Ear canal - Hosoital Health Vajira
advertisement

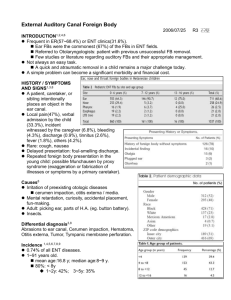
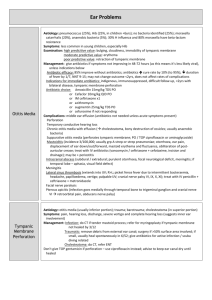
Otorrhea • • • • Site Age Type of otorrhea (mucoid,purulent) Characteristic of drainage (acute,pulsatile) • Systemic disea • ses. • Others(otalgia,neurologic deficit) Ear canal • Ear trauma-cotton-tip swabs, irrigators for cerumen removal. • Swimming-related water contamination. • Chronic dermatitis or eczema • Fungal infections. • Retained foreign body. • External otitis , Eczema • Acute OM with TM perforation • Chronic OM • Malignant OE • Otomycosis • Bullous myringitis • Herpes zoster oticus • Malignant Otitis Externa. • • • • -poor general health. -immunosuppressed. -diabetic -suffering from Steven-Johnson’s syndrome. • Malignant Otitis Externa. • -granulation tissue. • -preauricular and auricular edema and erythema. • -tympanic membrane necrosis. • -facial paralysis. • -Pseudomonas aeruginosa. • Otomycoses. • Aspergillus niger-pigmented fungal with hyphal threads. • Candida albicans-prolonged courses of antibiotic ear drops. • Secondary mycosis of temporal bone. • -Cryptococcus.-Blastomyces • -Mucor.- Candida. • Bullous external otitis & myringitis. • Hemorrhagic vesicles • Exquisite ear pain out of proportion to physical exam. • Conductive hearing loss. • Mycoplasma pneumoniae & Haemophilus influenzae • Ramsay Hunt syndrome. • -vesicles with erythematous base on EAC , pinna , or soft palate. • -Otalgia described as a burning sensation. • -hearing loss. • -vertigo. • -facial paralysis. • COM with or without cholesteatoma. • Granulomatous diseases of temporal bone (Wegener’s synd. Histiocytosis). • Tuberculous mastoiditis. • Neoplasms. • Aural tuberculosis & nontuberculous mycobacterial mastoiditis. • -chronic painless, thin , watery or serous otorrhea. • -denuded malleus and multiple TM perforations • -granulation tissue, polyps and inflammatory tissue, diffusely destructive. • Watery otorrhea = CSF leak • Idiopathic dural dehiscence. • Trauma. • Complication of neoplasm , infection. • Mondini malformation. • Spontaneous CSF leak. Otalgia • Innervation. • Anatomy. • Causes of referred otalgia. Tympanic branch of the glossopharyngeal nerve (Jacobson’s nerve) • medial surface of TM , mucosa of ME ,eustachian tube, mastoid air cells. • Cervical roots C2 & C3 –postauricular region • Facial N. –skin of lateral concha and antehelix, lobule , mastoid, posterior EAC , posterior pertion of TM Auriculotemporal branch of the mandibular div. of trigeminal nerve • Tragus , anterior pinna, anterior lateral surface of TM , anterosuperior EAC wall. • The auricular br. Of vagus N.(Arnold’s nerve) • -concha, inferioposterior EAC , TM , postauricular skin. • Glossopharyngeal N. –oropharynx, tonsils , tongue base. • Locallized otalgia. • Acute otitis media , mastoiditis • Otitis externa , impact cerumen. • Eustachian tube dysfunction. • Inflammation , infection of auricle. • Ear trauma. Referred otalgia • • • • • • • Tonsillitis, Tongue diseases. Thyroiditis. Temperomandibular joint arthritis. Periodontal , dental diseases. Parotitis. Sinusitis. Laryngitis , Tracheitis. Aural fullness • Eustachian tube dysfunction. • Impact cerumen. • Meniere’s disease. • Perilymphatic fistula. Hearing loss • • • • • • • Acute (sudden SNHL ,viral.) Progressive (autoimmune inner ear Dz , cancer.) Fluctuating (Meniere’s disease , multiple sclerosis.) Systemic diseases. Metabolic Family history. Others. Hearing loss in children • • • • • • • Perinatal infectionwith cytomegalovirus , rubella ,syphilis. Family history of hereditary chilhood SNHL. Craniofacial abnormalities. Birth weight < 1,500 gram. Hyperbilirubinemia. Apgar score 0-4 at 1 min. , 0-6 at 5 min. Syndromes (Sheibe dysplasia , Michel deformity.) Vertigo • • • • • • • Central VS Peripheral causes. Vestibular dysfunction VS Non vestibular. Trauma to labyrinth. Metabolic (DM, hyperlipoproteinemia, hypothyroidism.) Hormones. Collagen vascular disorders. Tumors.