handout
advertisement

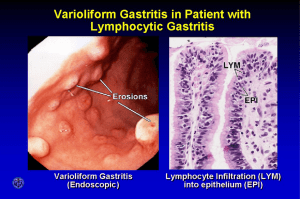
GORD & PUD Dyspepsia Non-specific group of symptoms related to the upper GI tract Alarm symptoms; GI bleed Weight loss Dysphagia Iron deficiency anaemia Persistent vomiting Epigastric mass (Suspicious barium meal) **if any of the above refer for urgent (2ww) endoscopy for patients of ANY age GORD Risk factors; Hiatus hernia Pregnancy/obesity Large meals Smoking, alcohol Drugs; calcium channel blockers, anticholinergics, nitrates Symptoms; ‘heartburn’; retrosternal, burning, related to meals, worse lying down/straining, relieved by antacids Epigastric or Chest pain Acid brash & waterbrash Odynophagia, dysphagia Extra-oesophageal;Nocturnal asthma, Chronic cough, Laryngitis Investigations; • ECG; if retrosternal/chest pain • Bloods • OGD; mucosal break or normal (ENRD) • 24 hour oophagia pH monitoring +/- manometry Treatment; • Life style changes; weight loss, stop smoking, raise head of bed, small regular meals • Drugs; Antacids, PPIs, H2 antagonists, prokinetic • Surgical; Nissen fundoplication Complications; • Oesophagitis • Benign stricture • Barrett’s oesophagus; premalignant condition when normal oesophageal squamous epithelium is replaced by gastric columnar epithelium (metaplasia). Peptic ulcer disease Incidence ratio Cause Pain Relieving factors Complications Gastric Ulcer 1 70% H/pylori, 30% other Worse on eating Duodenal ulcer 4 90% H.pylori, 10% other Worse before meals/at night eating More likely to perforate Risk factors; • H. Pylori • NSAIDs (block PGs that stimulate mucus + HCO) • Alcohol • Severe stress • Smoking • Steroids • Zollinger-Ellison syndrome; gastrin secreting adenoma H. pylori; • Gram negative urease secreting bacteria; converts human urea to ammonia to neutralise the acid around itself. • Ammonia raises pH locally, around the pH ‘sensors’; reduces somatostatin release (usually inhibits gastrin + histamine realise)….leading to excess acid production • Can lead to chronic gastritis + gastric carcinoma Symptoms; Asymptomatic Epigastric pain - DU; worse when hungry & night - GU; worse when eating Nausea Weight loss (GU) Investigations; Bloods ECG CXR, AXR Stool test; H. Pylori antigen Urea breath test; swallow urea labelled with C13, measure CO2. Serological IgG for H. Pylori (not for eradication) OGD; biopsy + urease test Management Lifestyle changes Acid reduction Eradication therapy - Test + treat; if H. Pylori +ve, triple therapy;PPI + Clarithromycin + Amoxicillin/Metronidazole Complications Perforation, bleeding, gastric outflow obstruction, malignancy