Joints of limbs
advertisement

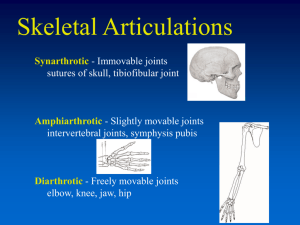
Joints of limbs SHANDONG UNIVERSITY Liu Zhiyu Joints of upper limb Joints of should girdle Sternoclavicular joint Bones: sternal end of clavicle, clavicular notch of sternum, and first costal cartilage Articular capsule: strong and is reinforced by anterior and posterior sternoclavicular ligaments Articular disc: attached to the capsule, dividing the joint into two cavities. Movements: elevation and depression, forward and backward, rotation and circumduction of the acromial end of the clavicle Joints of should girdle Acromioclavicular joint Bones: acromion and acromial end of clavicle Movement: rotation of scapula on clavicle Coracoacromial arch Composition coracoacromial ligament coranoid process Acromion Prevents the shoulder joint from superior dislocation Acromion Coracoacromial ligament Coranoid proce Joints of free upper limb ★Shoulder joint Type: ball and socket Bones: head of humerus and glenoid cavity of scapula Capsule: Thin and lax, especially lower part Attachments: proximal to glenoid labrum; distal to anatomical neck of humerus, except medially where it is slightly distal to surgical neck Tendon of long head of biceps brachii passes though the cavity ★Shoulder joint Tendon of long head of biceps brachii ★Shoulder joint Accessory structures Glenoid labrum : fibrocartilaginous ring on periphery of glenoid cavity Coracohumeral ligament : runs from coracoid process to greater tubercle Movements: flexion, extension, adduction, abduction, medial and lateral rotation, circumduction Radiograph of shoulder in a young female of 18 years in anteroposterior view (A) and axillary view with the arm abducted (B). dislocation Dislocation of Shoulder joint ★ Elbow joint Bones: lower end of humerus, upper ends of radius and ulna Humeroulnar joint : formed by trochlear of humerus and troclear noch (hinge) Humeroradial joint : formed by capitulum of humerus and head of radius (ball and socket) Proximal radioulnar joint : formed by articular circumference of radius and radial notch of ulna Capsule: thin and lax anteriorly and posteriorly, strongly thickened on either side by collateral ligaments ★ Elbow joint Ligaments: Radial collacteral ligament : attached to lateral epicondyle and annular ligament of radius Ulnar collacteral ligament : attached to medial epicondyle to medial border of trochlear notch Annular ligament of radius : attached to anterior and posterior margins of radial notch of ulna, surrounds the head of radius Movements: flexion and extension, pronation and supination Dislocation of elbow joint Anteroposterior (A) and lateral (B) radiographs of an adult elbow joint. The joint is semiflexed in B. In extension, the medial and lateral epicondyles and the top of the olecranon process are in a straight line; in flexion, the bony point form the boundaries of an equilateral triangle. Joints between radius and ulna Proximal radioulnar joint Interosseous membrane of forearm: a fibrous membrane between the shaft of radius and ulna Distal radioulnar joint formed by head of ulna, ulnar notch of radius and an articular disc Joints of hand ★ Radiocarpal joint (ellipsoid) Bones Carpal articular surface of radius and articular disc below the ulna Proximal row of carpal: scaphoid, lunate, and triquetral bones, but not pisiform Capsule: lax and strengthened by surrounding ligament Movements: flexion, extension, adduction, abduction, and circumduction Joints of hand Intercarpal joints Carpometacarpal joints Carpometacarpal joint of thumb Bones: trapezium and base of first metacarpal Movement: flexion, extension, adduction, abduction, and opposition Intermetacarpal joints Metacarpophalangeal joints Interphalangeal joints Joints of hand Intermetacarpal joints 腕骨间关节 Metacarpophalangeal joints 掌指关节 Interphalangeal joints 指间关节 Joints of Lower limb Joints of pelvic girdle Sacroiliac joint Bones: auricular surface of sacrum and ilium Capsule: very tight and strengthened by ligaments Ligaments of the gluteal region Sacrotuberous ligament Connects the lateral margins of sacrum and coccyx to the ischial tuberosity Sacrospinous ligament Connects the lateral margins of sacrum and coccyx to the spine of the ischium Foramina of the gluteal region Greater sciatic foramen Formed by the greater sciatic notch of the hip bone and the sacrospinous ligament. It provides an exit from the pelvis into the gluteal region. Lesser sciatic foramen Formed by the lesser sciatic notch of the ischium and the sacrospinous and sacrotuberous ligaments. It provides an entrance into the