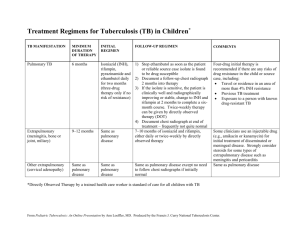
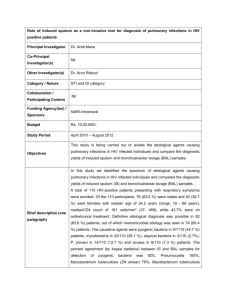
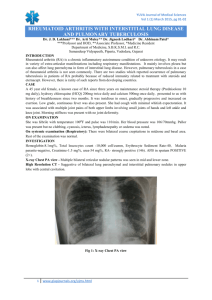
TB Basics 2011
advertisement

Tuberculosis: Basics Rick Speare Anton Breinl Centre School of Public Health, Tropical Medicine and Rehabilitation Sciences James Cook University 16 May 2011 1 Objectives To provide background on TB to assist understanding of tuberculosis and control strategies 2 Tuberculosis Due to the bacterium, Mycobacterium tuberculosis Small % due to M. bovis Pulmonary disease ± bloodstream spread to other organs Bacilli are coughed up and inhaled by others All ages can develop disease Infection can be acquired in childhood, remain latent and emerge as immunity wanes 3 Transmission Droplet transmission is usual route Mycobacterium aerosolised into droplets (coughing, speaking, breathing) Inhaled into alveoli of new host Grows in alveoli (Ghon focus) Carried to bronchial lymph nodes (Ghon complex) M. bovis can also be spread in milk from infected bovine udders 4 Histology of the normal alveolae http://www.anatomy.dal.ca/Human%20Histology/Lab11/59ll4la.html Histopathology of TB granuloma Risk of Transmission People in close contact with TB case have highest risk of infection (clustered) Transmission can result from casual and brief contact in highly endemic areas South African studies demonstrated this (Verver et al 2004) Greater risk when number of bacteria are higher Risk of transmission falls rapidly with treatment 7 http://www.health.vic.gov.au/ideas/diseases/tb_community Pulmonary TB Chronic cough Productive Haemoptysis Weight loss Night sweating 9 Fatal pulmonary TB: Prisoner in Lilongwe, Malawi 10 Very severe consolidation, caseating necrosis and cavities Another Malawaian patient with pulmonary TB and cavities Consolidation Cavities TB is a very destructive disease Diagnose & treat early! Death from TB Respiratory failure Severe haemoptysis Systemic TB (miliary TB) Meningeal TB Other 15 Severe haemoptysis: patient often drowns in their own blood 16 Very destructive disease Cavities due to patient coughing up necrotic lung Fibrosis is common Damaged tissue can not be replaced Diagnose and treat early! “Healed” Cavity TB is mainly a pulmonary disease, but extra-pulmonary disease is common Bacteraemia with seeding of multiple organs (miliary TB) Localised infection in any other organ Meningitis Osteomyelitis Arthritis Lymph node infection Other … 19 TB meningitis: infants & AIDS 20 Osteomyelitis Arthritis 21 Osteomyelitis of spine 22 Diagnosis of pulmonary TB Detection of Mycobacterium tuberculosis in sputum Culture of sputum Smear of sputum Acid fast bacilli (stained with acid fast stain) PCR Pulmonary TB can not be diagnosed from a chest X-ray 23 TB: Disease control The focus in control of TB is only on the person spreading TB Sputum positive case only (AFB+ = Sm+) Other cases are of minor significance in control of TB Sometimes, clinical aims and TB control aims clash 24 Breaking Transmission Droplet transmission is usual route Points to break the transmission cycle: Preventing viable Mycobacterium getting into droplets Preventing droplets with Mycobacterium getting into the alveoli of a new host Preventing Mycobacterium in alveoli from causing disease 25