Document
advertisement
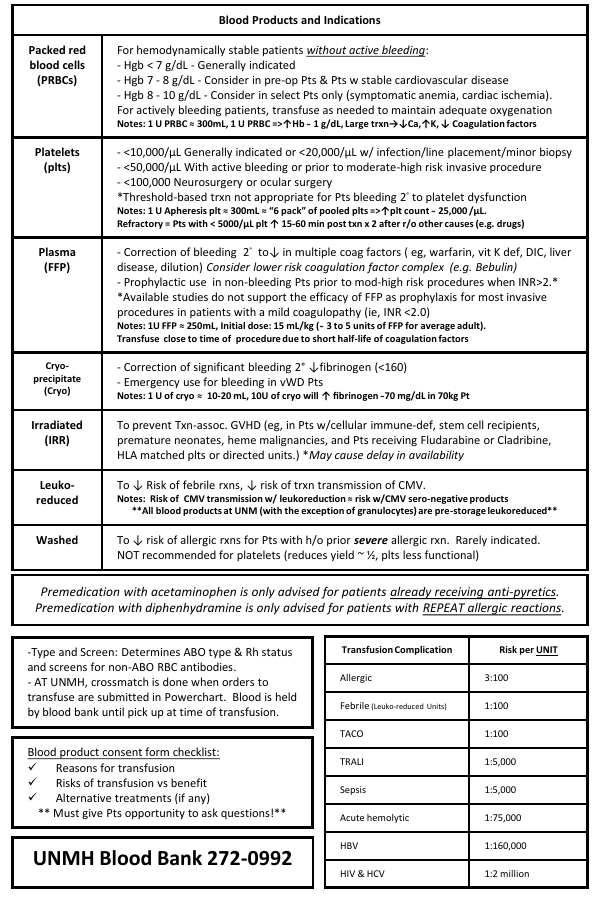
Blood Products and Indications Packed red blood cells (PRBCs) For hemodynamically stable patients without active bleeding: - Hgb < 7 g/dL - Generally indicated - Hgb 7 - 8 g/dL - Consider in pre-op Pts & Pts w stable cardiovascular disease - Hgb 8 - 10 g/dL - Consider in select Pts only (symptomatic anemia, cardiac ischemia). For actively bleeding patients, transfuse as needed to maintain adequate oxygenation Notes: 1 U PRBC ≈ 300mL, 1 U PRBC =>↑Hb ̴ 1 g/dL, Large trxn→↓Ca,↑K, ↓ Coagulation factors Platelets (plts) - <10,000/μL Generally indicated or <20,000/μL w/ infection/line placement/minor biopsy - <50,000/μL With active bleeding or prior to moderate-high risk invasive procedure - <100,000 Neurosurgery or ocular surgery *Threshold-based trxn not appropriate for Pts bleeding 2° to platelet dysfunction Notes: 1 U Apheresis plt ≈ 300mL ≈ “6 pack” of pooled plts =>↑plt count ̴ 25,000 /μL. Refractory = Pts with < 5000/μL plt ↑ 15-60 min post txn x 2 after r/o other causes (e.g. drugs) Plasma (FFP) - Correction of bleeding 2° to↓ in multiple coag factors ( eg, warfarin, vit K def, DIC, liver disease, dilution) Consider lower risk coagulation factor complex (e.g. Bebulin) - Prophylactic use in non-bleeding Pts prior to mod-high risk procedures when INR>2.* *Available studies do not support the efficacy of FFP as prophylaxis for most invasive procedures in patients with a mild coagulopathy (ie, INR <2.0) Notes: 1U FFP ≈ 250mL, Initial dose: 15 mL/kg ( ̴ 3 to 5 units of FFP for average adult). Transfuse close to time of procedure due to short half-life of coagulation factors Cryoprecipitate (Cryo) - Correction of significant bleeding 2° ↓fibrinogen (<160) - Emergency use for bleeding in vWD Pts Irradiated (IRR) To prevent Txn-assoc. GVHD (eg, in Pts w/cellular immune-def, stem cell recipients, premature neonates, heme malignancies, and Pts receiving Fludarabine or Cladribine, HLA matched plts or directed units.) *May cause delay in availability Notes: 1 U of cryo ≈ 10-20 mL, 10U of cryo will ↑ fibrinogen 7̴ 0 mg/dL in 70kg Pt Leukoreduced To ↓ Risk of febrile rxns, ↓ risk of trxn transmission of CMV. Washed To ↓ risk of allergic rxns for Pts with h/o prior severe allergic rxn. Rarely indicated. NOT recommended for platelets (reduces yield ~ ½, plts less functional) Notes: Risk of CMV transmission w/ leukoreduction ≈ risk w/CMV sero-negative products **All blood products at UNM (with the exception of granulocytes) are pre-storage leukoreduced** Premedication with acetaminophen is only advised for patients already receiving anti-pyretics. Premedication with diphenhydramine is only advised for patients with REPEAT allergic reactions. -Type and Screen: Determines ABO type & Rh status and screens for non-ABO RBC antibodies. - AT UNMH, crossmatch is done when orders to transfuse are submitted in Powerchart. Blood is held by blood bank until pick up at time of transfusion. Blood product consent form checklist: Reasons for transfusion Risks of transfusion vs benefit Alternative treatments (if any) ** Must give Pts opportunity to ask questions!