Pathology and Pathophysiology of the Upper Gastrointestinal Tract
advertisement
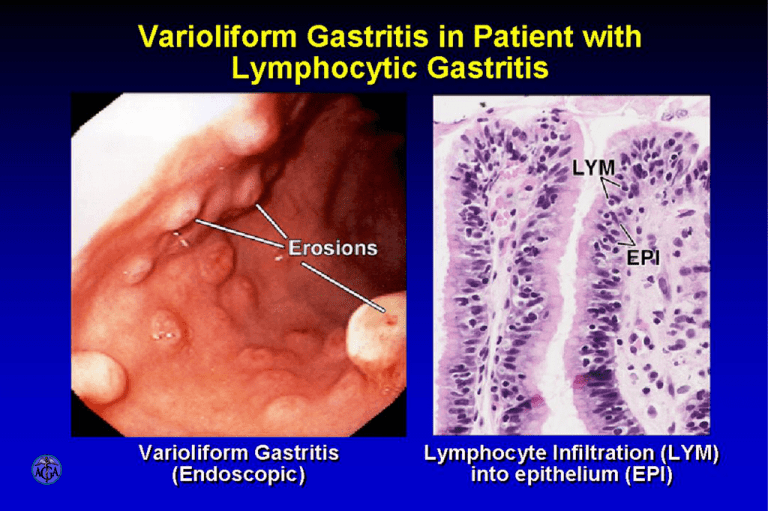
Varioliform Gastritis In Patient With Lymphocytic Gastritis Causes Of Large Gastric Folds Hyperplastic Gastropathies Gross Hyperplastic Gastropathies Histology (Zollinger-Ellison vs Ménétrier’s) Gastric Amyloidosis With Large Rugal Folds - Endoscopy And Histology (Congo Red) Watermelon Stomach: Gastric Antral Vascular Ectasia (GAVE) Accuracy In The Diagnosis Of Gastritis And Gastropathy As Documented By Histopathology Biopsy Strategy For Diagnosis Of Gastritis And Gastropathy Duodenum - Normal Anatomic Relationships Normal Duodenum Vs Hyperplastic Brunner’s Glands (BG) With Enlarged Intramucosal And Submucosal Glands (Located Above And Below Muscularis Mucosae (MM)). Gastric Metaplasia Of The Duodenal Bulb Correlates With Acid Exposure But NOT With H pylori Infection Chronic Peptic Duodenitis Histologic Findings And Definition ACTIVE Chronic Peptic Duodenitis - Defining Histologic Features (Acute Inflammation With H pylori Infection). H pylori And Duodenal Gastric Metaplasia Correlate With Active Peptic Duodenitis Duodenal And “Pre-Pyloric” Ulcers - Autopsy Specimen Duodenal Ulcer With Brunner Gland (BG) Hyperplasia, Pancreatic Penetration And Exposed Artery H pylori Alters Control Of Gastric Secretion By Decreasing Somatostatin Release H pylori Infection Causes A Reversible Decrease In Antral DCell Density And In Somatostatin Content And An Increase In Gastrin Content In Duodenal Ulcer Patients The Role Of H pylori In The Pathogenesis Of Duodenal Ulcer Principal Non-Peptic Causes Of Duodenitis Duodenal Inflammation And Ulceration In A Patient With Crohn’s Disease Celiac Disease Can Be Misdiagnosed When Only The Duodenal Bulb Is Biopsied