Lymphomas Clonal disorders of lymphoid cells at various stages of
advertisement

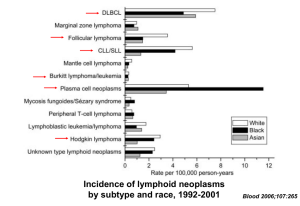
Lymphomas Clonal disorders of lymphoid cells at various stages of differentiation HODGKIN L. Distinction clinical histological NON-HODGKIN L. immature cells (precursors) mature cells Note: B Hodgkin lymphoma is also a (mature)B-cell T lymphoma. B-cell lymphoma Clonal disorders of B-cells at various stages of differentiation B-cell lymphomas of immature cells - lymphoblasts B-acute lymphoblastic leukaemia - frequent, children B-lymphoblastic lymphoma - rare B-cell lymphomas of mature B-cells most common:follicular, diffuse large B-cell lymphoma; plasma cell myeloma Classifications • • • • • Kiel Rappaport Working formulation REAL WHO – 2001, 2008 Lymphomas - classification • Practical standpoint • Low grade - B-CLL, follicular, MALT lymphoma, lymphoplasmacytic lymphoma Hairy cell leukemia • High grade - diffuse large B-cell lymphoma • Burkitt lymphoma (lymphoblastoma, ALL) • Inbetween (LG - HG): mantle cell lymphoma • Plasma cell tumors Chronic leukemia • • • • B or T – cell derived B: B-chronic lymphocytic leukemia Hairy cell leukemia B-cell lymphomas of mature B-cells B-cell chronic lymphocytic leukemia (B-CLL/SLL) most common chronic lymphoid leukaemia • PB- lymphocytosis, BM; lymph nodes, spleen, liver, extranodal • Hist.:dark areas of small B-cells + pale pseudofollicles (= proliferation centres) • median age: 50, survival:5, asympt. OR fatigue, AIHA, infections, enlargement of organs • SLL • Richter - DLBCL; prolymphocytic variant Hairy cell leukemia Hairy cell BM, PB, spleen older man pancytopenia + splenomegaly Follicular lymphoma Over 60 LN, spleen, later BM often asympt. Histology grades transformation - DLBCL t (14;18] bcl2/JHa Extranodal marginal zone B-cell lymphoma of MALT GIT - stomach lung, head, neck (thyroid, salivary, eyes), skin Chronic antigenic stimulation stomach - Helicobacter pylori thyroid - Hashimoto Sjogren IPSID localized - good prognosis RISK: transformation - DLBCL Lymphoplasmacytic lymphoma /Waldenstrom macroglobulinemia Monoclonal IgM paraprotein - hyperviscosity Bleeding –interference with clotting factors, plts Cryoglobulinemia – Raynaud phenomenon, cold urticaria Visual acuity impairment - red cell sludging,, Neurolog. problems – headaches, dizziness, deafness, cerebrovascular accidents, Waldenstrom macroglobulinemia any condition producing large Ig rare, old (HCV) BM, LN, spleen, (PB) Mantle cell lymphoma Aggressive t(11; 14] LN, extranodal cyclin D1 Advanced More frequent in men over 50 Diffuse large B-cell lymphoma aggresive, potentially curable VERY COMMON! 1/3 of all lymphomas of adults (med. 64 ys) nodal OR extranodal (1/3) GIT, skin, CNS, testis bone, soft tissue, salivary glands, Waldeyer ring, lung, kidney, liver, spleen, female genital tract Diffuse large B-cell lymphoma Primary OR secondary Chronic lymphocytic leukemia Follicular lymphoma Marginal zone B-cell lymphoma Nodular lymphocyte predom. Hodgkin l. Risk factor: immunodeficiency (often EBV+) Diffuse large B-cell lymphoma Morphologic variants Centroblastic Immunoblastic T-cell/histiocyte rich Anaplastic Plasmablastic Clinicopathologic subtypes mediastinal (thymic) intravascular primary effusion, pyothorax associat. Diffuse large B-cell lymphoma Differential diagnosis Tumors Haematological: lymphomas – peripheral - B, T precursors - B, T myeloid neoplasm Non-haematological: carcinoma, sarcoma, GIST, melanoma, seminoma, glial tumors Reactive disorders: infectious mononucleosis, Kikuchi Mediastinal DLBCL Thymus Female, 30 ys Anterior mediastinal mass Superior vena cava syndrome Clinicopathological differential diagnosis? Mediastinal DLBCL Compartmentalising fibrosis Polymorphic large cells, abundant pale cytoplasm CD20, CD23, CD30, CD45 Intravaskulární B-lymfom HE PCR FRII–FRIV IgH Intravascular B-cell lymphoma CD20 Burkitt lymphoma • endemic (Africa) • sporadic (young, rare) • immune deficiencyassociated - HIV! • t(8;14) • starry sky Burkitt lymphoma:starry sky Plasma cell neoplasms Terminally differentiated B-cells Clone of Ig secreting plasma cells Serum: monoclonal Ig or its parts M protein; paraprotein; Bence Jones proetin Plasma cell neoplasms 1. Plasma cell myeloma 2. Solitary plasmacytoma - bone extraosseous 3. Precursor lesions - MGUS 4. Other M-component !no significant lymphadenopathy! Plasma cell myeloma Problems: 1. Infiltration of organs 2. Excessive Ig 3. Immune disorder Sites of involvement axial skeleton – liver, spleen, kidney hypercalcemia, infections hyperviscosity,amyloidosis Myeloma kidney Proteinuria - in 70% of patients Bence Jones proteinuria and cast nephropathy 1. direct toxicity of IgL Combinatiom with Tamm-Horsfall protein – casts Obstructs tubules; inflammation; giant cells, granulomas 2. Amyloidosis 3. Light-chain nephropathy – deposits in glomeruli, around tubules 4. Hypercalcaemia, hyperuricemia 5. Vascular disease 6. Infections renal failure multifactorial