** UNMH Blood Bank 272-0992 Transfusion Complication Risk per UNIT Allergic 3:100 Febrile (Leuko-reduced Units) 1:100 TACO 1:100 TRALI 1:5,000 Sepsis 1:5,000 Acute hemolytic 1:75,000 HBV 1:160,000 HIV & HCV 1:2 million STOP Transfusion Transfusion Reaction Suspected - Stabilize patient - Notify attending - Perform Clerical Check Fill out Trxn Rxn form & call Blood Bank All other symptoms Trxn can resume AFTER symptoms resolve (Rx with diphenhydramine) Draw 2 purple tops and send to BB with remainder of unit for trxn rxn work-up. Send urine if s/s of hemolysis. Unless emergent, wait for results and pathology approval to transfuse another unit. Febrile nonhemolytic Allergic/ Anaphylactic TACO TRALI Sepsis (Transfusion – Assoc. Circulatory Overload) Symptoms & Signs*: Fever, chills, hypotension, dyspnea, chest pain, flank pain, and anxiety Severity: Life threatening Ddx: Febrile Non-Hemolytic, Sepsis, TRALI Prevention & Tx: Proper ID of Pt and blood product. Only transfuse RBC with normal saline. Maintain urine output (IV fluids, mannitol and/or diuretics), CV support. Symptoms & Signs*: Dyspnea, hypertension, hypoxia, pulmonary edema, ↑BNP Severity: Moderate morbidity to life threatening Ddx: TRALI, Acute Hemolytic Transfusion Rxn, Anaphylaxis, Non-Txn ARDS Prevention & Tx: Conservative transfusion, ID at risk Pts (eg, elderly, h/o heart disease, and pediatric Pts) and transfuse slowly over max of 4hrs . Rx with supplemental O2 and diuretics. (TransfusionRelated Acute Lung Injury) Symptoms & Signs*: Urticaria, pruritus Anaphylaxis =>Dyspnea, tightening of throat, ↓BP Severity: Low morbidity (simple allergic) to life threatening (anaphylaxis) Ddx: TRALI, TACO (consider both in Pt’s with shortness of breath) Prevention & Tx: Reactions dose-dependent => STOP Trxn and wait for symptoms to resolve with treatment. For repeated rxns, consider pre-medication with diphenhydramine, famotidine and/or steroids. Rx anaphylaxis w/ Epi. Consider washed units for Pts with h/o anaphylaxis. Acute Hemolytic Acute Transfusion Reactions Symptoms & Signs*: Fever (>1C°↑ and >38°) and chills Severity: Low morbidity Ddx: Acute Hemolytic Rxn, Sepsis & TRALI Prevention & Tx: Prevented by using leukoreduced products. In RCTs acetaminophen not shown to ↓ incidence; premed advised only if Pt is already febrile. Symptoms & Signs*: SOB, fever, hypoxia, pulmonary edema, ↓ BP, within 6 hrs of transfusion. Severity: Life threatening Ddx: TACO, Sepsis, Acute Hemolytic Transfusion Reaction, Anaphylaxis, non-Trxn ARDS Prevention & Tx: Conservative transfusion. Treat like ARDS. Symptoms & Signs*: Hypotension, fever, and rigors Severity: Life threatening Ddx: Acute Hemolytic Transfusion Rxn, TRALI, Febrile Non-Hemolytic Rxn Prevention & Tx: Bacterial testing of blood units. Rx w/antibiotics and supportive care. * Not all signs and symptoms may be present 2013 UNMH Transfusion Service (Ramos, Reyes, Crookston & Koenig)