The Use of Decision Support Systems in Continuous Quality Improvement Janice Kaczmarek
advertisement

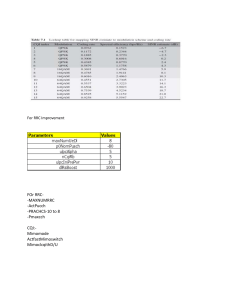
The Use of Decision Support Systems in Continuous Quality Improvement Janice Kaczmarek Susan Lovejoy Problem with CQI in Health Care Many healthcare organizations have implemented quality improvement measures as a means to improve outcomes, but do not have an information tracking system to: – Analyze clinical data – Monitor utilization and costs – Track outcomes Intermountain Health Care “Given that ‘you manage what you measure,’ we have to extend our efforts beyond the financial measures that have traditionally driven healthcare delivery systems.” Dr. Brent James, V.P. Intermountain Health Care’s Medical Research What is Driving the Need for CQI? Provider accountability by insurers, consumers, government Need to eliminate unnecessary treatment and procedures Attempt to minimize the large variations in practice patterns Control medical expenses Improve patient outcomes What is CQI? Continuous Quality Improvement: strategies or methods used to improve upon existing systems or techniques in an effort to provide better quality products and/or services to consumers. CQI is not limited to health care, it has been used throughout the centuries in all types of industries. Other Names – Total Quality Management (TQM) – Quality Assurance (QA) – Quality Improvement (QI) Clinical QI at IHC Clinical Project Cost Structure Improvement Fast track extubation in TICU Long-term Ventilator management HFOV (RDS in premature newborns Shock Trauma Respiratory ICU Antibiotic Assistant Pediatric ICU Infection prophylaxis in surgery Adverse drug event prevention Community-acquired pneumonia Ventilator support for hypoxemia Group B strep sepsis of newborn $5.5 $4.7 $3.7 $2.5 $1.2 $.7 $.6 $.5 $.5 $.5 $.3 $20.7 Tools for Quality Improvement Plan-Do-Check-Act Cycle (PDCA) Guidelines Clinical/critical pathways Computer-based clinical decision support systems (CDSS) – – – – – Alerting Systems Assisting Systems Critiquing Systems Diagnosing Systems Reminding Systems Outcomes-FYI Outcomes are states or conditions of individuals and populations attributed to antecedent health care. Not a direct reflection of quality of care. Relationship between process and outcome is a probability and may be modified by factors other than health care. Large sample sizes required to obtain results that are meaningful, which take a long time to collect. Three Classes of Outcomes Physical Outcomes – Complications – Changes in biological function – Functional status measures Service Outcomes – Satisfaction surveys Cost Outcomes NovaMedica Application Clinical Performance Improvement Package Developed in collaboration with Intermountain Health Care. Designed to track clinical performance and patient outcomes. Utilized by clinicians, managers other members of Intermountain as outcomes, educational, and marketing tool. Example of NovaMedica http://www.novamedica.com/ Gaps in Existing Approaches Lack of integration of current systems Inability to generate useful information with existing system Lack of consensus on most meaningful outcomes measures Limited implementation of electronic medical record Resistance to utilize information systems for outcomes purposes Potential Solutions Investment in information system integration, including the electronic medical record Consensus on a limited set of appropriate outcome measures Increased education to provider community on the benefits of electronic outcomes tracking