Female Reproductive Hormones Worksheet - High School Biology
advertisement

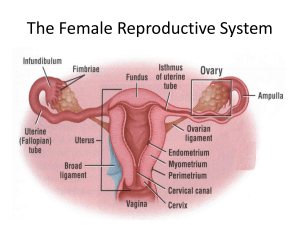
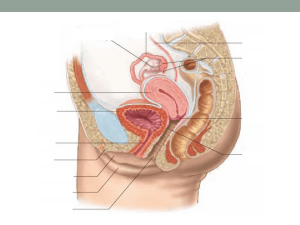
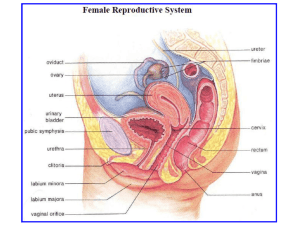
SBI4U DATE: _______________________ NAME: ____________________________ Female Reproductive Hormones You will need more space to complete these questions than what is provided here! 1. What is shed at menstruation? __________________________ 2. Why bother? 3. Complete the table below of The Male Reproductive System Structure Function -produce the hormones estrogen and progesterone -site of ovum (egg) development and ovulation -carry the ovum from the ovary to the uterus -usually the site of fertilization -sweep the ovum into the oviduct following ovulation -pear-shaped organ in which the embryo and fetus develop -involved in menstruation -separates the vagina and uterus -holds the fetus in place during pregnancy -dilates during birth to allow the fetus to leave the uterus -extends from the cervix to the external environment -provides a passageway for sperm and menstrual flow -functions as the birth canal 4. Complete the table below of the The Female Menstrual Cycle Phase Description of events Hormone produced -menstruation n/a -follicles develop in ovaries Estrogen produced by follicle cells -endometrium is restored -oocyte bursts from ovary -corpus luteum forms and endometrium Estrogen and progesterone thickens Days 5. Can menopausal woman become pregnant? 6. What enters at the oviduct? 7. Complete the table below. Hormone Location Description of function Follicle cells (ovary) Inhibits growth of facial hair, initiates secondary female characteristics, and causes thickening of the endometrium Corpus luteum (ovary) Inhibits ovulation, inhibits uterine contractions, and stimulates endometrium Pituitary Stimulates the development of the follicle cells in the ovary Pituitary Stimulates ovulation and the formation and maintenance of the corpus luteum SBI4U DATE: _______________________ NAME: ____________________________ ANSWERS - Female Reproductive Hormones You will need more space to complete these questions than what is provided here! 4. What is shed at menstruation? endometrium 5. Why bother? The buildup of endometrium causes weight gain and may even serves as a source of nutrients for invading microbes 6. Complete the table below of The Male Reproductive System Structure Ovaries Function Fallopian tubes (oviducts) Fimbria Uterus (womb) Cervix Vagina -produce the hormones estrogen and progesterone -site of ovum (egg) development and ovulation -carry the ovum from the ovary to the uterus -usually the site of fertilization -sweep the ovum into the oviduct following ovulation -pear-shaped organ in which the embryo and fetus develop -involved in menstruation -separates the vagina and uterus -holds the fetus in place during pregnancy -dilates during birth to allow the fetus to leave the uterus -extends from the cervix to the external environment -provides a passageway for sperm and menstrual flow -functions as the birth canal 8. Complete the table below of the The Female Menstrual Cycle Phase Description of events Hormone produced Flow -menstruation Follicular -follicles develop in ovaries Estrogen produced by follicle cells -endometrium is restored Ovulation -oocyte bursts from ovary Luteal -corpus luteum forms and endometrium Estrogen and progesterone thickens Days 1-5 6-13 14 15-28 9. Can menopausal woman become pregnant? No longer produces eggs However, should an egg be transferred from a donor, she could 10. What enters at the oviduct? Secondary ooctye, which undergoes MII 11. Complete the table below. Hormone Location Description of function Estrogen Follicle cells (ovary) Progesterone Folliclestimulating hormone (FSH) Luteinizing hormone (LH) Corpus luteum (ovary) Pituitary Inhibits growth of facial hair, initiates secondary female characteristics, and causes thickening of the endometrium Inhibits ovulation, inhibits uterine contractions, and stimulates endometrium Stimulates the development of the follicle cells in the ovary Pituitary Stimulates ovulation and the formation and maintenance of the corpus luteum