Joints of limbs
advertisement

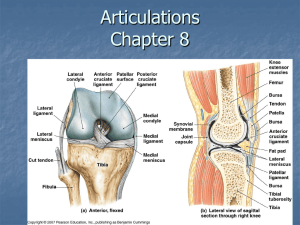
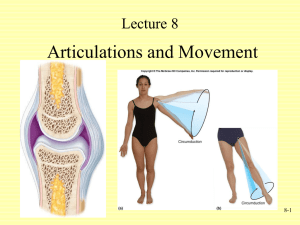
Chapter 2 The Arthrology Section 3 Joints of limbs 陈龙菊 YunYang Medical College 【目的与要求】 掌握: 1. 肩关节、肘关节、腕关节、髋关节、膝 关节和 踝关节的构成、特点及运动。 2.髋骨与脊柱间的韧带连结,骨盆的组成与分部。 了解: 胸锁关节、肩锁关节、骶髂关节的构成,足弓的 构成及功能。 The General Description Owing to the erect standing of human being,the upper limb has been freed and more movable from weight bearing and become a laboring organ.The joints of the upper limb are chiefly for the mobility in action,whereas the joints of the lower limb are for the stability. Ⅰ. Joints of upper limb Ⅰ) Joints of the girdle of the upper limb 1.Sternoclavicular joint胸锁关节 Joint formed by the sternal end of clavicle and clavicular notch of sternum and the first costal cartilage. Its capsule is strengthed by several ligaments. 2.Acromioclavicular joint 肩锁关节 ( plane joint) 3.Coracoacromial ligament喙肩韧带 喙肩弓 Coracoclavicular lig. 喙锁韧带 Ⅱ)Joints of free upper limb Incluing the shoulder joint, the elbow joint, the joints of the ulna and radius, the wrist joint and the joints of the hand. 1.Shoulder joint 肩关节 ◆ Composition: Joint formed by the head of humerus and glenoid cavity of scapula. ◆Type of should joint Synovial joint, ball-and-socket type. ◆ Feature: Its capsule is thin and loose. ◆ Accessory structures : ◆ Glenoid labrum盂唇 ◆ Coracohumeral ligament 喙肱韧带 ◆ Movements of shoulder joint It is the most movable joint of the body. flexion, extension, adduction, abduction medial rotation, lateral rotation and circumduction of the arm. ◆ Clinical application Dislocation of the shoulder joint 头大盂小囊松薄 最易发生前下脱 2. Elbow joint 肘关节 Definition: Joint formed by the trochlea of the humerus, the trochlea notch of the ulna and the head of the radius. □ Humeroulnar joint 肱尺关节 □ Humeroradial joint肱桡关节 □ Proximal radioulnar joint 桡尺近侧关节 ◆ Feature: Compound joint Its capsule is thin and loose anteriorly and posteriorly. ◆ Ligaments: 1.Radial collateral ligament 桡侧副韧带: 2. Ulnar collateral ligament 尺侧副韧带: 3. Annular ligament of radius 桡骨环状韧带: ◆ Movements: flexion and extension, rotation. ◆ Clinical application Dislocation of the radial head ◆ Elbow landmarks medial epicondyle of the humerus lateral epicondyle of the humerus tip of the olecranon 3.Joints between radius and ulnar Proximal radioulnar joint 桡尺近侧关节 Distal radioulnar joint 桡尺远侧关节 Interosseous membrane of forearm 前臂骨间膜 ◆ Movements:pronation and supination 4.Joints of hand 1) Radiocarpal joint桡腕关节 ◆ Definition: It is a typical ellipsoid joint. The articular fossa is formed by the distal end of radius and under surface of the articular disc beneath the head of ulna; and the articular head by the proximal surface of scaphoid, lunate, and triangular bones. ◆ Movements:(biaxial joint) Flexion, extension, abduction, adduction and circumduction. ★ Carpometacarpal joint of thumb 拇指腕掌关节 ◆ Definition: Joint formed by trapezium and base of the first metacarpal. ◆ Feature:saddle joint ◆ Movement: flexion, extension, adduction, abduction, and opposition Ⅱ.Joints of Lower limb Ⅰ) Joints of pelvic girdle 1.Sacroiliac joint 骶髂关节 ◆ Definition: It is formed by the auricular surfaces of the sacrum and the ilium. ◆ Feature: Its capsule is very tight and strengthened by ligaments. 