Female GU 2a - Porterville College
advertisement

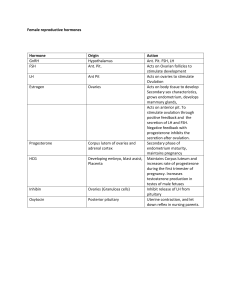
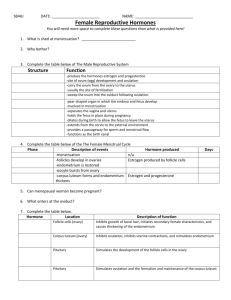
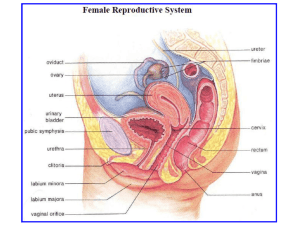
Genital Urinary System Female Reproductive System Brunner and Suddarth’s Medical Surgical Nursing Text: Ch. 46-48 Behavioral Objectives: • • • • Review the anatomy and physiology of the female GU systems Describe the physical assessment of the female GU systems Discuss the application of the nursing process as it relates to patients with disorders of the female GU system Describe etiology, pathophysiology, clinical manifestations, nursing management and patient education for the following female GU disorders: – Vaginitis – Pelvic inflammatory disease (PID) – Endometriosis • • Discuss incidence, prevention & tx of the pts with CA of the GU system Discuss the nursing interventions in pre and post-operative care of patients undergoing the following surgeries – Hysterectomy – Mastectomy Anatomy Review: Breast • Female breast development – 10-16 yrs • Tail of Spence – Into axillary area • • • • Cooper’s ligament 12-20 lobes Nipple Areola Anatomy Review Internal Reproductive Structures Vagina – – Mucus membrane Posterior to bladder & urethra Anterior to rectum Anterior & posterior walls touch Upper vagina surrounds cervix – – – • Inferior uterus Anatomy Review Internal Reproductive Structures Uterus • Pear-shaped – Muscular Size – – ? Variable • • # pg Anatomy Review Internal Reproductive Structures • Location – Posterior to bladder • Ligaments Uterus • Two parts of the uterus – Cervix • Projects into the Vagina – Fundus • Body of the uterus • Endometrium: – Lining of the uterus Anatomy Review Internal Reproductive Structures Ovaries • Connected to uterus by the fallopian tubes • Contains – • 1000’s of ova @ birth Ova / Ovum – – – Egg cells (immature) Ova – plural Ovum - Singular Physiology Review – Discharge of a mature ovum from the ovary Start Ovulation • Definition Physiology Review Ovulation • Follicular Stage – – – Ovum enlarges cyst (graafian follicle) Reaches the surface (of the ovary) Ovum is discharged • Ovulation Physiology Review After Ovulations • • • • Ovum Fallopian tube Uterus IF is meets a spermatozoon – Union & conception – Location of fertilization? Physiology Review After ovulation • Ovum cyst – Corpus luteum – Stays in the ovary • Produces progesterone • Prepares the uterus for the fertilized ovum The Menstrual Cycle • 2 system control menstruation process – – Reproductive Endocrine Hormones The Menstrual Cycle • Ovaries – Estrogen – Progesterone The Menstrual Cycle Pituitary gland • FSH – – • Stim. Ovaries to secrete estrogen LH – – Ovulation Stim. Progesterone The Menstrual Cycle • Cyclic pattern – – Changes in the endometrium and menstruation 28 day cycle Follicular Phase Estrogen Increasing Progesterone Low FSH High decreasing LH Low increasing Ovaries Growth of follicle Endometrium Proliferation of superficial layer Day(s) 5 - 13 Ovulation Estrogen High Progesterone Low FSH Low LH High Ovaries Ovulation Endometrium Continued growth Day(s) 14 Luteal Phase Estrogen Drops then increases Progesterone Increasing FSH Low LH High Ovaries Active corpus luteum Endometrium Highly vascular & thick Day(s) 15 - 25 Premenstrual Phase Estrogen Decreasing Progesterone Decreasing FSH Increasing LH Decreasing Ovaries Degeneration of corpus luteum Endometrium Vasoconstriction, degeneration Day(s) 26 - 28 Menstrual Phase Estrogen Low Progesterone None FSH Increasing LH Low Ovaries follicular development begins Endometrium Degeneration and shedding of superficial layer Day(s) 1-5 Menopausal Period • End of reproductive capacity Age 45 – 52 yrs Menstruation ceases • • – No periods for 1 year > Menopausal Period • Ovaries not active – – • • _?__ estrogen i Reproductive organs i size No ova mature Physical assessment Health history • Menstrual hx – Menarche • – – – • Beginning of menstruation Length Amount Cramps/pain ? Hx of pregnancies • Medication history – Hormone therapy – Hormonal contraceptives – Fertility treatment Assessment: History & Clinical Manifestations • Pain – – • Hx vaginal discharge – – • • Dysmenorrhea Dyspareunia Odor Itching Hx urinary functions Hx B&B control Assessment: History & Clinical Manifestations • • • • • Sexual history History of sexual or physical abuse History of surgery History of chronic illness or disability History of genetic disorders • Physical Exam • Breast – Frequency: • Monthly Breast Exam – Assessment • • • • • • • Palpable masses Skin changes Pain Swelling Redness Nipple changes Self exam Abnormal breast findings • Erythema – Benign local infection or – Superficial neoplasm • Prominent venous pattern – h blood supply required by tumor • Edema & pitting – Neoplasm blocking the lymphatic drainage tubes • Orange-peel appearance / Peau D’orange (edema) – Advanced breast cancer • Nipple inversion – If new requires evaluation • Signs of dimpling, creasing, changes in contour • Breast Cancer Mass - palpate – Single mass – One breast – Firm, hard, embedded in surrounding tissue – Non-tender Mammography • Duration – 15 minutes • Recommended frequency – Annually – > age 40 Physical Assessment • Pelvic – Frequency • – Initial • • – – • Annual > age 18 sexually active breast pelvic Positioning – Supine lithotomy position Physical Assessment • Inspection – Inspects external genitilia Speculum examination – • • Vaginal canal Cervix Physical Assessment • Pap smear – Tissue sample of cervix Purpose: – • – Dx Cervical Ca No douche before visit Physical Assessment • Bimanual palpation – – Cervical palpation Uterine palpation • Colposcopy – Portable microscope – Obtain sample