BAN-poster-summMed[2..
advertisement

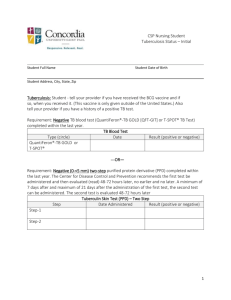
Tuberculosis WHO strategy for control of the pandemic spread of tuberculosis embraces: Monitoring transmission of tuberculosis Evaluation of multidrug-resistant Mycobacterium tuberculosis strains incidence Epidemiology and surveillance are estimated by advanced molecular biology methods: Fingerprinting (IS6110 PCR) Spoligotyping MIRU-VNTR typing Genotypic detection of drug resistant mutations [Map of Mycobacterium tuberculosis genome] : - Molecular characterisation of Mycobacterium tuberculosis strains improves the case detection rate of multidrug-resistant tuberculosis in Bulgaria. - Scientific cooperation of Institute of Microbiology (BAS), Sofia, with Institut Pasteur of Saint-Petersburg and Institut Pasteur of Guadeloupe (world database), contributes to effective control of the global spread of tuberculosis. Balkan Endemic Nephropathy (BEN) Role of hantaviruses in the BEN pathogenesis → severe endemic disease in North West Bulgaria, Central Serbia (Shumadiya), North East Bosnia, South East Croatia and Romanian regian close to Iron Gate. Viruses – Diabetes New proves on the role of neurotropic viruses in the insulin-dependent diabetes melitus → by a model of herpesvirus infection in organ cultures of Langerhans islets. Human Papillomaviruses (HPV) Molecular epidemiological studies (genotyping) on the role of HPVs in pre-canceral diseases and invasive cervical cancer in Bulgarian women. Food Control Emerging zoonotic diseases, especially when food-borne, have significant social and financial impact in Europe, being addressed across the whole food supply chain. Polymerase chain reaction (PCR) has been developed for detection of food-borne pathogens in meat, milk and their products. This highly specific and sensitive method allows detection of 1 to 10 bacterial cells per gram sample. Effective control has been carried out against Campylobacter, Salmonella and Listeria from farm to dish. Vaccines Development of new generation of live carrier vaccines with economic impact primarily for veterinary medicine has been carried out. Enteric Yersinia species, selected for carrier, were attenuated by targeted disruption of genes encoding virulence factors. Taking advantage of protein secretion apparatus of Yersinia, antigens of classical swine fever are fused and a novel mucosal vaccination approach is created. Introduction of DNA vaccines is a new approach to vaccination. Such a hybrid DNA molecule was constructed by us, encoding a T and B cell epitope-containing influenza hemagglutinin peptide and a scFv antibody fragment binding to mouse complement receptors I and II (CR1 and CR2). A single immunization with a plasmid containing the described construct induced a strong anti-influenza cytotoxic response lasting for more than six months and a weak antibody response. Treatment of Autoimmune Diseases A major event in the pathogenesis of systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) is the breaking of tolerance to native (double stranded, ds) DNA and the appearance IgG anti-DNA antibodies. Pathological DNA-specific B cells in SLE are logical targets for a selected therapeutic intervention. Our data show that it is possible to suppress selectively the activity of targeted autoreactive B-lymphocytes and to change the natural course of an autoimmune disease by administering chimeric molecules that cross-link the inhibitory receptor with the immunoglobulin B cell receptor. Chemotherapy of Viral Infections Development and application of large-spectrum screening system for antiviral activity New antivirals: Adenostatin® → antiviral agent for treatment keratoconjunctivitis and other human adenoviral infections of epidemic Cycluridine → antiviral agent for treatment of mucosal diseases-viral diarrhea in calves and other flavivirus infections Mopyridone → antiviral agent active against influenza (M1 protein inhibitor) and alfavirus infections Oxoglaucine → antiviral agent active against broad-spectrum enteroviruses Synergistic combinations of anti-enteroviral replication inhibitors → a new approach for effective anti-enteroviral chemotherapy directed to overcoming drug-resistance development New Generation Antiviral Microbicide Manorapid® Synergy → broad-spectrum hand disinfectant with low-alcoholic content (in