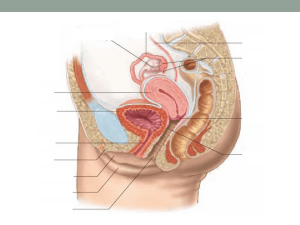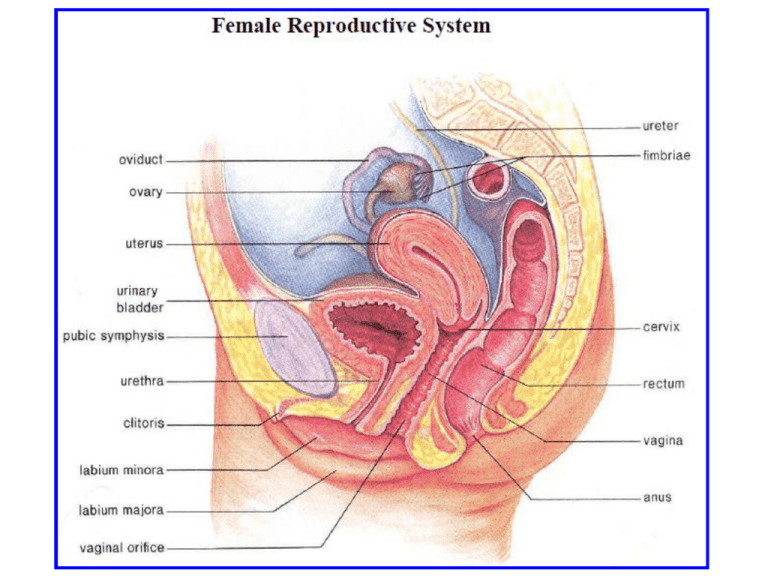
Female External Genitalia
Labia majora and Labia minora
Ø
Protective folds of skin
Vestibule
Ø Cleft between the labia minor
Ø Contains openings (orifices) to the urethra and vagina
Clitoris
Ø Female sensory organ; homologous to the male penis provides
sensitivity during intercourse
Vagina
Receives penis during sexual intercourse and serves as a birth
canal
Cervix
Ø Narrow end of uterus leading to the vagina dilates at birth to
allow baby to exit
Uterus (Womb)
Houses developing fetus
Oviduct
Conducts egg towards the uterus
Also called the Fallopian tubes or uterine tube
Fimbriae
Ø Finger-like projections of the oviducts which brush over the
ovaries.
Ø Along with cilia in the oviducts, they cause a current which
sweeps the egg into the oviduct
Ovaries
Ovarian Cycle
Day 1 –13 Follicular Phase
Day 14 Ovulation
Day 15 –28 Luteal Phase
Day 1 –13 Follicular Phase
1. Hypothalamus produces a GnRH to stimulate Anterior lobe
of pituitary
2. FSH and LH from pituitary gland stimulate the ovary for
folliclular growth
2. Primary follicle (46 chromosomes) contains primary
oocyte which divides. (produces female sex hormones)
3. One oocyte gets most of the cytoplasm and 23 chromosomes.
(called a secondary oocyte, which is inside the now secondary
follicle)
4. The Other oocyte called the polar body disintegrates
5. The secondary follicle grows into a Graafian (vesicular)
Follicle.
Day 14 Ovulation
6. Graafian Follicle bursts (ovulation) LH is at its highest
and triggers ovulation
Day 15 –28 Luteal Phase
7. The follicle has lost its oocyte (or “egg”) and forms into the
Corpus Luteum. (LH causes the corpus luteum to form.)
- The corpus luteum secretes hormones
- Estrogen and progesterone
If pregnancy does not occur: Corpus Luteum breaks down
(about 10 days) and cycle repeats.
If pregnancy does occur: Corpus Luteum remains for
3 – 6 months and continues to produce hormones.
Uterine Cycle
Day 1 – 5 Menstruation
Day 6 – 13 Proliferative phase
Day 14 Ovulation
Day 15 –28 Secretory Phase
Day 1 –5 Menstruation
1. Low levels of sex hormones (Corpus Luteum has just
disintegrated)
2. Endometrium (lining of Uterus) breaks down
3. Cells of the endometrium, blood vessels, and blood are
shed from the uterus and exit the vagina.
4. A flow of blood (called menses) passes out of the vagina
during a period called menstruation.
Day 6 – 13 Proliferative phase
1. Increased estrogen by the ovarian follicle causes the
endometrium to rebuild.
2. Endometrium becomes thick and vascularized
Day 14
1. Ovulation occurs (release of the egg)
Day 15 –28 Secretory Phase
1. Increased level of progesterone by the corpus luteum
2. Endometrium doubles in thickness
3. Glands produce mucous
4. Uterus prepared to receive embryo
* If no pregnancy. The corpus luteum degenerates, decrease in
progesterone production occurs and the endometrium breaks
down Cycle continues
Pituitary Hormones
Follicule Stimulating Hormone (FSH)
Hypothalamus secretes GnRH (gonadotropic releasing
hormone) and causes the anterior pituitary to secrete
• FSH (days 1-13)
• LH (days 14-28)
FSH causes follicles to mature. Maturing follicles produce
estrogen.
The increase in estrogen concentration causes the anterior
pituitary to stop producing FSH
Luteinizing Hormone (LH)
LH is released day 14 – 28
Causes the corpus luteum to form
Corpus luteum produces progesterone as well as estrogen
Increase in progesterone cause the anterior pituitary gland to
stop producing LH
Ovarian Hormones
1. Estrogen: responsible for uterine and vaginal growth
as well as female secondary sex
characteristics like breasts development,
deposition of fat around the hips, growth
of armpit & pubic hair.
2. Progesterone: prevents the breakdown of the inner
wall of the endometrium and calms
the uterus during pregnancy
(prevents its contractions).
Implantation
Implantation occurs in the uterus
Fertilization occurs in the oviduct.
Embryo embeds itself in the endometrium several days after fertilization.
Membrane surrounding the embryo produces a hormone called HCG (Human
Chorionic Gonadotropic hormone) Then the Placenta develops.
It is found immediately in blood and a few days later in the urine. (Pregnancy test about one week later)
HCG prevents the breakdown of the Corpus Luteum. The Corpus Luteum
produces progesterone that keeps the endometrium from breaking down.
FSH and LH being produced stop the egg from being released.
Placenta
Contains both maternal and fetal tissue
Area where gas and nutrients exchange occurs.
No exchange of blood
Diffusion of gases and wastes and nutrients occur over the cell layers
Placenta produces HCG, progesterone (prevents breakdown of the endometrium)
and estrogen (keeps new egg from developing)
Oxytocin causes
mammary glands to
release milk. Lobules
containing milk
contract forcing milk
into ducts which lead
to the nipple.
Oxytocin is used to
induce birth