FERTILIZATION & IMPLANTATION
advertisement

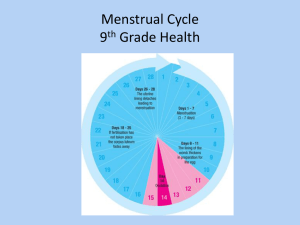
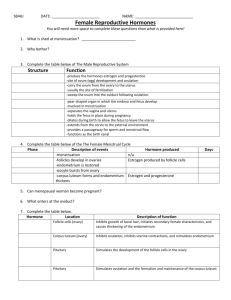
NOTES: CH 46, part 2 – Hormonal Control / Reproduction Hormones Involved in Reproduction - MALES ● Androgens: produced in Leydig cells in testes (i.e. TESTOSTERONE) ● GnRH: from hypothalamus; stimulates anterior pituitary to release FSH and LH ● FSH: acts on seminiferous tubules to increase sperm production ● LH: stimulates androgen production *primary sex characteristics: -development of internal and external reproductive organs -sperm production *secondary sex characteristics: -deepening of voice -distribution of facial & pubic hair -muscle growth Hormones Involved in Reproduction - FEMALES ● MENSTRUAL CYCLE = changes that occur in uterus ● OVARIAN CYCLE = changes that occur in ovaries Menstrual cycle occurs in 3 phases: 1) Menstrual flow phase (3-5 days): endometrium is being shed from uterus 2) Proliferative phase (1-2 weeks): regeneration & thickening of endometrium Menstrual cycle occurs in 3 phases: 3) Secretory phase (2 weeks): endometrium continues to thicken, becomes more vascularized & develops glands which secrete a glycogen rich fluid which serves as nutritional fluid for the embryo (IF embryo does NOT implant in uterine lining by the end of this phase, a new menstrual flow phase begins) Ovarian Cycle: 1) Follicular phase: several follicles in ovaries begin to grow 2) Ovulatory phase: follicle & adjacent wall of ovary rupture, releasing the egg (2° oocyte) (Follicular phase) Ovarian Cycle: 3) Luteal phase: the remaining follicular tissue in ovary after ovulation becomes the CORPUS LUTEUM which is endocrine tissue that secretes hormones (Luteal phase) Menstrual and Ovarian Cycles are closely related: ● increased amts. of estrogen secreted by growing follicle stimulates endometrium to thicken in preparation for embryo (PROLIFERATIVE PHASE) ● after ovulation, estrogen & progesterone secreted by the CORPUS LUTEUM stimulate continued development & maintenance of the endometrium (SECRETORY PHASE) Menstrual and Ovarian Cycles are closely related: ● decreased concentration of estrogen & progest. due to disintegration of the C.L. reduces blood flow to the endometrium; the endometrium breaks down & passes out of the uterus ● IF embryo is present, it secretes HCG which maintains estrogen & progest. secretion by the C.L. so the endometrium is maintained MENOPAUSE Menopause: cessation of ovulation and menstruation -between ages of 46 and 54 -ovaries lose their responsiveness to FSH/LH -decline in production of estrogens FERTILIZATION & IMPLANTATION ● fertilization occurs in the OVIDUCT ● female repro. tract produces secretions which capacitate sperm cells ● a capacitated sperm cell reaches the egg and must penetrate the ZONA PELLUCIDA FERTILIZATION & IMPLANTATION ● when sperm cell binds to receptor molecules in zona pellucida, the ACROSOME releases its contents (i.e. digestive enzymes) so that it can penetrate the plasma membrane of the egg (= “acrosomal reaction”) FERTILIZATION & IMPLANTATION ● binding of sperm cell to egg triggers depolarization of egg membrane (functions as a “fast block” to polyspermy) (= “cortical reaction”; a series of changes in outer zone, “cortex,” of the egg cytoplasm) FERTILIZATION & IMPLANTATION ● CLEAVAGE (cell division) begins approx. 24 hours after conception ● after 3 days, embryo contains approx. 16 cells (MORULA) ● embryo reaches uterus approx. 7 days after fertilization & contains approx. 100 cells (BLASTOCYST) FERTILIZATION & IMPLANTATION ● implantation occurs within next 5 days ● for the first 2-4 weeks, embryo obtains nutrients directly from endometrium ● in 2nd trimester, fetus secretes its own progesterone to maintain pregnancy BIRTH ● high estrogen levels during the last weeks of pregnancy trigger formation of oxytocin receptors in uterus ● oxytocin secreted by fetus & posterior pituitary of mother stimulate smooth muscles of uterus to contract BIRTH ● oxytocin stimulates prostaglandin secretion by placenta which enhances muscle contraction of uterus ● decreased levels of progesterone after birth remove inhibition from anterior pituitary which allows for prolactin secretion BIRTH ● PROLACTIN stimulates milk production after 2-3 days ● OXYTOCIN controls release of milk from mammary glands BIRTH CONTROL: Methods of Contraception: 1) COITUS INTERRUPTUS: withdrawal of penis before ejaculation 2) RHYTHM METHOD: requires abstinence from sexual intercourse a few days before/after ovulation 3) MECHANICAL BARRIERS: -condom (male, female) -diaphragm -cervical cap 4) CHEMICAL BARRIERS: -creams, foams, jellies w/spermicide -easy to use, but high failure rate unless used with a condom or diaphragm 5) ORAL CONTRACEPTIVES: -“the pill” -contain synthetic hormones to disrupt the ovarian cycle and prevent ovulation -can be taken in pill form, injected, or implanted 6) INTRAUTERINE DEVICE (IUD): -small, solid object placed within the uterus -prevents implantation of blastocyst 7) SURGERY: -in males: VASECTOMY -in females: TUBAL LIGATION