2.Vertebropelvic ligaments 1) Iliolumbal ligament髂腰韧带: 2) Sacrotuberous ligament 骶结节韧带 3) Sacrospinous ligament 骶棘韧带 These two ligaments convert the sciatic notches the greater and lesser sciatic foramen 坐骨大、小孔 3. Pubic symphysis 耻骨联合 4.Obturator membrane 闭孔膜 obturator canal 闭膜管 5. Pelvis骨盆 1)Composition: 2)Terminal line界线:formed by promontory of sacrum, arcuate line, pecten pubis, pubis tuberosity and upper border of pubic symphysis . 3)Two portions: ◆ Greater pelvis ◆ Lesser pelvis 4)Lesser pelvis 小骨盆 (1)pelvic inlet 骨盆上口 (terminal line): (2)Pelvic outlet 骨盆下口: formed by tip of coccyx, sacrotuberous ligament, ischial tuberosity, ramus of ischium, inferior ramus of pubic, symphysis (3)Pelvic cavity (4)Pubic arch, subpubic angle 骨盆的性差 骨盆形状 骨盆上口 骨盆下口 骨盆腔 骶骨 男性 窄而长 呈心形 狭小 呈漏斗形 窄长, 曲度大 骶骨岬 突出 明显 耻骨下角 70º ~ 75º 女性 宽而短 椭圆形 男性 宽大 圆筒形 宽短, 曲度小 突出 不明显 90º ~ 100º 女性 70º~75º 90º~100º The fracture of the pelvis. Ⅱ) Joints of free lower limb The joints of the free lower limb include the hip joint, the knee joint, the joints between the tibia and fibula and the joints of the foot. 1. hip joint 髋关节 Definition of hip joint Jointed formed by the head of the fumur and the acetabulum of the hipbone. Type of hip joint Synovial, ball-and-socket(spheroid) type Feature: Acetabulum labrum 髋臼唇 transverse acetebular ligament髋臼横韧带 The articular capsule is strong and dense. In the front the joint,it attaches to the intertrachanteric line;behind, to the 2/3 parts of the neck. down Iliofemoral lig. 髂股韧带 Pubofemoral lig. 耻股韧带 Ischiofemoral ligament 坐股韧带 Ligament of head of femur 股骨头韧带 Zona orbicularis 轮匝带 down ◆ Movements of hip joint: flexion and extension adduction and abduction medial and lateral rotationcircumduction ◆ Clinical application The dislocation of the hip joint. 2.Knee joint 膝关节 (the largest and the most complicated joint) Composition: lower end of femur, upper end of tibia and patella ◆ ◆ Accessory □ structures Ligments: Patellar lig. 髌韧带 Fibular collateral lig. 腓侧副韧带 Tibial collateral lig. 胫侧副韧带 Anterior cruciate lig. 前交叉韧带 Posterior cruciate lig 后交叉韧带 Obligue popliteal lig 膕斜韧带 down □ Articular discs(menisci) Medial meniscus内侧半月板 (C-shaped) Lateral meniscus外侧半月板 (Oshaped) lateral Medial □ Suprapatellar bursa 髌上囊 Infrapatellar bursa 髌下囊 Alar folds 翼状襞 ◆ Movements of knee joint flexion and extension slight medial rotation lateral rotation of the leg in flexed position ◆ Clinical application Knee injury Medial collateral ligament Anterior cruciate ligament Medial meniscus Knee injury 3)Tibiofibular syndesmosis 胫腓连结 Tibiofibular joint 胫腓关节 ◆ Crural interosseous membrane 小腿骨间膜 ◆ Anterior and posterior tibiofibular ligaments 胫腓前、后韧带 ◆ 4)Joints of foot: 1)Talocrural joint 距小腿关节 (ankle joint) 踝关节 ◆ Composition: lower ends of tibia and fibula, trochlea of talus ◆ Feature: Articular capsule: thin and loose in front and behind ◆ Movements Dosiflexion (extension) and plantar flexion (flexion) 2)The others:自学 Arches of the foot 足弓 ◆ Composition : tarsals and metatarsals and ligaments between them. ◆ Function: Give to foot strength stability and resilience; protect plantar vessels and nerves Normal arch Flatfoot 【Questions】 1. Which direction is easiest from the dislocation of the shoulder joint? 2.What are the composition and accessory structures of the knee joint? Summary