perineum from the gluteal region Joints of pelvic girdle Pubic symphysis Articulation: symphysial surface and interpubic disc (fibrocartilage) Ligaments: superior pubic ligament and arcuate pubic ligament Obturator membrane Obturator canal Bony pelvis Composition: formed by paired hip bones, sacrum, coccyx, and their articulations In anatomical position: anterior superior iliac spines and pubic tubercles on same vertical plane, while the tip of coccyx and superior border of pubic symphysis on same horizontal plane Terminal line: formed by promontory of sacrum, arcuate line, pecten of pubis, pubic tubercle, upper border of pubic symphysis Two portions: greater pelvis lesser pelvis Bony pelvis Lesser pelvis pelvic inlet (terminal line): Pelvic outlet : formed by tip of coccyx, sacrotuberous ligament, ischial tuberosity, ramus of ischium, inferior ramus of pubic, symphysis Pelvic cavity Pubic arch subpubic angle Main difference between male and femal pelvis Female Male Overall Wide and short Narrow and long Iliac ala More horizontal More vertical Inlet Round Oval or heart shaped Outlet Larger Small Pelvic cavity Shallower, wide Deep narrow Subpubic angle Right angle (90~1000) Acute angle (70~750) Main difference between male and femal pelvis Female Male 90~1000 70~750 Pelvic inlet Pelvic outet Pelvic cavity Pubic arch Main difference between male and femal pelvis Anteroposterior radiograph of adult female pelvis. Joints of free lower limb ★ Hip joint Bones: acetabulum and femoral head Articular capsule attachments Above: margins of acetabulum and transverse acetebular ligament Below: in front to intertrochanteric line; behind, to the neck of femur above 1 cm above the intertrochanteric crest ★ Hip joint Accessory structures Acetabulum labrum ; transverse acetebular ligament Acetabulum labrum Ligaments Iliofemoral lig. Ligament of head of femur Pubofemoral lig. Ischiofemoral ligament Zona orbicularis Movement: flexion, extention, adduction, abduction, medial and lateral rotation, circumduction Transverse acetebular lig Ligament of head of femur ★ Hip joint Pubofemoral lig. Iliofemoral lig. Ischiofemoral lig. Zona orbicularis Head of femur is driven posteriorly, out of acetabulum Poterior dislocation of the hip bone ★Knee joint Bones: lower end of femur upper end of tibia patella Articular capsule: Superapatellar bursa Deep infrapatellar bursa Ala folds ★Knee joint Accessory structures ligaments Patellar lig. Fibular collateral lig. Tibial collateral lig. Anterior cruciate ligment Posterior cruciate ligament Oblique popliteal ligament Meniscus Medial meniscus (C-shaped) lateral meniscus (O-shaped) ★Knee joint Posterior cruciate lig. Anterior cruciate lig. Oblique popliteal lig. Tibial collateral lig. Fibular collateral lig. ★Knee joint Movements: flexion and extension; flexed knee joint may be passively rotated through 700 lateral Medial Hip joint Knee joint Radiograph Coronal T1-weighted magnetic resonance image (MRI) of the knee in an adult male. Tibiofibular syndesmosis Tibiofibular joint Crural interosseous membrane Anterior and posterior tibiofibular ligaments Joint of foot Talocrural joint (ankle joint ) Bones: lower ends of tibia and fibula, trochlea of talus Articular capsule: thin and lax in front and behind, and supported on each side by strong collateral ligaments Ligments Medial lig. Lateral lig. Anterior talofibular lig. Calcaneofibular lig. Posterior talofibular lig. Joint of foot Medial lig. Posterior talofibular lig. Calcaneofibular lig. Anterior talofibular lig. Joint of foot Talocrural joint Movements: dorsiflexion (extension) plantar flexion (flexion); when the ankle joint is fully plantar flexed, small amounts of abduction, and adduction are possible Torn fibers of anterior talofibular lig. Joint of foot Intertarsal joints Talocalcaneal joint Talocalcaneonavicular joint Calcaneocuboid joint Tarsometatarsal joints Intermetatarsal joints Metatarsophalangeal joints Interphalangeal joints Inversion and eversion of foot transverse tarsal joint Arches of foot Medial longitudinal arch formed by calcaneus, talus, navicular, three cuneiforms and first to third metatarsal bones, head of talus is the keystone of this arch Lateral longitudinal arch: formed by calcaneus, cuboid, fourth and fifth metatarsals; cuboid is is the keystone of this arch Arches of foot Tranverse arch: formed by cuboid, three cuniforms and all metatarsals; the intermediate cuneiform is the keystone of this arch Function: give to foot strength stability and resilience; protect plantar vessels and nerves Arches of foot Normal arch Flatfoot