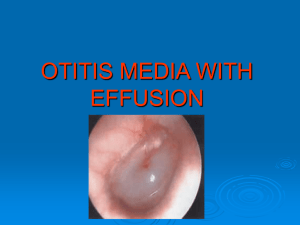
Blocked or Painful Ears. Wax and Otitis Media
advertisement

Blocked or painful ears Wax and otitis media Mike Smith ENT Consultant Hereford County Hospital and Worcester Royal Hospital UK 2009 Ear canal: 2-3cm long Cartilage Outer 1/3 Skin Thick Glands 1. Cerumen 2. Sebum Hair 1. Fine 2. Thick (older men) Bone Inner 2/3 Thin None None What is wax? Cerumen In hair follicles. Thin sweat like secretion. Long coiled tubes with muscle walls. Sebum In hair follicles. Secrete Oily fluid. Epithelial debris Hairs Shed, and mat with secretions. Dust, sand, f.b.’s etc Functions of wax Waterproofing layer Protective layer from trauma Cleansing by migration outward with dust, foreign material (e.g. sand, grommets) Acid pH is antiseptic Contains antibacterial agents Canal Skin Migration Squamous epithelium and keratin / dead skin Moves from drum centre along canal to meet the secretions in outer canal Keratosis Obturans Failure of migration. Epithelial build up and canal expansion. Rare. Health education Harmful : Scratching Cotton buds (‘Nothing smaller than elbow’) False : ‘Wax is dirty and must be removed’ ‘Wax often causes reduced hearing’ Ear ‘candling’ and other gadgets Problems with wax? Hearing loss Non-obstructive wax (no loss) Apparent total obstruction (hearing loss 5dB) Totally obstructed canal (conductive hearing loss 45dB) Otitis Externa Damp, itchy Hearing aid Treatment options Solvent drops Manual Syringe Electric pulsed irrigation Aural speculum and loops/hooks Microscopic suction Wax Solvent Drops Effectiveness ? Exterol Cerumol Oil Waxsol Bicarbonate ++++ +++ ++ ++ + Cost Irritation Ear Syringing Method Solvent beforehand Straighten canal (Pull up and back) Water at 37-38 deg. C Brace nozzle with hand on head Point syringe up and back After syringing check canal/drum (Dr?) Indications for syringing Total occlusion Examination of obscured tympanic membrane Otitis Externa ( if other cleansing not available) Foreign body Contra-indications to syringing Normal wax (be more selective of patients) Past ear disease or surgery (thin drum) Perforation (may force debris into middle ear, dislocate ossicle, damage oval/round window, or infect middle ear) Only hearing ear (no risks) Recurrent Otitis Externa (keep dry) Anti-coagulant (care to avoid trauma) Vegetable f.b.’s (swell) Perfs and pockets Risks of syringing Complications requiring specialist referral in 1:1000 e.g. pain, dizziness, bleeding, infection, perforation, tinnitus, hearing loss Rupture of ear drum by syringing Study by Sorenson et al 1995 Tested on 10-48 hr post mortem cadavers Large variations in pressure needed to rupture, but well above that generated by syringing (if TM not atrophic) Treatment of complications Otitis externa Acute sensori-neural prompt treatment hearing loss or vertigo refer if canal occluded by Urgent referral debris or oedema Refer early if in any doubt. Perforation Do not blindly reassure the specialist referral patient, check (it usually heals) Canal wall bleeding bicarbonate drops follow up to ensure clot clears Acute Otitis Media Acute otitis media Treatment <3yrs-70% at least one Analgesia episode Antibiotics? Prophylaxis? Grommets Varieties Adenoidectomy AOM with discharge Prevention: parental AOM with smoking, pre-school complications Rhinitis Resistant AOM Immunity Recurrent AOM AOM on ME Effusion Chronic MEE/Glue ear Grommet With Discharge Treatment Oral antibiotic? Drops? Grommets/T-tubes Water prevention? Commonest operation Tube removal? ~20% discharge Adenoids Acute Allergy Organisms same as Immunity AOM IV antibiotics Chronic Surgery Often Pseud. Or Staph. Biofilms? Ear drops and ototoxicity Ototoxicity Ototoxicity of the infection itself. Inflammation acts as barrier to RW membrane. Vestibulo-toxicity also an issue. Familial trait / genetic susceptibility. Use endorsed for infected perfs by Am. Acad. of ORL, H & N and ENT-UK Alternatives (ciprofloxacin unlicensed as ear drop in UK so far, but widely used) Complications of AOM Perforation and otorrhoea Hearing loss Glue ear Mastoiditis Facial palsy Meningitis Chronic Suppurative Otitis Media (CSOM) CSOM Mucosal Safe? Active/Inactive Discharge character Treatment None Medical Surgical Squamous Pockets/atelectasis Cholesteatoma Discharge character Treatment Stable pocket Unstable pocket Established cholesteatoma Thankyou