Intussusception
advertisement

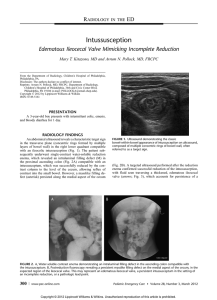
Intussusception Intussusception is a telescoping of the intestine into itself statistical analysis morbidity: 1/2000 age :The disease occurs most commonly in children between 6 and 18 months of age, but has been described in all age groups including babies in metra and in adults. the ratio of male and female :2:1-3:1 The most common form is ileo-colic in 80–90% of cases(the other forms including ileo-ileo-colic、 ileo-ileal、colo-colic、jejuno-jejunal、caeco-colic) aetiology 1、Idiopathic (or Primary) Intussusception(do not have a pathologic lead point): the vast majority of cases of intussusception do not have a pathologic lead point and are classified as primary or idiopathic intussusceptions ; Most cases of primary intussusception occur in children between the ages of 6 to 36 months of age ; there is a high susceptibility to these viruses which is generally attributed to hypertrophied Peyer’s patches (lymphoid tissue)within the ileal wall leading to intestinal stenosis。 aetiology 2、Secondary Intussusception(especially after 2 years of age). The most common pathologic lead point is a Meckel’s diverticulum 、 polyps and duplications . Other benign lead points are the appendix, hemangiomas, carcinoid tumors, ectopic pancreas and lipomas. Malignant causes, which are very rare, include lymphomas ,lymphosarcomas, small bowel tumors, and melanomas. clinical presentation Intermittent, crampy abdominal pain :The abdominal pain is sudden in onset in a child who was previously comfortable. During painless intervals, the child might look comfortable。the cramping episodes usually occur every 15 to 30 minutes accomanying the rate of regular peristaltic activities. vomitting:As the obstruction worsens, the child will have bilious emesis physical examination abdominal mass:During painless intervals,a tender mass might be palpable anywhere in the abdomen or even visualized if the child is relatively thin,The right lower abdominal quadrant may appear flat or empty (Dance’s sign) 。 fecal blood:The progression of bowel ischemia, sloughing of mucosa, and compression of the mucous glands within the intussusceptum leads to the evacuation of dark, or “currant jelly” stool. The latter is often a late sign. Abdominal Radiography In about half of cases, the diagnosis of intussusception can be suspected on plain flat and upright abdominal radiographs:include “coiled spring ” sign ;However, plain films have limited value in confirming the diagnosis and cannot be used as the sole diagnostic test。 Ultrasonography This transverse sonographic finding has been referred to as a “target” lesion ,The “pseudokidney” sign is seen on a longitudinal section; nonoperative managemant(enema) Enema:Hydrostatic Reduction and Pneumatic Reduction The advantages of nonoperative : are decreased morbidity, cost, and length of hospitalization. contraindications to nonoperative reduction are: intestinal perforation, peritonitis, or persistent hypotension. Hydrostatic or Pneumatic reduction hydrostatic or Pneumatic reduction are preferred under fluoroscopic or ultrasound guidance 。 Complications of the reduction are perforation and contrast medium intraperitoneally。 nonoperative managemant 1、Hydrostatic reduction:Hydrostatic reduction was always done by a barium 。Successful reduction patients is seen in about 85% of cases; 2、Pneumatic Reduction:The procedure is fluoroscopically monitored as air is insufflated into the rectum; The maximum safe air pressure is 80 mm Hg for younger infants and 110 to 120 mm Hg for older infants; In comparison to barium enema ,the method is quicker and safer, decreases the exposure time to radiation , no risk of barium peritonitis and a higher reduction rate (75 vs. 90%). operative treatment Surgery is indicated when nonoperative reduction is unsuccessful or incomplete for peritonitis, for the presence of a pathologic lead point, or for radiographic evidence of pneumoperitoneum; Once the leading edge of the intussusceptum is identified, it is gently manipulated back toward its normal position in the terminal ileum; recurrent intussusception Recurrent intussusception has been described in 2% to 20% of cases (average about 5%), with about one third occurring within 24 hours and the majority within 6 months of the initial episode; they are less likely to occur after surgical reduction or resection comparing to enema reduction。