Quality Management lecture
advertisement

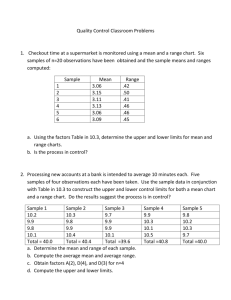
By Christina Lauderman RN, BSN, CEN The learner will be able to.. Define Quality Care Identify Standards of Care/Benchmarks Identify drivers of quality and their roles in the continuous quality improvement (CQI) process. Describe How Total Quality and Continuous Quality Management, Six Sigma, and Lean Six Sigma Addresses Quality. Identify when an Incident report needs filed. Perform a Chart Review on Given Stroke Charts Develop a continuous quality improvement project on a nursing unit. What Is Quality? Right Care at the Right time to the Right Patient. Compassionate/Empathetic Competent No Harm Meets Standards No Complications Nondiscriminatory/Fair Involves the pursuit of excellence in the delivery of care and ongoing prevention of potential errors The degree to which patient care services increase the probability of desired patient outcomes and reduce the probability of undesired outcomes given the current state of knowledge (JCAHO, 2009) Florence Nightingale Jean Watson- Theory of Caring Dorothea Orem-Self care Deficit June Larabee-Quality Theories Medicare and Medicaid The Joint Commission (JCAHO) State regulators Payers Professional groups Patients Why Is Poor Care Sometimes Given? Under Or Inexperienced Staff Human Error Time, Money, and Space Constraints Attitude Ineffective Communication Complications Inability To Meet Patient’s Expectations. System Error Care Deemed Appropriate Based on Scientific Evidence and Expertise of Expert Professionals in that Area of Care. Come From JCAHO, DOH, ANA, NLN, NIH, AHA, ATA, ABA, UPMC Standards, Medicare/Medicaid, Insurance Companies etc. First learn standards in Nursing School. Learn Policies and Procedures of Facility employed by. As you incorporate Evidence Based Practice As you become involved in Research. Structure Standards- Physical Environment, Organization Process Standards-Delivery Of Care Outcome Standards-The End Results Examples of Standards After the Fact Identification Prevention of Failed Standards and Problems Based on Data Collection and Accountability Uses Measurement Tools Focus on “No Blame” 4 Characteristics Customer/Client Focused Total Organizational Involvement Use of Quality Tools and Statistics for Measurement Key Processes for Improvement Identified Customer Client Focused Internal Clients Employees, lab, housekeeping External Clients Patients, Visitors, Physicians Insurance Companies Total Organizational Involvement Team Approach Empowerment of Employees Management-Team Use of Quality Tools and Statistics for Measurement Tools such as Graphs, charts Statistic tools such as percentages, Probability Key Processes for Improvement Identified Systems Related Clinical Managerial Plan, Do, Check, Act Cycle TQM Philosophy CQI Process Never Ending Process Involves Evaluation, Actions, and a Mind Set to Constantly Strive for Excellence 4 Key Players Resource Group Coordinator Team Leader Team Comprehensive Quality Management Plan Multidisciplinary Standards Benchmarking Critical Paths Indicators Performance Appraisals Intra/Interdisciplinary Assessments and Improvements Audits Retrospective Concurrent Peer Reviews Utilization Reviews Outcomes Management Six Sigma Uses Quantitative Data As a Measure As a Goal As a Management System Customer focus Data Driven Process Emphasis Proactive Management Boundary-less Collaboration Aim for Perfection, Tolerate Failure Institute of Medicine- To Err Is Human: JCAHO- Patient Safety Goals Institute of Healthcare Improvement Right Patient, Right Medication, Right Dose, Right Route, Right Time Patients Involved In Own Care Educate Patients About Medications Errors Need Reported Problem Focused Identify Analyze Evaluate Risks Develop Plan Education Based Monitors Laws and Codes Related To Patient Safety. Collects Data In Legal Complaints Provides Reports to Administration, Medical Staff, and Board of Directors. Incident Actual or Potential Risk. Document in Chart and in Incident Report. Be Factual, Non Disciplinary, Honest Case Followed Up by Risk Management Medication Errors Falls Complications from diagnostic or treatment procedures Patient/Family dissatisfaction with care Refusal of Treatment or to sign consent Skin Breakdown Iv Infiltrations Encourage Staff To Report Incidents No Blame or Disciplinary Action Unless Absolutely Necessary No Finger Pointing Encourage a Culture of Safety and Quality Clear Communication Maintain Professional Caring Attitude Listen to Complaints Determine Expectations of Patient or Family Quick Follow Up and Action Personal Contact-Utilize Charge Nurse, Nurse Manager, Nursing Supervisor. Maintain Safety For Yourself and For the Patient. Make Restitution/Meet Expectations When Applicable. Meeting Standards Helps to Provide Quality TCM- Philosophy Uses Plan, Do, Check, Act CQM-Never Ending, Strive for Excellence. Six Sigma- Reduce Waste Increase Productivity Risk Management Role in Quality Increase Patient Safety Incident Reporting Handling Complaints Textbook- Effective Leadership and Management in Nursing by Pearson Google Images