively as route-thrus:
1
4,800
1%
2,400 6%
2,400 6%
1,200
0%
57
Map Report Example –
Resource Utilization (2)
Slice Logic Distribution:
Number of occupied Slices:
Number of MUXCYs used:
Number of LUT Flip Flop pairs used:
Number with an unused Flip Flop:
Number with an unused LUT:
Number of fully used LUT-FF pairs:
Number of unique control sets:
Number of slice register sites lost
to control set restrictions:
IO Utilization:
Number of bonded IOBs:
58 out of
32 out of
162
109 out of
13 out of
40 out of
7
600
1,200
162 67%
162 8%
162 24%
35 out of 4,800
43 out of
9%
2%
1%
102 42%
58
Map Report Example –
Resource Utilization (3)
Specific Feature Utilization:
Number of RAMB16BWERs:
Number of RAMB8BWERs:
…….
Number of DSP48A1s:
…….
0 out of
0 out of
5 out of
12
24
0%
0%
8 62%
59
Post-PAR Static Timing Report
Clock to Setup on destination clock clk_i
---------------+---------+---------+---------+---------+
| Src:Rise| Src:Fall| Src:Rise| Src:Fall|
Source Clock
|Dest:Rise|Dest:Rise|Dest:Fall|Dest:Fall|
---------------+---------+---------+---------+---------+
clk_i
|
7.530|
|
|
|
---------------+---------+---------+---------+---------+
60
PAR Report
---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------Constraint
|
Check
| Worst Case | Best Case | Timing |
Timing
|
|
Slack
| Achievable | Errors |
Score
---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------Autotimespec constraint for clock net clk | SETUP
|
N/A|
7.530ns|
N/A|
0
_i_BUFGP
| HOLD
|
0.457ns|
|
0|
0
----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
61
Timing Report (1)
Timing constraint: Default period analysis for net "clk_i_BUFGP"
3354 paths analyzed, 309 endpoints analyzed, 0 failing endpoints
0 timing errors detected. (0 setup errors, 0 hold errors)
Minimum period is 7.530ns.
-------------------------------------------------------------------------------Delay (setup path): 7.530ns (data path - clock path skew + uncertainty)
Source:
a_register/q_o_4 (FF)
Destination:
x_reg_inst/q_o_3 (FF)
Data Path Delay:
7.453ns (Levels of Logic = 2)
Clock Path Skew:
-0.042ns (0.513 - 0.555)
Source Clock:
clk_i_BUFGP rising
Destination Clock: clk_i_BUFGP rising
Clock Uncertainty: 0.035ns
62
Timing Report (2)
Maximum Data Path at Slow Process Corner: a_register/q_o_4 to x_reg_inst/q_o_3
Location
Delay type
Delay(ns) Physical Resource
Logical Resource(s)
------------------------------------------------- ------------------SLICE_X4Y36.AQ
Tcko
0.447
a_register/q_o<4>
a_register/q_o_4
DSP48_X0Y3.B4
net (fanout=21)
1.194
a_register/q_o<4>
DSP48_X0Y3.M3
Tdspdo_B_M
3.364
Mmult_mult_unsigned
Mmult_mult_unsigned
SLICE_X8Y39.C4
net (fanout=1)
2.050
mult_unsigned<3>
SLICE_X8Y39.CLK
Tas
0.398
x_reg_inst/q_o<3>
Mmux_x_57
Mmux_x_4_f7_2
Mmux_x_2_f8_2
x_reg_inst/q_o_3
------------------------------------------------- -------------------Total
7.453ns (4.209ns logic,
3.244ns route)
(56.5% logic, 43.5% route)
63
Timing Report (3)
-------------------------------------------------------------------------------Delay (setup path): 7.484ns (data path - clock path skew + uncertainty)
Source:
a_register/q_o_7_1 (FF)
Destination:
x_reg_inst/q_o_3 (FF)
Data Path Delay: 7.391ns (Levels of Logic = 2)
Clock Path Skew: -0.058ns (0.513 - 0.571)
Source Clock:
clk_i_BUFGP rising
Destination Clock: clk_i_BUFGP rising
Clock Uncertainty: 0.035ns
Clock Uncertainty:
0.035ns ((TSJ^2 + TIJ^2)^1/2 + DJ) / 2 + PE
Total System Jitter (TSJ): 0.070ns
Total Input Jitter (TIJ):
0.000ns
Discrete Jitter (DJ):
0.000ns
Phase Error (PE):
0.000ns
64
Timing Report (4)
Maximum Data Path at Slow Process Corner: a_register/q_o_7_1 to
x_reg_inst/q_o_3
Location
Delay type
Delay(ns) Physical Resource
Logical Resource(s)
------------------------------------------------- ------------------SLICE_X2Y33.AQ
Tcko
0.447
a_register/q_o_7_2
a_register/q_o_7_1
DSP48_X0Y3.B7
net (fanout=13)
1.132
a_register/q_o_7_1
DSP48_X0Y3.M3
Tdspdo_B_M
3.364
Mmult_mult_unsigned
Mmult_mult_unsigned
SLICE_X8Y39.C4
net (fanout=1)
2.050
mult_unsigned<3>
SLICE_X8Y39.CLK
Tas
0.398
x_reg_inst/q_o<3>
Mmux_x_57
Mmux_x_4_f7_2
Mmux_x_2_f8_2
x_reg_inst/q_o_3
------------------------------------------------- -------------------Total
7.391ns (4.209ns logic,
3.182ns route)
(56.9% logic, 43.1% route)
65