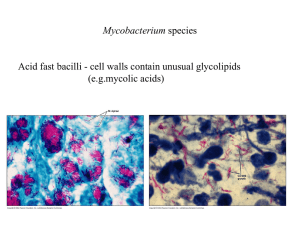
Tuberculosis
advertisement
TUBERCULOSIS Paige Derouin History • • • Began infecting the first human ancestors as long as 500,000 years ago In 1882 – claimed the lives of 1 in 7 people • Ran rampant in crowded European and American cities • March 24 – Robert Koch discovers Mycobacterium tuberculosis • Koch’s discovery allowed scientists to begin working on a treatment and vaccine for TB. 1908 - Albert Calmette and Camille Guérin: BCG vaccine o First used in 1921 preventatively History Cont’d • 1943 - microbiologist Selman Waksman discovered • • • • streptomycin 1970s – Most people believe TB is completely irradiated 1998 – genetic sequencing of Mycobacterium tuberculosis 2006 – first case of extensively drug resistant TB in South Africa 2008 – 49 countries reported cases of extensively drug resistant TB Incidence • • • In 2008 highest incidence was in Southeast Asia 98% of TB related deaths occur in developing countries In the US, there were 4.2 cases per 100,000 people in 2008 • Most of the US cases occurred in Florida, Texas, California, and New York World Incidence 2006 World map showing reported cases of tuberculosis per 100,000 citizens. Red = >300, orange = 200-300; yellow = 100-200; green 50-100; blue = <50 and grey = n/a. Mycobacterium tuberculosis • • • Rod shaped, gram positive bacterium Infection begins with phagocytosis into a macrophage can remain inside the host in a dormant form and reactivate later Diagnosis Diagnosis is based on: Symptoms Producing cough, chest pain, night sweats, fatigue, fever Medical history TB tests Tuberculin Skin Test Blood Tests Chest X-Rays Diagnostic microbiology Sputum smear – acid-fast bacilli TB Tests Tuberculin Skin Test Injection of fluid into the skin of the lower arm 48-72 hours later – checked for a reaction Diagnosis is based on height of the skin Blood Test Newer test Based white blood cells’ response to the test Results available in 24 hours http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=s3v8M2Q6AGI&feature =channel Treatment • Latent TB • • • • Not symptomatic or contagious Usually treated with Isoniazid for 9 months Confirmed with a chest X-Ray Infectious TB • • Treatment is very expensive Treated in phases - Isoniazid, Rifampicin, Pyrazinamide and Ethambutol 1. 2. Usually 3 drugs 2 different drugs Treating Drug Sensitive TB Treating Drug Resistant TB Treating Extensively Drug Resistant TB Problems with Treatment Very long treatment Large number of drugs is expensive Resistant Strains 3rd World countries Steps to Prevention WHO’s Stop TB Strategy DOTS – reduce deaths from TB by 50% by 2015, eliminated by 2050 March 24 – World TB Day Research for a new vaccine to replace or boost BCG Works Cited “I am stopping TB” image. : http://www.tac.org.za/community/files/stop- tb_medium.jpg Treating extensively drug resistant TB: http://www.niaid.nih.gov/topics/tuberculosis/Understanding/WhatIsTB/Sci entificIllustrations/Pages/extensivelyDrugResistantIllustration.aspx Treating drug resistant TB: http://www.niaid.nih.gov/topics/tuberculosis/Understanding/WhatIsTB/Sci entificIllustrations/Pages/multidrugResistantIllustration.aspx Treating drug susceptible TB: http://www.niaid.nih.gov/topics/tuberculosis/Understanding/WhatIsTB/ScientificIllu strations/Pages/firstLineIllustration.aspx Mycobacterium: http://www.students.stedwards.edu/aruiz5/interview.htm World Incidence: http://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/File:Tuberculosis_reported_cases_2006.PNG