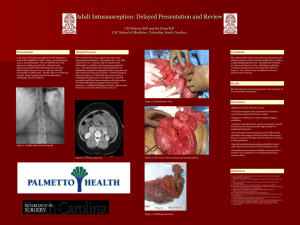
Intussusception is a medical condition that occurs when one segment of the intestine telescopes or folds into another segment, causing a blockage. This can lead to reduced blood flow to the affected area, inflammation, and potentially serious complications if not treated promptly. Intussusception most commonly affects the small intestine but can also occur in the large intestine. Key points about intussusception: Symptoms: The symptoms of intussusception can vary and might include sudden, severe abdominal pain, often described as colicky or cramp-like. Children with intussusception may draw their knees up to their chest in response to the pain. Other possible symptoms include vomiting, bloody stools, and a palpable mass in the abdomen. Demographics: Intussusception is most commonly seen in infants and children, particularly those aged 6 months to 2 years. However, it can occur at any age, including in adults. Cause: In most cases, there is no underlying cause identified for intussusception. It's often referred to as "idiopathic." In some cases, conditions like tumors or polyps in the intestine can serve as a lead point that initiates the telescoping process. Diagnosis: The diagnosis of intussusception is typically made based on the patient's symptoms, physical examination, and imaging studies. Abdominal ultrasound and sometimes a barium enema are commonly used to visualize the intestines and confirm the diagnosis. Treatment: Intussusception is considered a medical emergency and requires prompt treatment. The primary treatment is a procedure called a reduction, in which the telescoped portion of the intestine is gently pushed back into its proper position. This can sometimes be achieved using a barium enema, air pressure, or by manual manipulation under medical supervision. Surgery might be necessary if nonsurgical methods are not successful or if there are complications. Complications: If left untreated, intussusception can lead to severe damage to the involved portion of the intestine, infection, and tissue death nnecrosis.. This can result in serious health consequences and may require removal of the affected intestine. Prognosis: With prompt medical attention and appropriate treatment, the prognosis for intussusception is generally good. Most patients recover fully after the telescoped intestine is reduced. Intussusception is a serious condition that requires immediate medical evaluation and treatment. If you suspect that you or someone else may be experiencing symptoms of intussusception, it's important to seek medical attention without delay.