Continuous Quality Improvement
advertisement

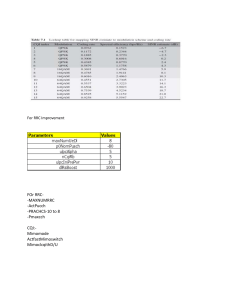
CONTINUOUS QUALITY IMPROVEMENT Continuous Quality Improvement @ Stony Brook Medicine Continuous Quality Improvement (CQI) is: • A journey to satisfy the needs and exceed the expectations of our customers • A means of performance improvement • Aligned with our Mission to improve the lives of our patients, families, and communities, to educate skilled healthcare professionals and to conduct research that expands clinical knowledge What does CQI Encompass? • • • • • • • Patient care Patient satisfaction Patient safety Employee safety Employee satisfaction Regulatory agency requirements Administrative/financial functions CQI Principles • All work is a part of a process • • • • • Quality is achieved through people Decision making is done with facts Patients and customers are our first priority Quality requires continuous improvement CQI focuses on the process not the person Find a process to improve • Administration, Clinical Service Groups, other Committees charter a CQI team • Criteria used to prioritize opportunities for improvement – – – – – High Risk High Cost High Volume Problem Prone Patient Safety related Core Measures of Excellence are a variety of evidence-based, scientificallyresearched standards of care which have generally been shown to result in improved clinical outcomes for patients. Those areas reviewed include: Surgical: (SCIP) timeout/ timeliness of antibiotics / blood glucose control / urinary catheters, death among surgical inpatients with serious treatable complications, Iatrogenic pneumothorax rates, post op respiratory failure, Pulmonary embolism, DVT, wound dehiscence, accidental puncture / lacerations, hip fracture mortality Abdominal Aortic Aneurysm Repair mortality rates Children’s Asthma: specific medication use Stroke, Acute Myocardial Infarction & Heart Failure (drugs during admission and upon discharge, specific procedures) Community – Acquired Pneumonia: immunizations, blood cultures, antibiotic choices Emergency Department – departure/admit times, timeliness to diagnosis, pain management Imaging Efficiency: MRI for Lumbar spine; mammography follow up, use of contrast material Central line associated bloodstream infection 6 Core Measure of Excellence •CMS (the Center for Medicare & Medicaid Services) established the (Core) Measures in 2000 and began publicly reporting data relating to the (Core) Measures in 2003 •CMS ties some parts of reimbursement to reporting the data; in the future reimbursement will be tied to how well we do in delivering the elements of care (Value-Based Purchasing) 7 Methodology for Improving a Process • Find a process to improve • Organize a team that knows the process • Clarify current knowledge of the process • Understand causes of process variation • Select the process to improvement How does FOCUS PDCA help us to Adhere to the Simple Rules of Work? • Patients First • Prevent Failure (a breakdown in operations or functions) • Use World Class Processes • Redesign the Process to meet the best standard of care without compromise to the patient • Encourage Growth in Knowledge • Use Resources Wisely Examples of CQI projects • Early recognition of sepsis through the electronic medical record • BOOST: identification of the elderly high risk patient & medication reconciliation • Surgical Booking sheet discrepancy’s • ED to Medicine bed time / ED to CACU flow • Preventing Central Line and Catheter Associated Urinary Tract Infections • Reducing “Door to Balloon Time” • Improve the care of patients with Heart failure • Avoiding Readmissions within 30 days • Inducing Hypothermia post cardiac arrest • Medication Reconciliation upon admission in the ED • Time to pain medication for long bone fractures • Minimizing pain during procedures for the pediatric patients - “Ouch less” Reducing CLBSI’s (Central Line Blood Stream Infections) Efforts to improve the quality of care also can reduce the cost of care Sentinel Event • A sentinel event is an unexpected occurrence involving death or serious physical or psychological injury, or the risk thereof. • Examples include: --Suicide --Rape --Loss of limb -- Elopement --Death Root Cause Analysis • A process for identifying the contributing factors that underlie variations in performance; includes the occurrences of the sentinel events, adverse event or close calls. • Process that features interdisciplinary involvement of those closest to and/or most knowledgeable the situation to find out: --What happened? --Why did it happen? --How can we prevent it? --How do we know we made a difference Failure Mode and Effects Analysis (FMEA) • Proactive risk assessment • A team based, systematic, and proactive approach for identifying the ways a process or design can fail, why it might fail, and how it can be made safer. Joint Commission Requirement • What performance improvement initiative has our department implemented recently? • Hint: It MUST be supported by data (graphs) CONTINUOUS QUALITY IMPROVEMENT How to contact the CQI Department • If you have any questions or ideas for a potential CQI project in your department, please call us at: (631) 444-9975 14