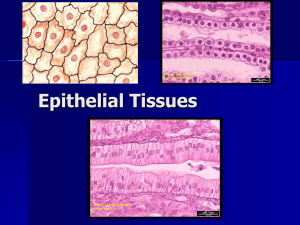
Epithelial Tissue
advertisement

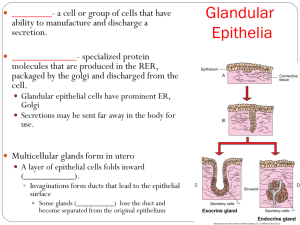
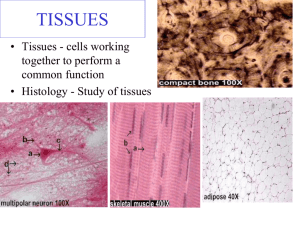
Journal#1: The human body contains trillions of cells, how many different types do you think there are? • Fun Fact: The human heart creates enough pressure to squirt blood 30 feet in the air. • Objective: – List the 4 major tissue types in the body – Discuss the types and functions of epithelial cells Epithelial Tissue Pgs. 107-118 Intro to Tissues • Combinations of specialized cells that work together to perform a function • The study is called Histology • Four Basic Tissue Types – Epithelial – Connective – Muscle – Neural Epithelial Tissue • Includes : – Epithelia: Layers of cells that cover internal & external surfaces – Glands: Structures that make fluid secretions and are attached to or derived from the epithelia • Characteristics – Cellularity: cells bound by cell junctions – Polarity: has an exposed & attached surface – Attachment: the base is bound to a thin basal lamina with connective tissue below – Avascularity: no blood vessels – Regeneration: Replaced by stem cells in the epithelium (high mitotic rate) Functions of Epithelial Tissue • Protection: from abrasion, dehydration, and destruction • Control permeability: create a semi permeable barrier • Provide Sensation: sensory receptors (skin) • Produce Secretions: gland cells produce enzymatic fluids, hormones, etc. Specialization • • • • Move fluids over surface Move fluids through the epithelium Produce Secretions Specialized Structures – Microvilli (increase surface area for absorption and secretions) – Ciliated epithelium (beat cilia to move fluids across cell) Intercellular Connections • Epithelial Cells firmly attached to each other • Also attached to basal lamina – Where stem cells or germinative cells are located • Adjacent cells connected by proteins called cell adhesion molecules (CAMs) • Types of cell junctions (connections) – Tight: lipid portion of membrane joined by interlocking proteins (adhesion belt) • Prevent diffusion between cells – Gap: held together by interlocking proteins • Allows diffusion between cells – Desmosome: attach cells to extracellular structures like the basal lamina Journal#2: What are the 3 types of cell junctions or connections in epithelial tissue? • Fun Fact: Feet have 500,000 sweat glands and can produce more than a pint of sweat a day. • Objective: – List the 4 major tissue types in the body – Discuss the types and functions of epithelial cells Classification of Epithelium • Cell shape: – Squamous: thin and flat – Cuboidal: little boxes – Columnar: tall and slender • Layers: – Simple: 1 – Stratified: more than one Squamous • Simple – Delicate – Diffusion ready – Blood vessels, tubules of kidneys, lining of cornea, mesothelium (lining of body cavities) • Stratified – Protection – Skin, lining of mouth, throat, esophagus Cuboidal • Simple – Limited protection – Absorption/Secretion – Kidney Tubules, Glands, Ducts • Stratified (rare) – Protection – Absorption/Secretion – Ducts of sweat glands Transitional • Tolerates stretching without damage • Urinary bladder – Empty: seems to be layered w/cuboidal on surface – Full: appears flattened like simple squamous Columnar • Simple – Absorption/secretion – Lining of stomach & intestines • Pseudostratified ciliated – Protection/secretion – Nasal cavity, trachea, & bronchi • Stratified (rare) – Protection – Pharynx, epiglottis, anus, & urethra Glandular • Endocrine Glands – Release fluids (hormones) into interstitial fluid – Directly to bloodstream • Exocrine Glands – Release fluids on to epithelial surface – Skin/sweat, tears in eyes, milk by mammary glands Modes of Secretion • Merocrine – Exocytosis of secretory vesicle – Perspiration, mucus • Apocrine – Loss of cytoplasm becomes secretion – Milk production • Holocrine – Lysis releases secretory products – Sebaceous glands (hair follicles) Types of Secretions • Serous glands – Watery solution (saliva) • Mucous glands – mucous • Mixed Exocrine glands – both Gland Structure • Unicellular (goblet cells) • Multicellular – Secretory sheet – Simple: single duct – Compound: duct divides many times




![Histology [Compatibility Mode]](http://s3.studylib.net/store/data/008258852_1-35e3f6f16c05b309b9446a8c29177d53-300x300.png)